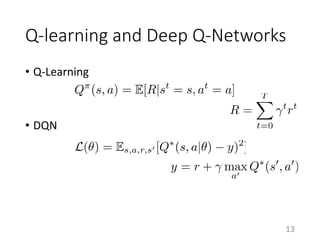
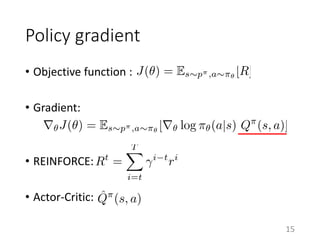
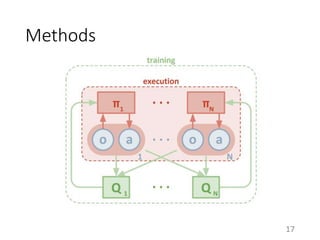
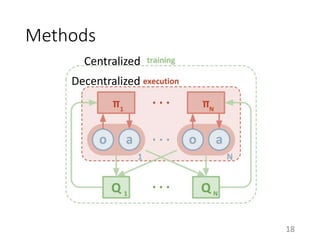
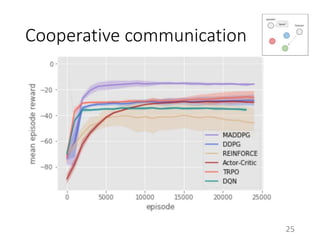
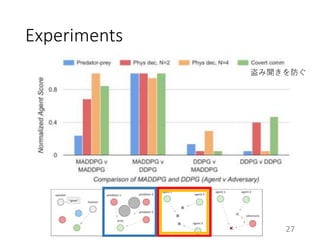
This document proposes a multi-agent actor-critic method for mixed cooperative-competitive environments. The method extends traditional actor-critic by having the critic use extra information about other agents' policies while keeping the actor decentralized by using only local information. This allows agents to learn cooperative behaviors while still handling competitive scenarios. The method is evaluated on cooperative communication tasks where it successfully learns the desired policies, unlike traditional reinforcement learning approaches.