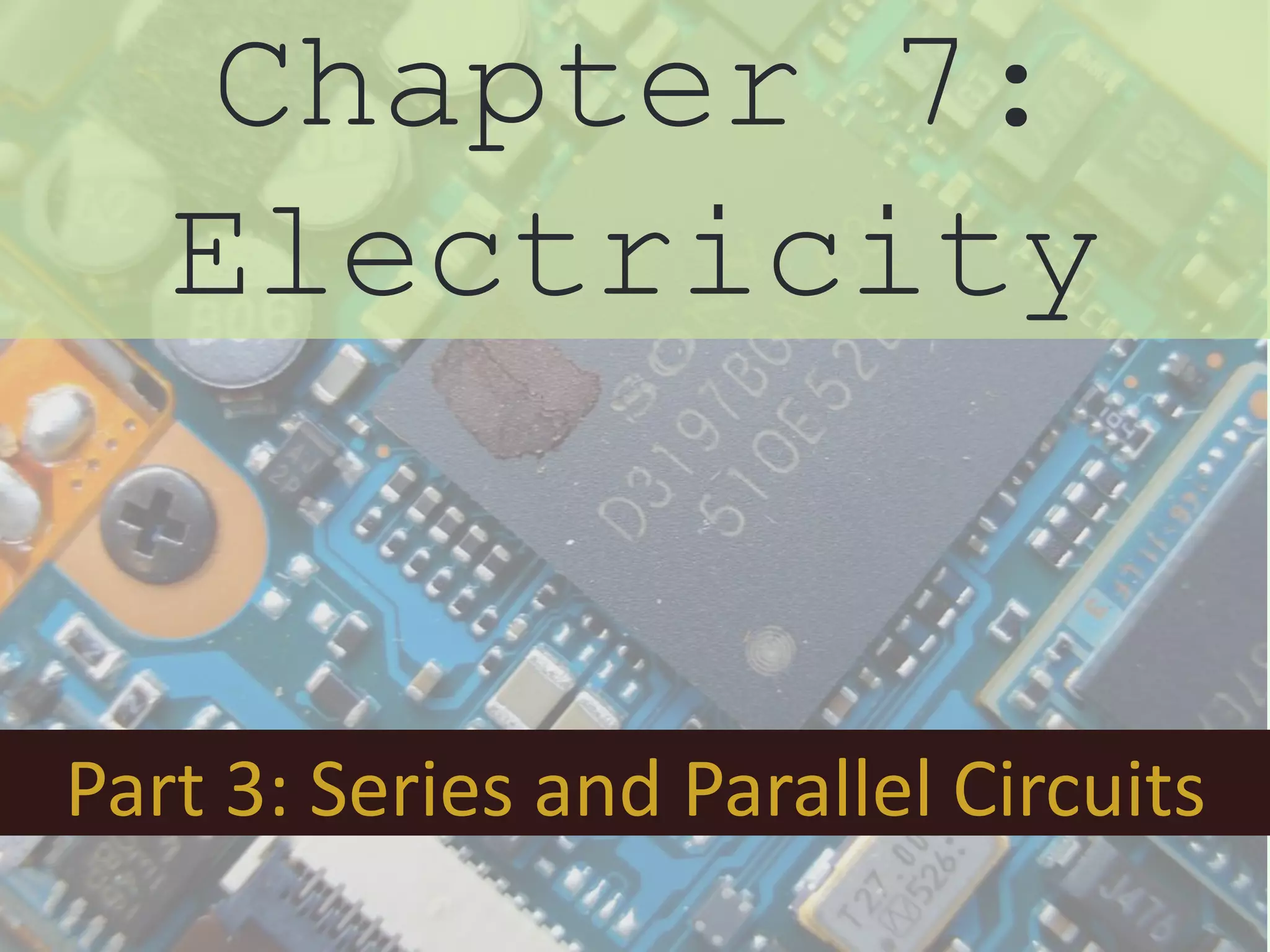
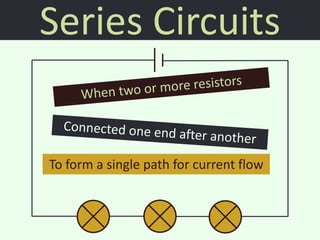
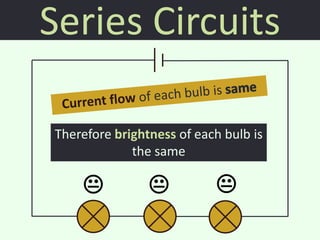
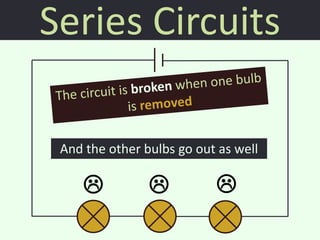
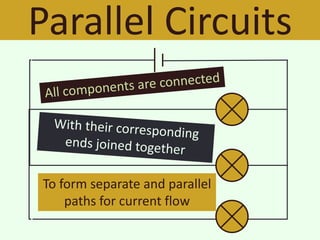
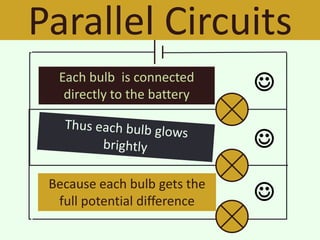
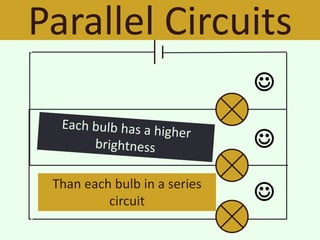
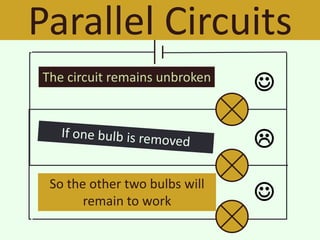
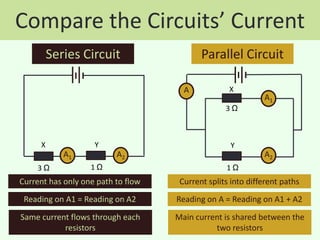
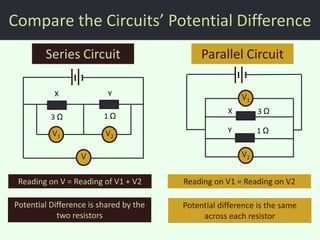
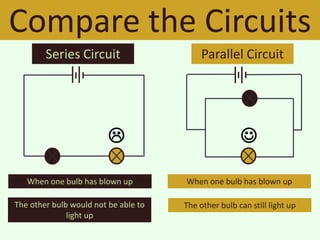
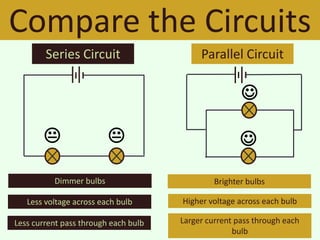
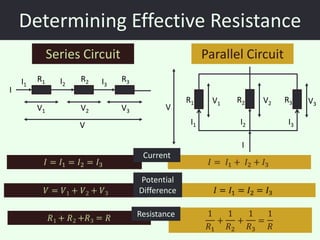
The document discusses series and parallel circuits in electricity, highlighting that series circuits provide a single path for current, causing bulbs to glow dimly and go out if one bulb fails. In contrast, parallel circuits offer multiple paths, allowing bulbs to maintain full brightness even if one fails, as each is directly connected to the battery. It also compares the behavior of current and potential difference in both circuit types, noting differences in resistance and current distribution.