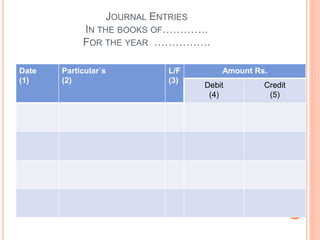
The document discusses journal entries and their characteristics. It defines a journal as a chronological record of financial transactions. Every transaction is recorded through a journal entry that includes the date, amount, accounts affected, and description. Journal entries follow double-entry bookkeeping by debiting one account and crediting another. They provide a basis for recording transactions in individual ledger accounts and help locate errors. The document also discusses types of journal entries, their advantages and limitations.