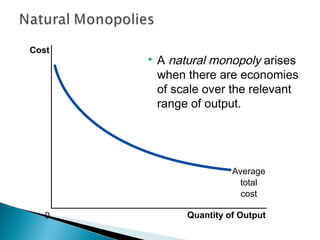
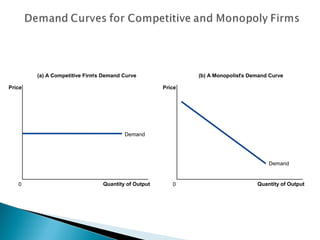
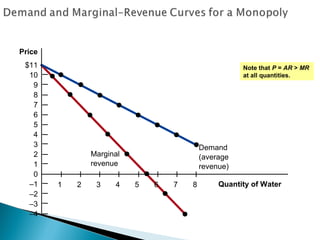
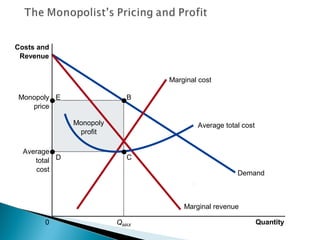
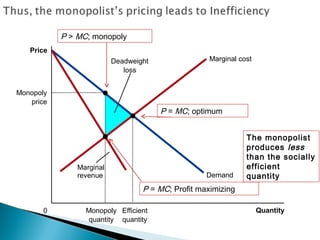
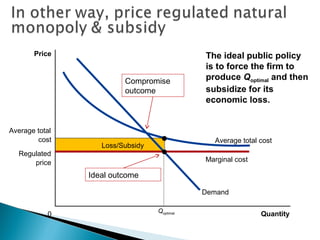
A monopoly is a firm that is the sole seller of a product without close substitutes and faces barriers to entry. There are three sources of barriers to entry: owning a key resource, government protections like patents, and natural monopoly. A natural monopoly exists when economies of scale mean a single firm can supply a market more efficiently than multiple firms. Utilities like electricity are often natural monopolies. Unregulated, a natural monopoly would produce where marginal revenue equals marginal cost, resulting in deadweight loss from underproduction. Regulated, a natural monopoly could be required to produce where price equals marginal cost, the efficient quantity, but would suffer losses requiring subsidy. Compromises include allowing a normal rate of return to limit profits and incentives problems but