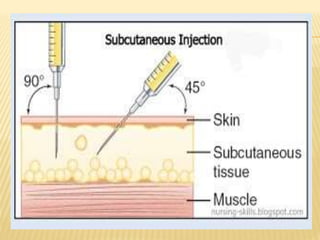
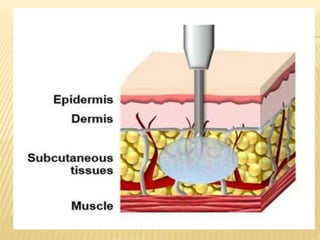
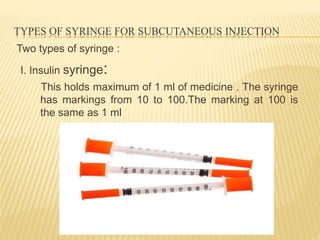
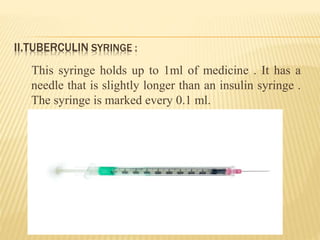
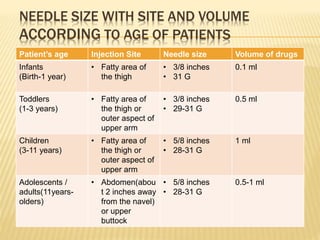
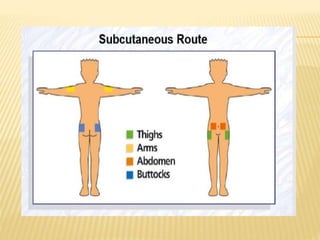
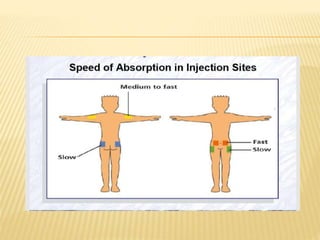
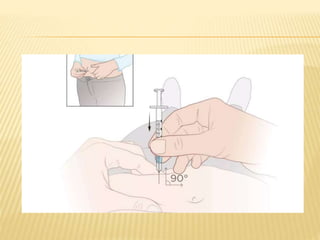
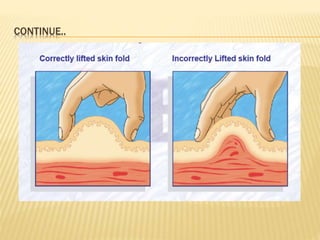
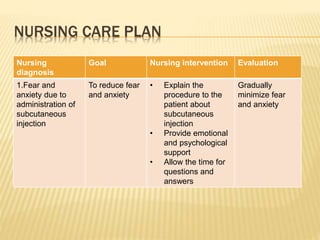
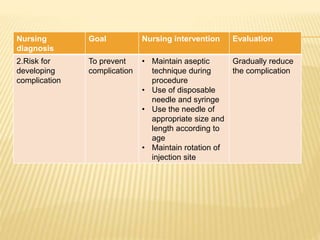
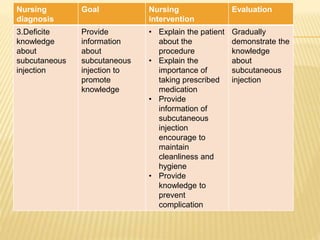
Subcutaneous injection is a vital nursing intervention used to administer medication into the fatty tissue beneath the skin, effective for continuous delivery of drugs like insulin and vaccines. Proper technique is crucial to minimize pain and complications, necessitating knowledge of anatomy, patient care, and proper equipment handling. Key aspects of administration include appropriate syringe choice, site rotation, and adherence to safety precautions to prevent adverse effects.