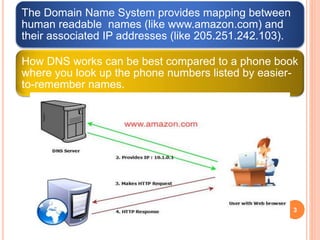
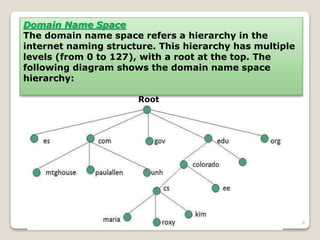
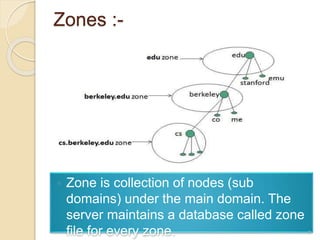
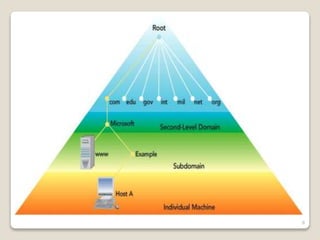
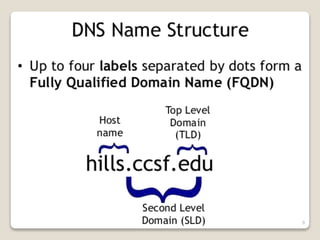
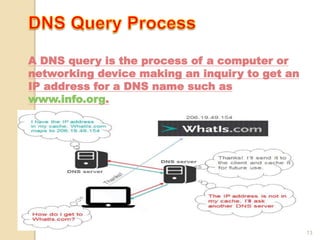
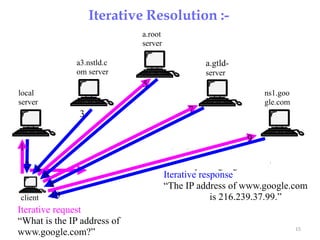
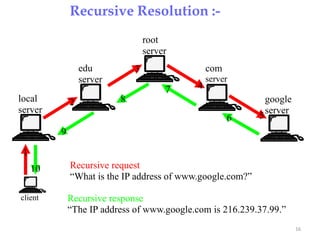
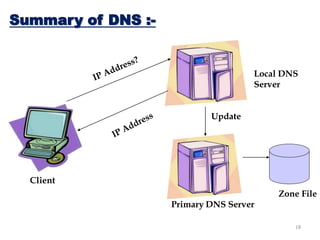
The Domain Name System (DNS) provides translation between human-readable domain names and machine-readable IP addresses. DNS works like a phone book, allowing users to look up IP addresses using easier to remember domain names. DNS has a hierarchical structure with top-level domains at the root and subordinate domains below. DNS servers store and serve DNS records to resolve domain names to IP addresses through either iterative or recursive queries. Authoritative DNS servers maintain definitive records for their registered domains.