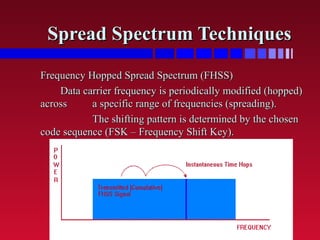
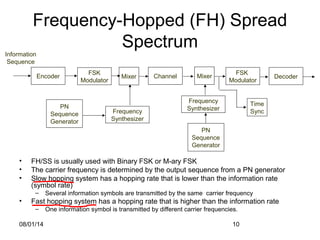
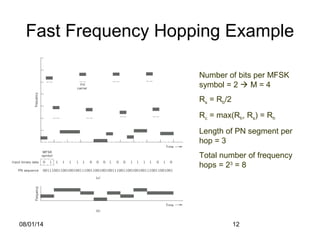
The document discusses Frequency Hopped Spread Spectrum (FHSS) techniques used in radio communications, highlighting the modulation process where data is sent over a range of frequencies in a predictable sequence to minimize interference and improve security against jamming. Key distinctions are made between slow and fast hopping systems, their configurations, and advantages such as reduced impact from electrical noise and coexisting access points in the same area. Limitations include the need for complex frequency synthesizers for efficient operation.