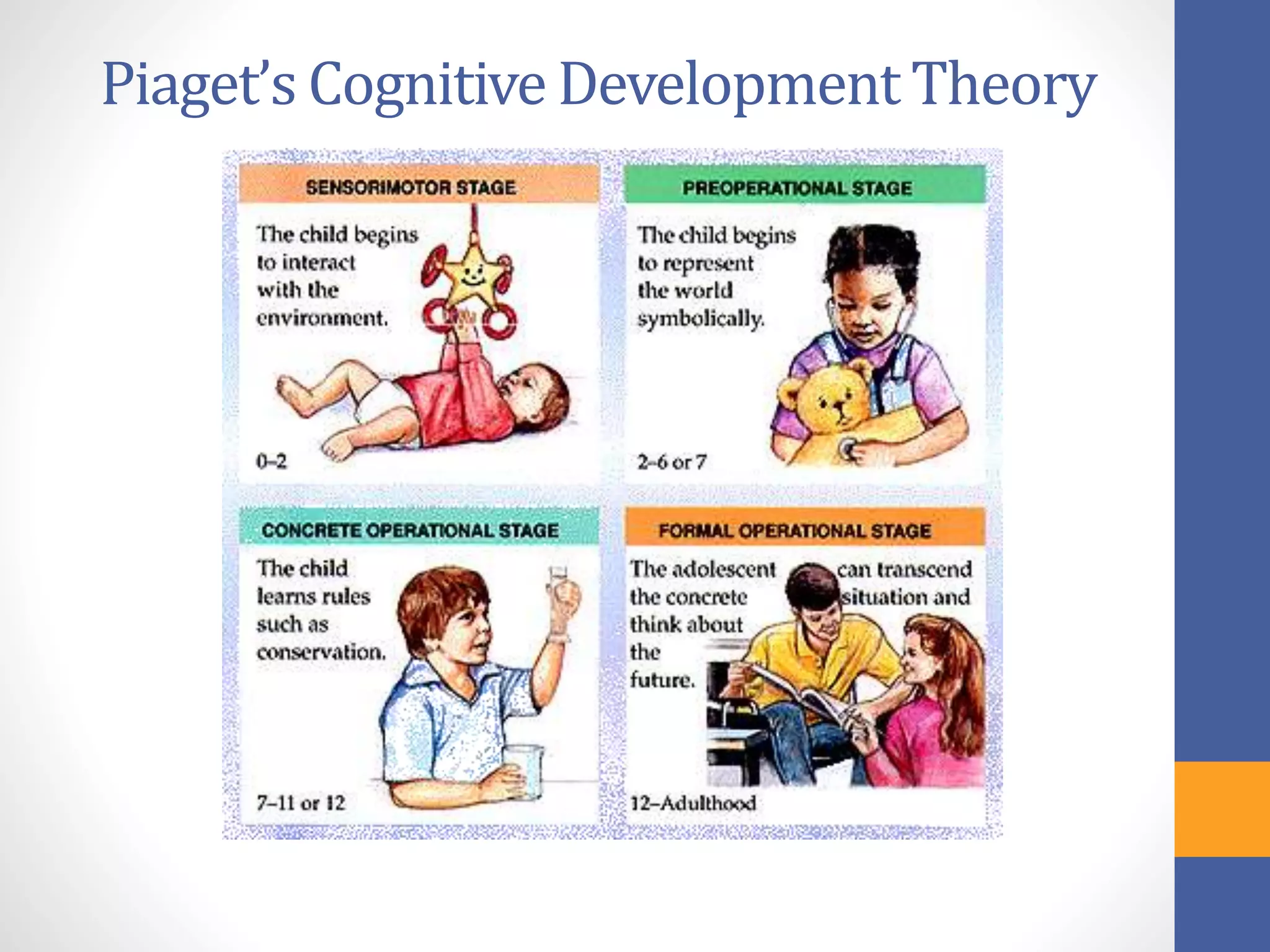
This document provides an overview of key concepts in developmental psychology. It discusses three domains of development - physical, cognitive, and social/emotional. Nature and nurture both impact child development, as seen through comparisons of monozygotic and dizygotic twins. Child behavior is also influenced by parenting styles like authoritarian, authoritative, and permissive parenting. Several theories of development are presented, including Piaget's stages of cognitive development, Kohlberg's stages of moral development, Erikson's psychosocial stages, and Vygotsky's sociocultural theory emphasizing social learning.