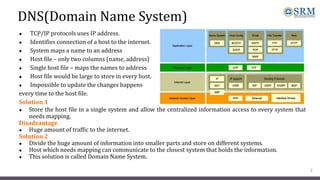
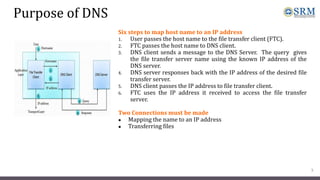
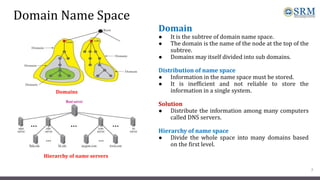
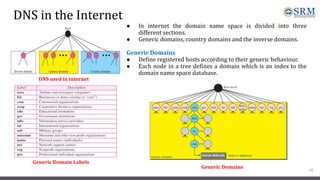
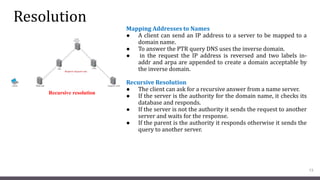
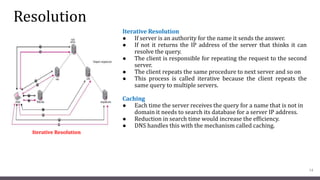
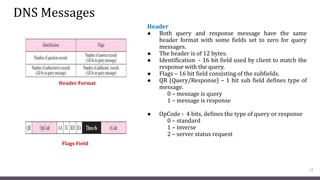
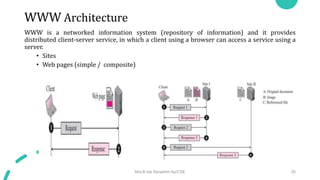
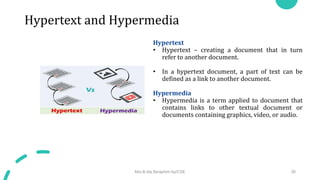
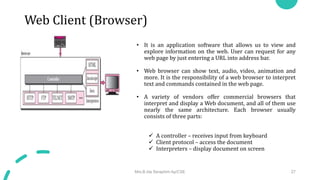
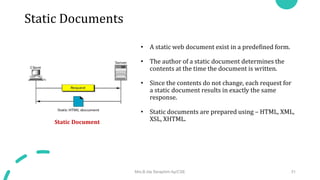
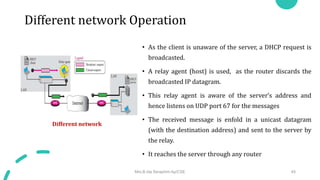
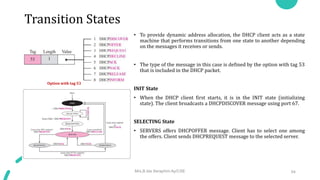
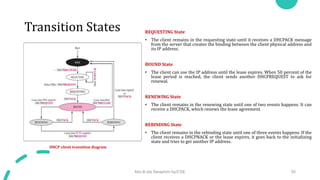
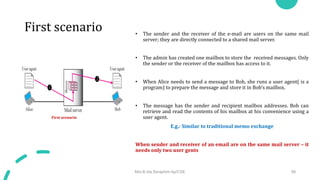
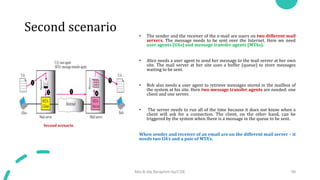
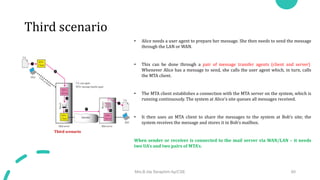
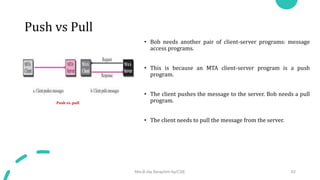
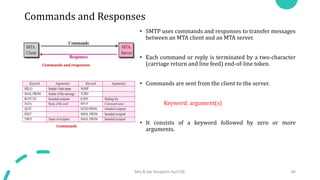
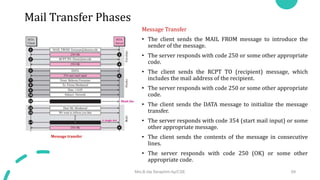
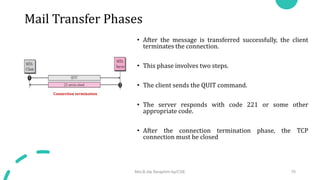
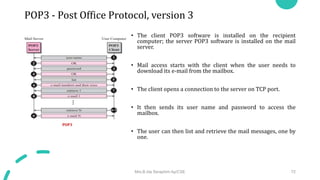
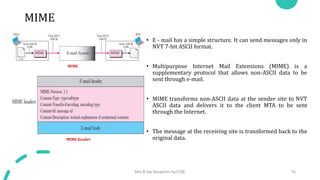
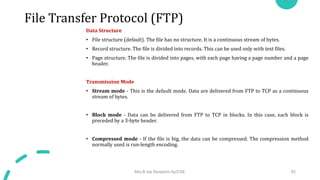
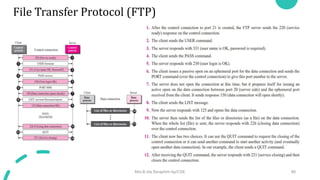
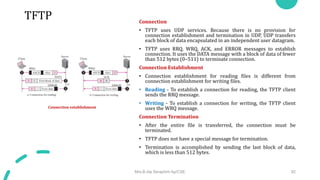
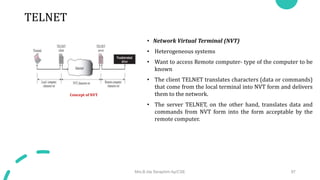
DNS maps host names to IP addresses in a hierarchical distributed system. It uses a client-server model where DNS clients query DNS servers to map names to addresses. DNS servers are authoritative for different zones of the domain name space, which is divided hierarchically into domains. DNS servers can provide recursive or iterative resolution of queries. Responses contain the requested mapping along with additional caching and timing information.