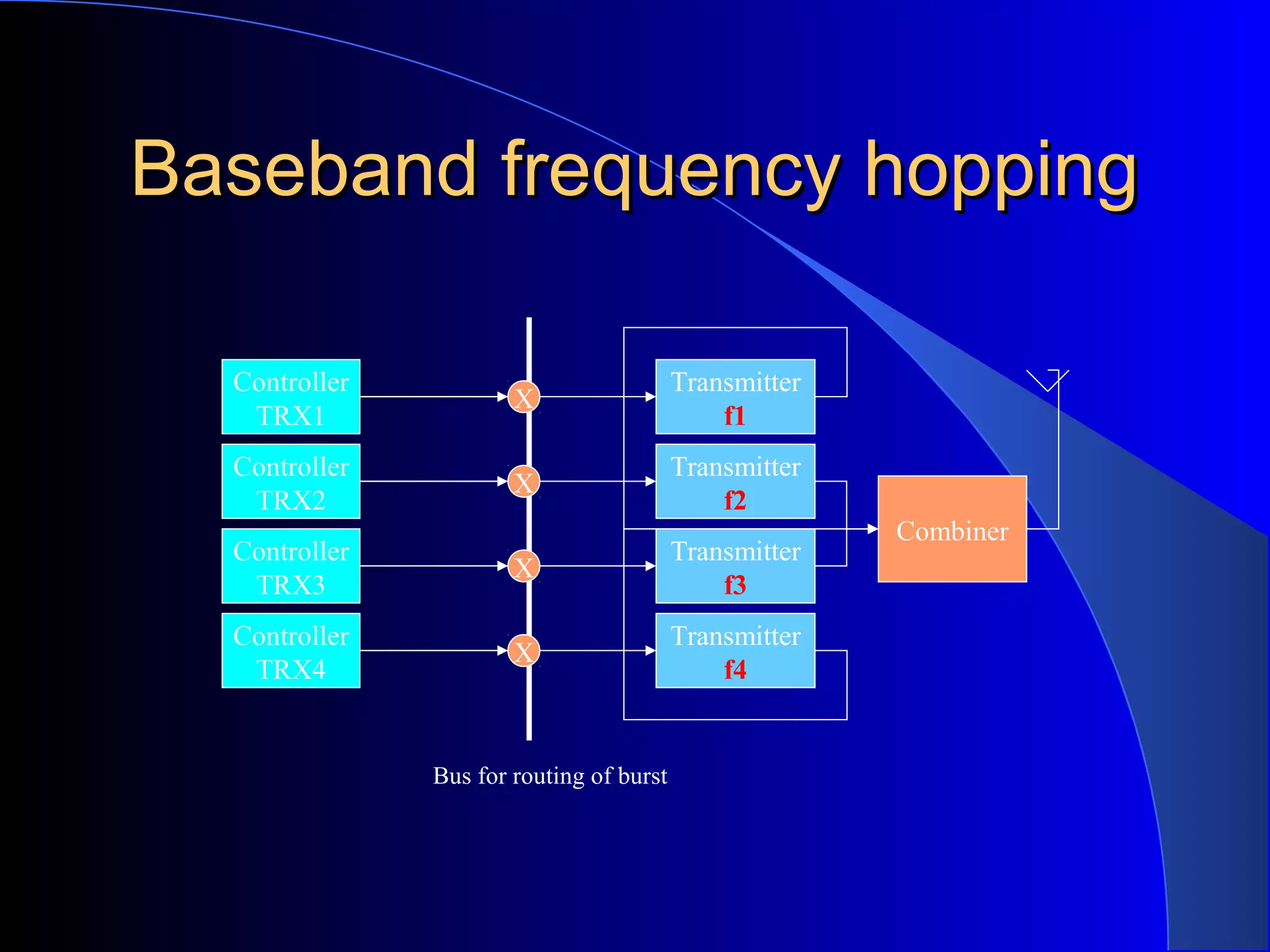
This document discusses frequency hopping in wireless communication systems. It begins by explaining that in frequency hopping systems, each call hops between a defined set of frequencies to reduce the impact of poor signal quality on any single frequency. This provides frequency diversity and averages out interference. The document then discusses various types of frequency hopping including baseband and synthesizer hopping. It also covers topics like why frequency hopping is used, factors like multipath fading and interference, and specifications of frequency hopping systems including hopping sequences, mobile allocation lists, and fractional loading.