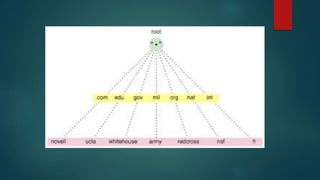
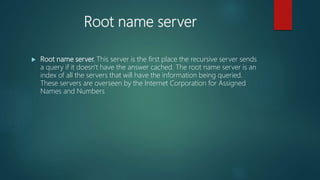
The document discusses DNS (Domain Name System) which is a naming system that translates domain names to IP addresses. It explains that DNS servers map domain names that people use, like "example.com", to the corresponding IP addresses that computers use to locate websites. DNS is necessary because computers communicate using IP addresses, not domain names. The document provides details on how DNS works, the different types of DNS servers involved in lookups, and concepts like DNS caching and DNS resolution.