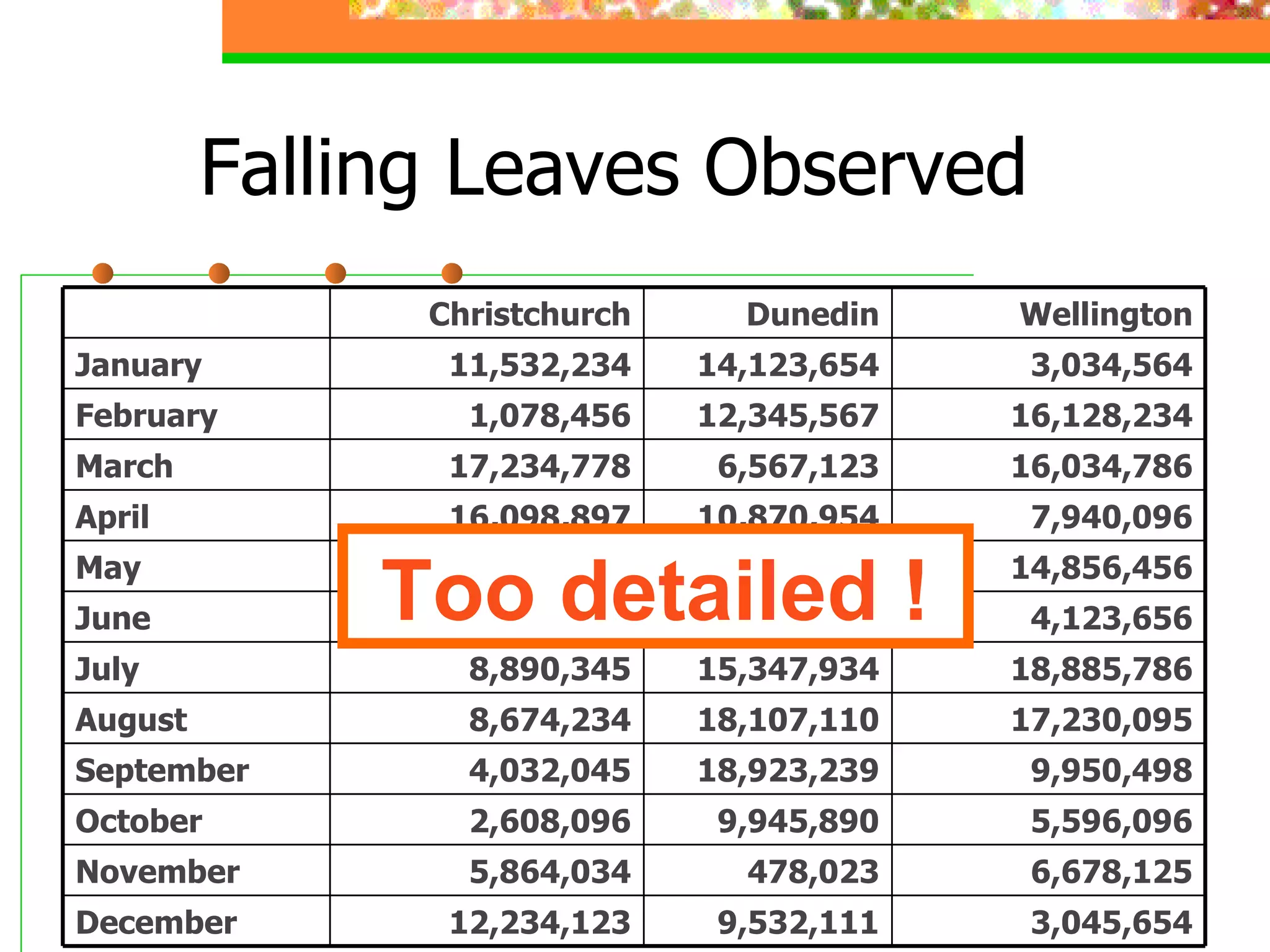
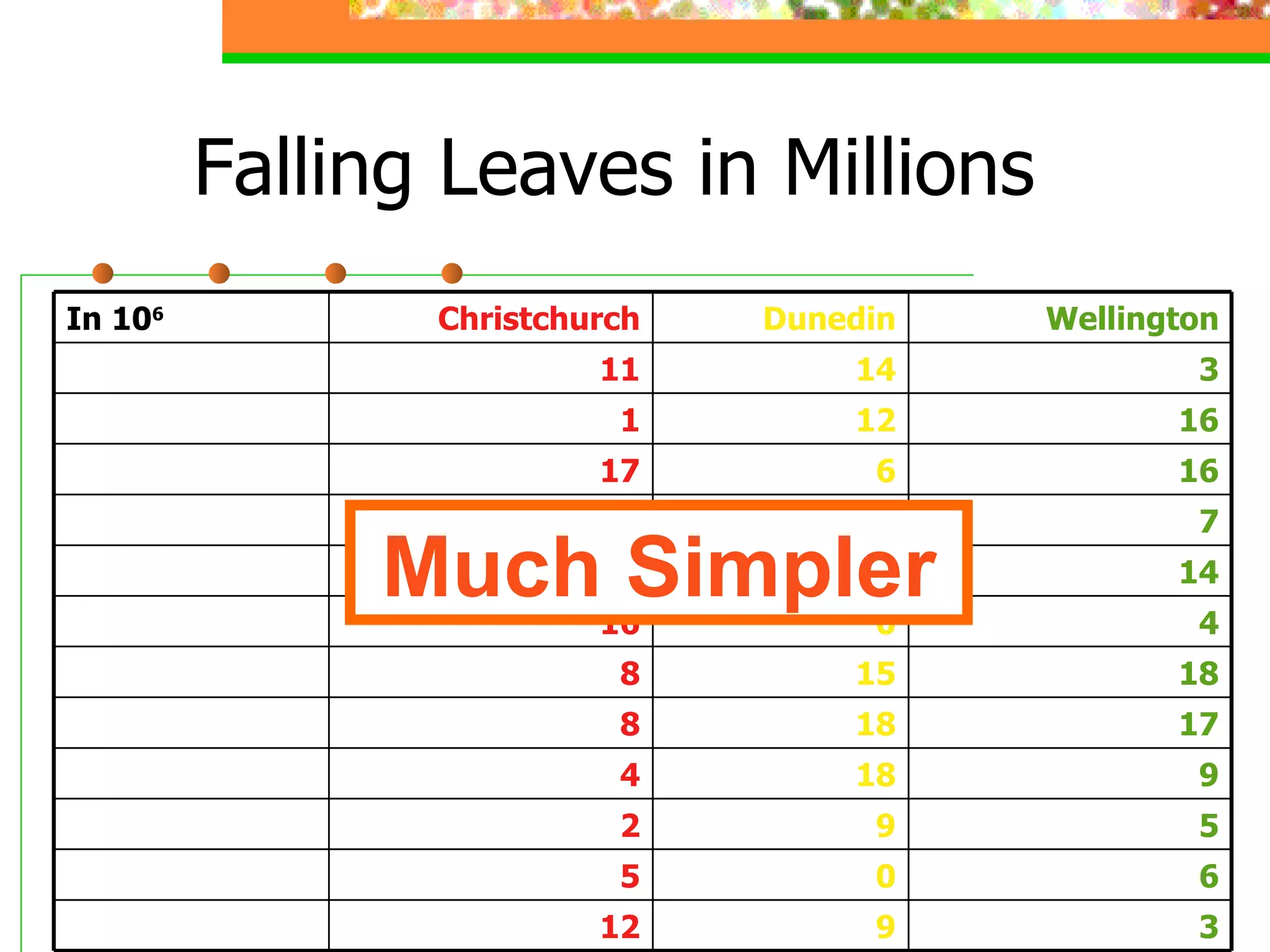
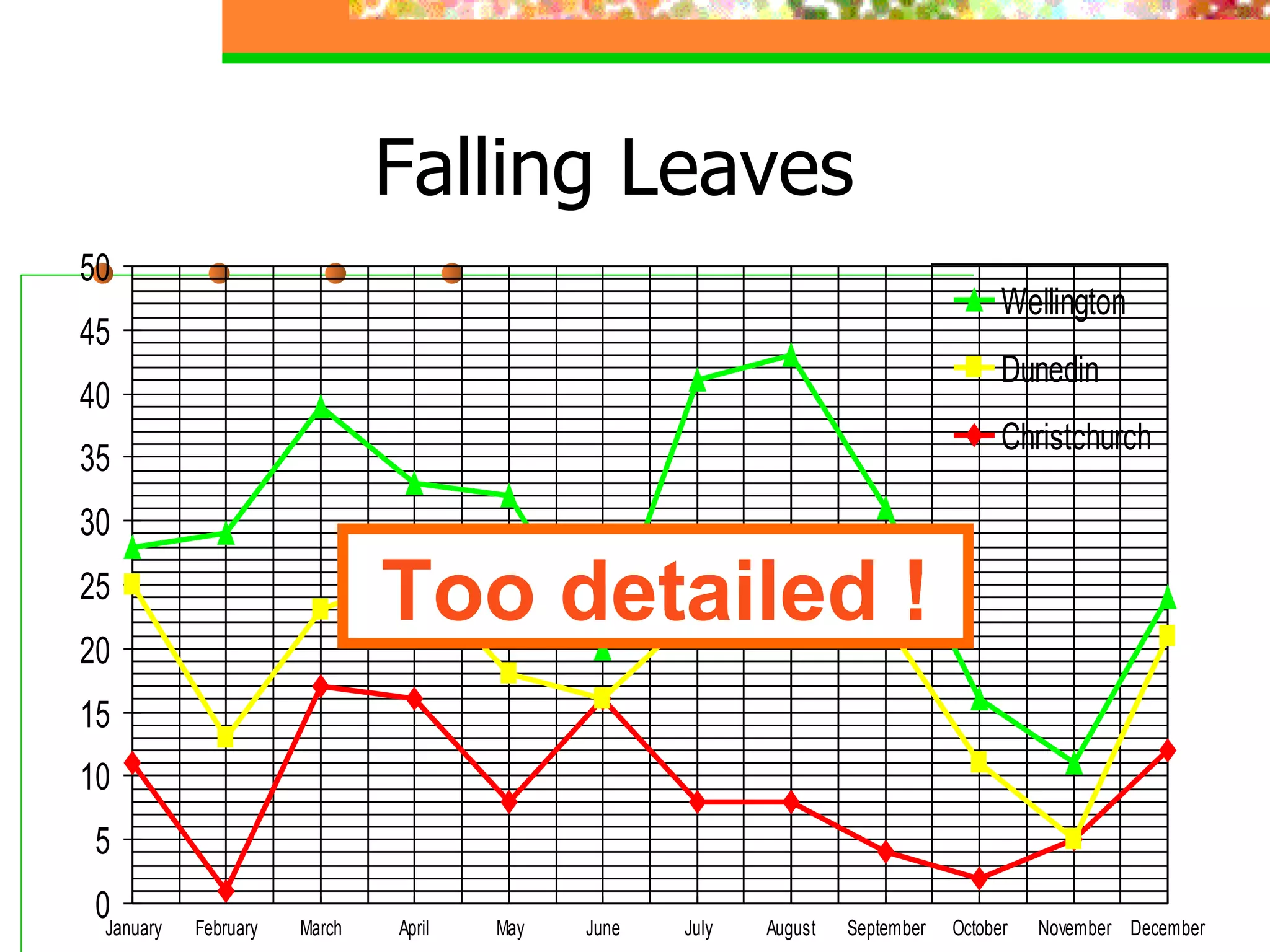
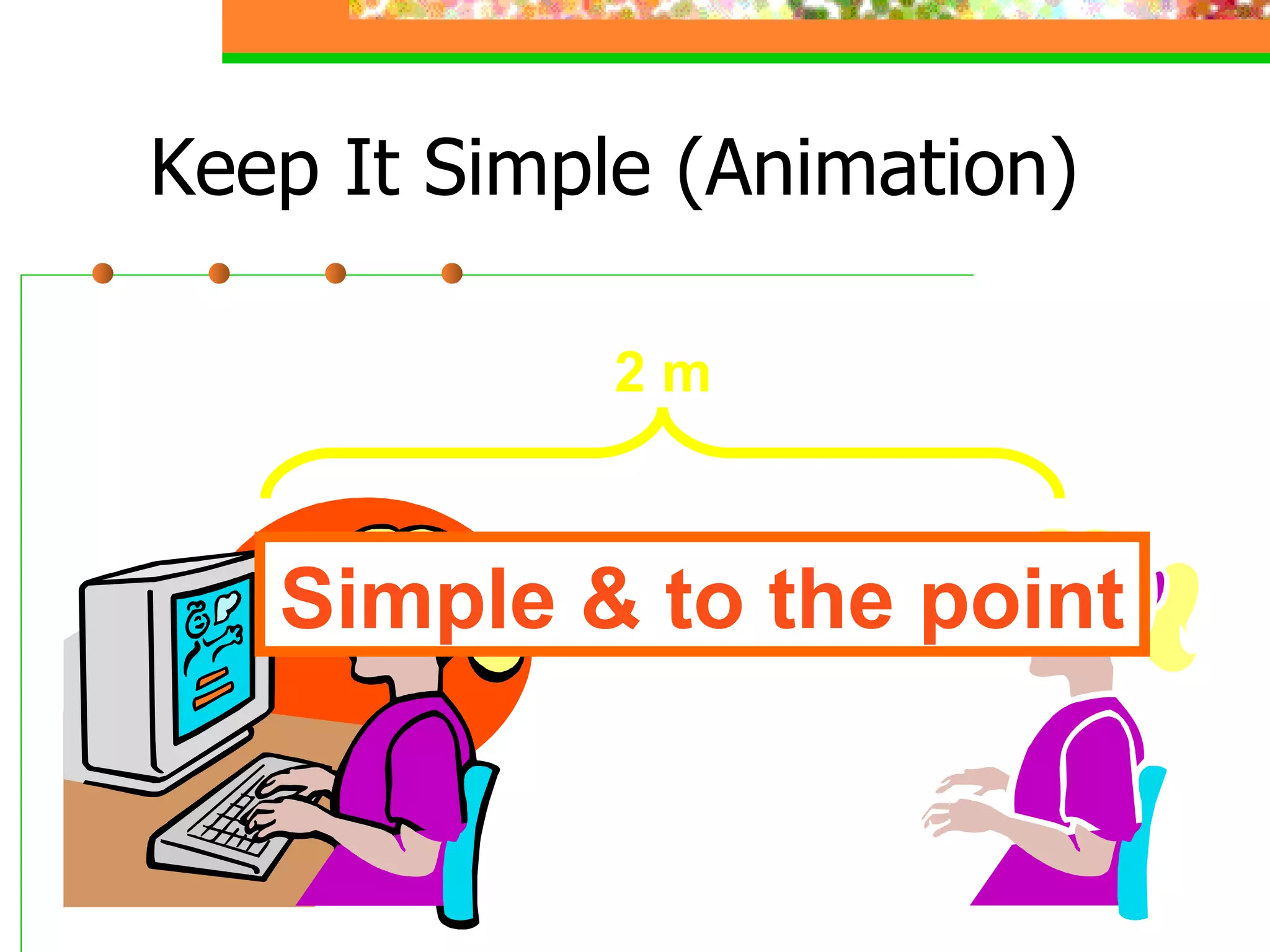
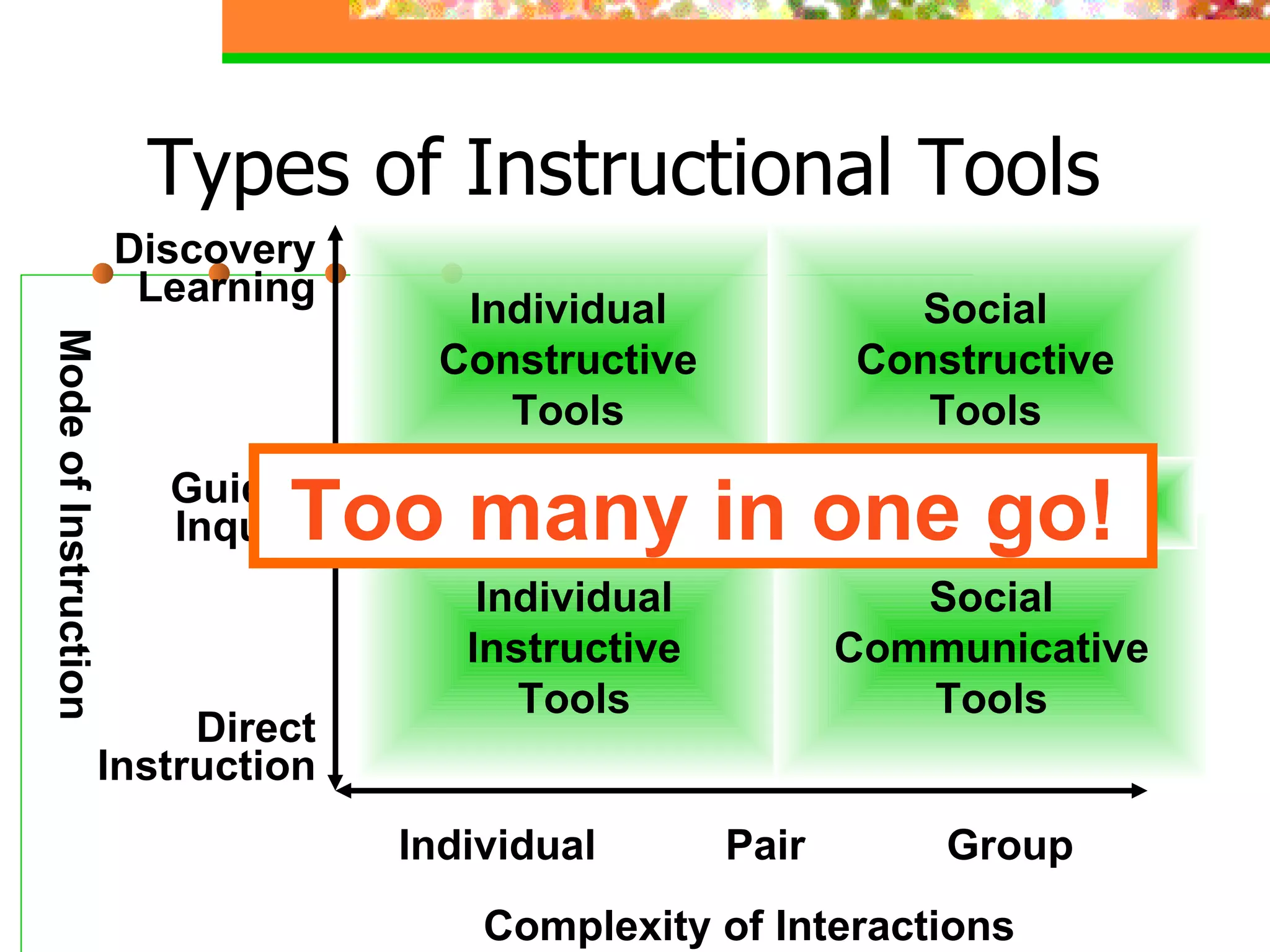
The document discusses effective presentation skills, authored by Dr. Alaa Sadik, emphasizing crucial aspects such as media types, message design principles, and technology for creating impactful presentations. It outlines various presentation tools and techniques, advises on simplicity and clarity in content, and highlights the importance of visual aids in supporting communication. The overall focus is on enhancing the effectiveness of educational presentations through thoughtful design and execution.
![مهارات العرض الفعال Effective Presentation Skills Alaa Sadik, PhD [email_address] www.alaasadik.net](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/effectivepresentationskillsnew01-091116001613-phpapp02/75/Effective-Presentation-Skills-1-2048.jpg)