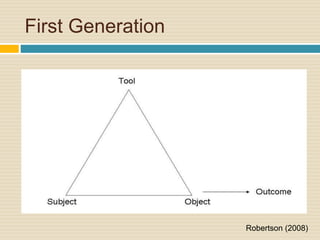
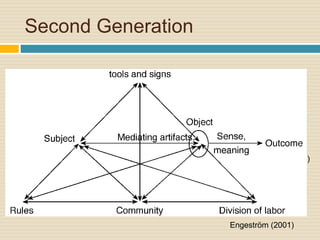
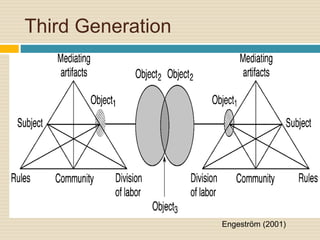
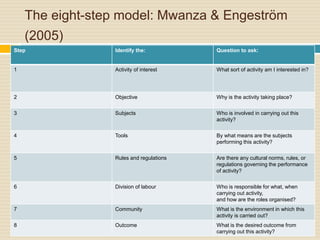
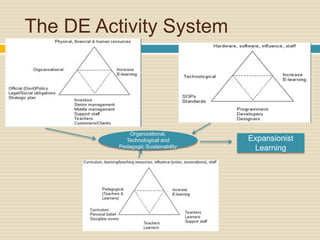
This document provides an overview of Cultural Historical Activity Theory (CHAT) and its application as a learning theory. It discusses key aspects of CHAT including that human development occurs through social interaction and activity, and that internalization of cultural tools and symbols plays an important role. The document also summarizes the three generations of activity systems and expansive learning, which involves questioning existing practices and opening new possibilities. Finally, it provides examples of how activity theory has been applied to areas like distance education and offers references for further reading.