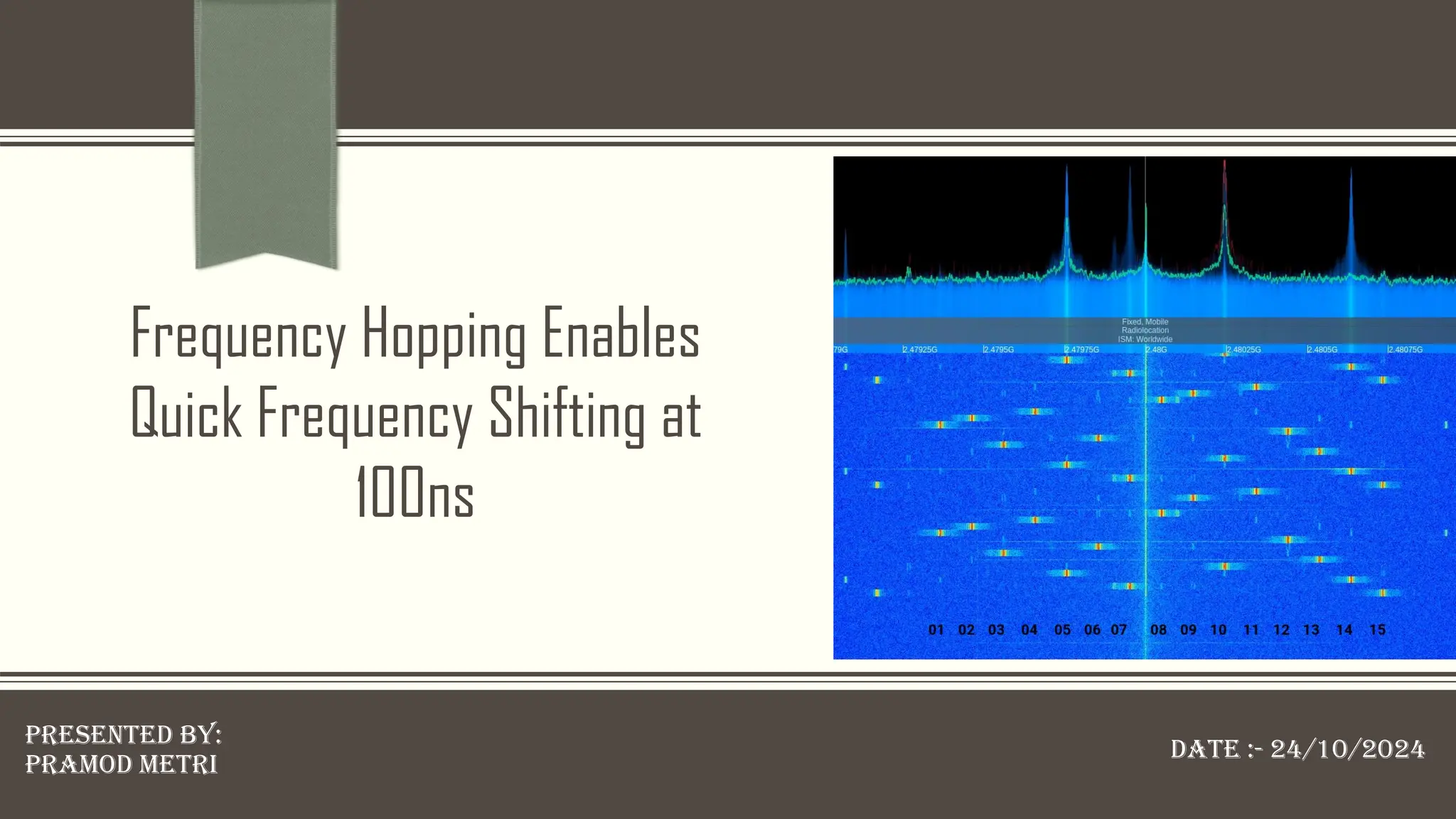
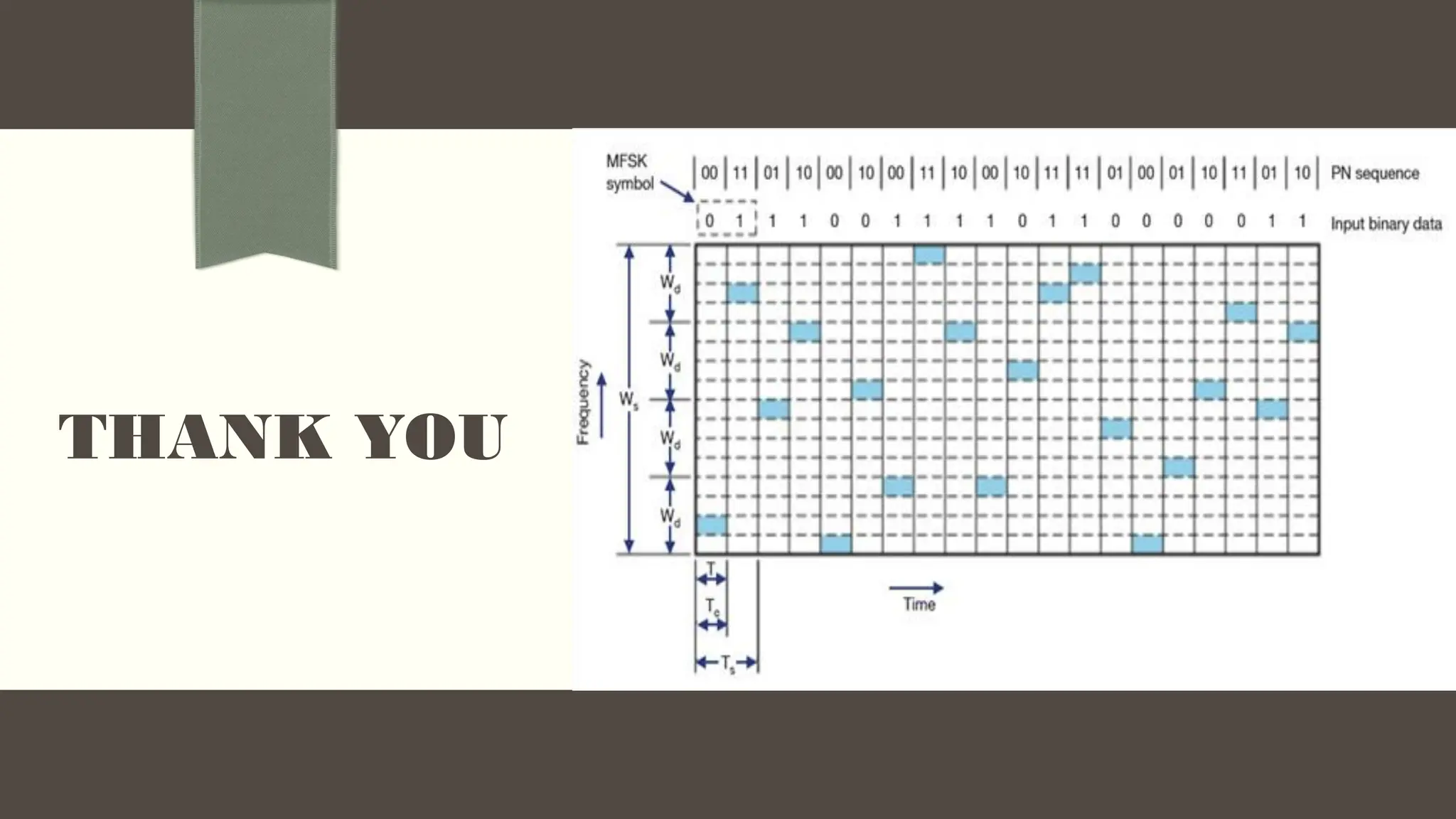
The document discusses frequency hopping spread spectrum (FHSS), a method of transmitting radio signals by rapidly changing the carrier frequency to improve resistance to interference and enhance signal security. It details the types of FHSS, specifically fast frequency hopping, and includes theoretical calculations for key metrics such as hop rate and bandwidth. Key applications mentioned include Bluetooth technology, military communications, wireless sensor networks, and health monitoring systems.