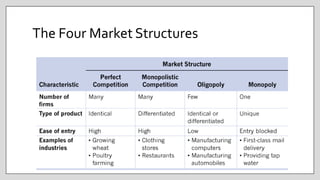
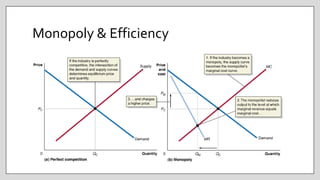
This document discusses monopolies and their characteristics. It notes that monopolies exist when there is only one producer of a good or service in a market. Monopolies may engage in behaviors like raising prices and earning economic profits due to their lack of competition. Barriers to entry like government restrictions, control of key resources, and natural monopolies can allow monopolies to persist by preventing competitors from entering the market. While monopolies are inefficient compared to competitive markets and reduce consumer and economic surplus, they may also incentivize innovation with the prospect of earning large profits.