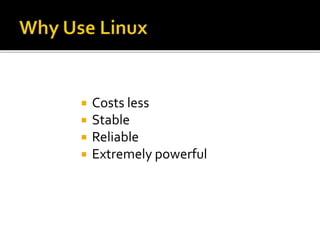
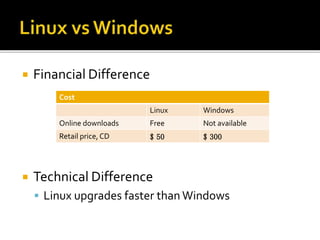
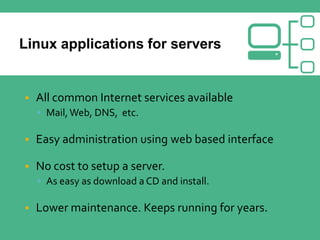
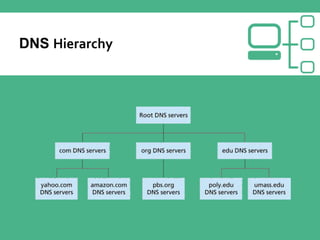
This document provides an overview of Linux and DNS server administration. It discusses what Linux is, where it is used, advantages of using Linux like low cost and security. It also explains what a DNS server is, components of DNS like domains, hostname, zones and how to configure a DNS server in Linux. Hackers prefer Linux due to its availability, customizability and prevalence on servers. Using public DNS services like Google DNS can help speed up internet access. Linux provides a flexible, secure and low-cost operating system for applications including web servers.