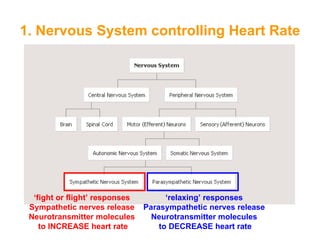
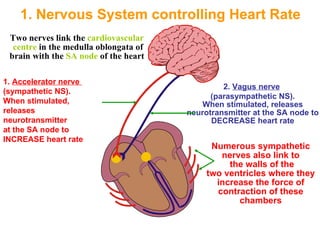
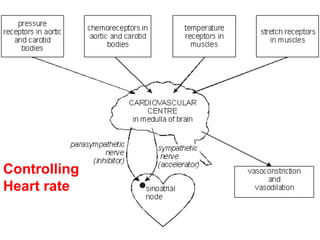
The document discusses how the nervous system and hormonal system modify the heart rate to meet the body's demands. The nervous system controls heart rate through the sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves. The sympathetic nerves increase heart rate during exercise or stress while the parasympathetic nerves decrease it during rest. The hormonal system also increases heart rate through the hormone adrenaline.