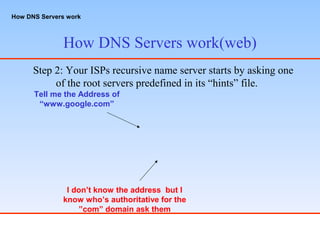
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical distributed naming system for computers, services, or any resource connected to the Internet or a private network. It associates various information with domain names assigned to each of the participating entities. A domain name represents an Internet Protocol (IP) resource ultimately identifiable by a numeric IP address. DNS servers store records that map domain names to IP addresses and vice versa. The DNS hierarchy consists of root name servers at the top, authoritative name servers for top-level domains and their subdomains below them. When a user enters a domain name, the DNS server first checks its cache and if it doesn't find a match, it queries authoritative name servers to resolve the IP address associated with the domain name.