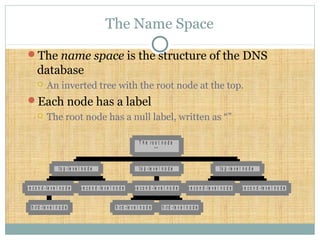
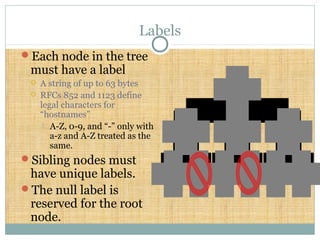
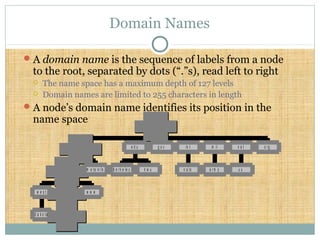
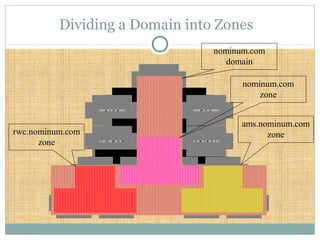
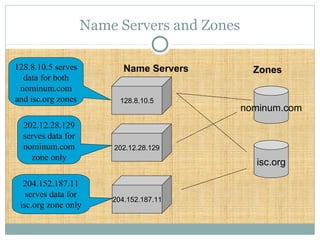
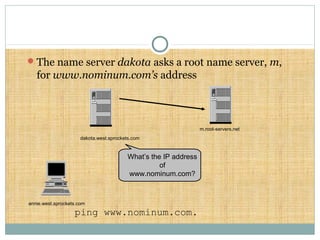
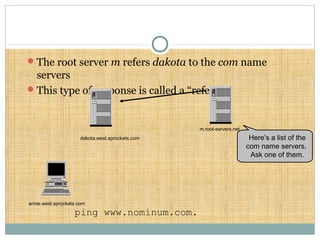
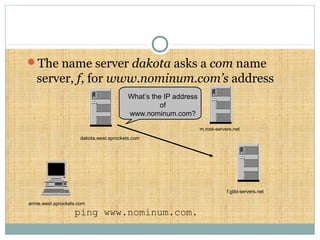
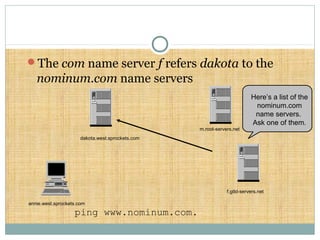
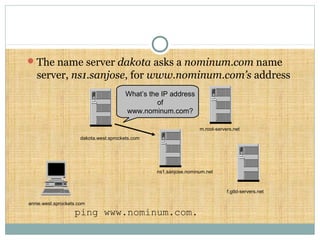
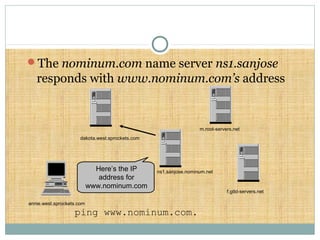
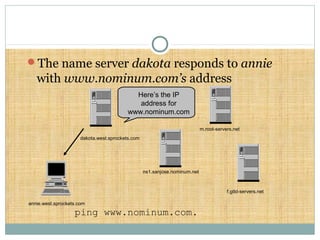
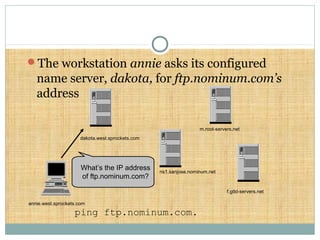
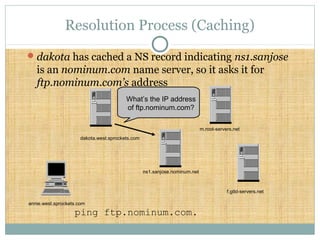
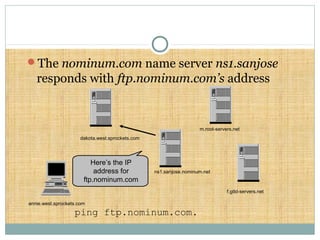
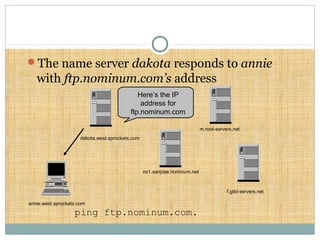
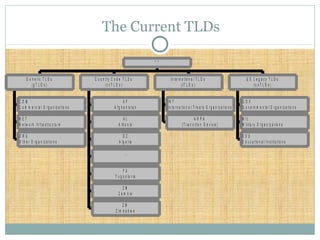
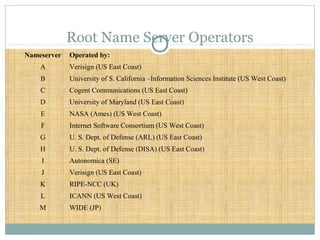
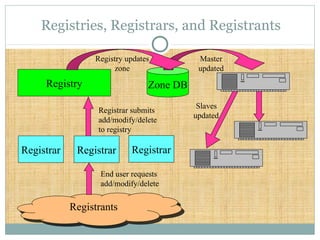
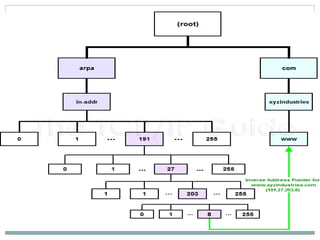
DNS is a globally distributed database that translates domain names to IP addresses. It consists of a name space organized in a hierarchical tree structure, servers that store data about parts of the name space, and resolvers that query servers to map names to addresses. The resolution process involves recursively querying servers at higher levels, like root and TLD servers, until reaching an authoritative name server that can provide the address. Caching improves performance by storing previous lookups.