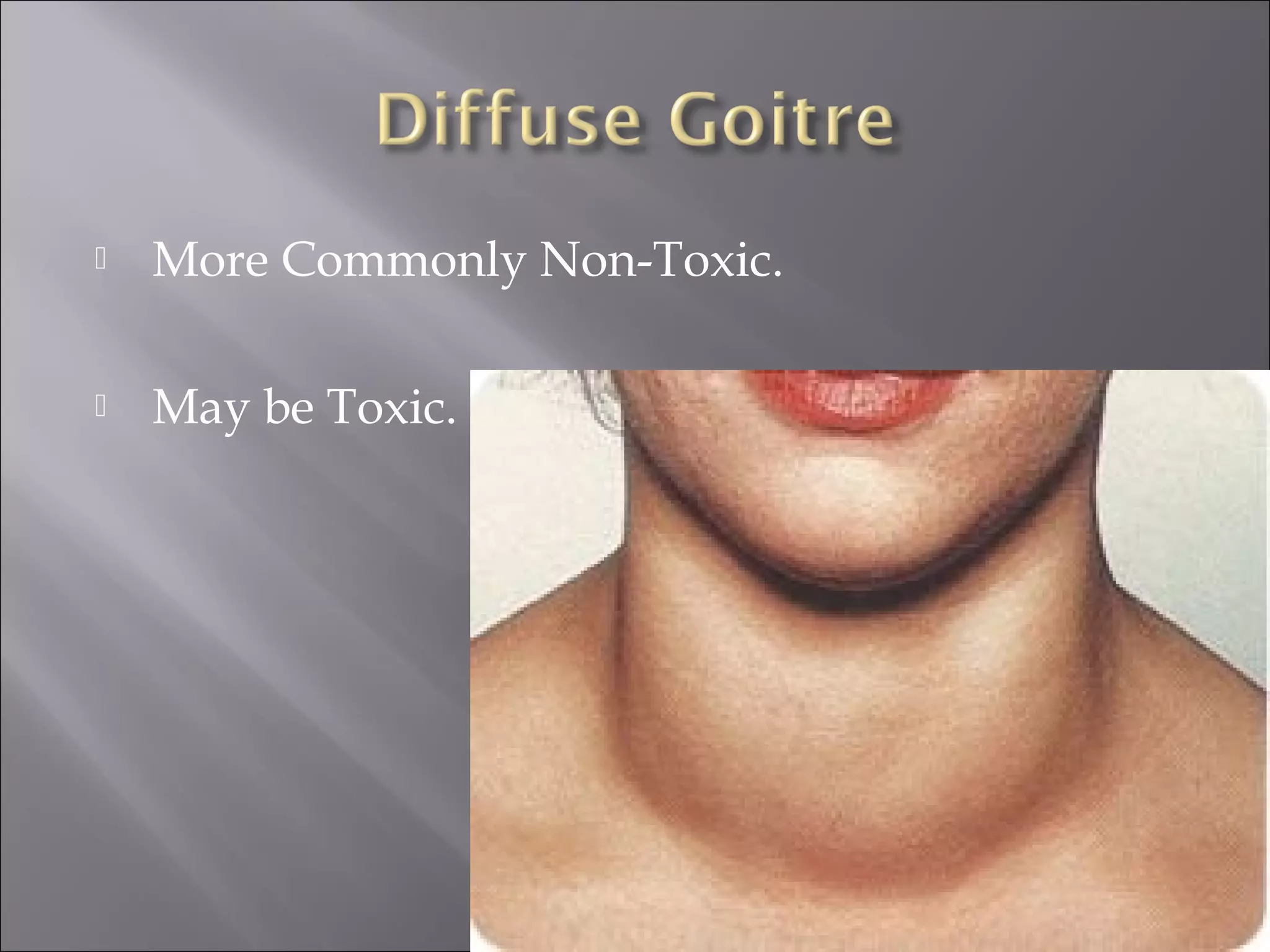
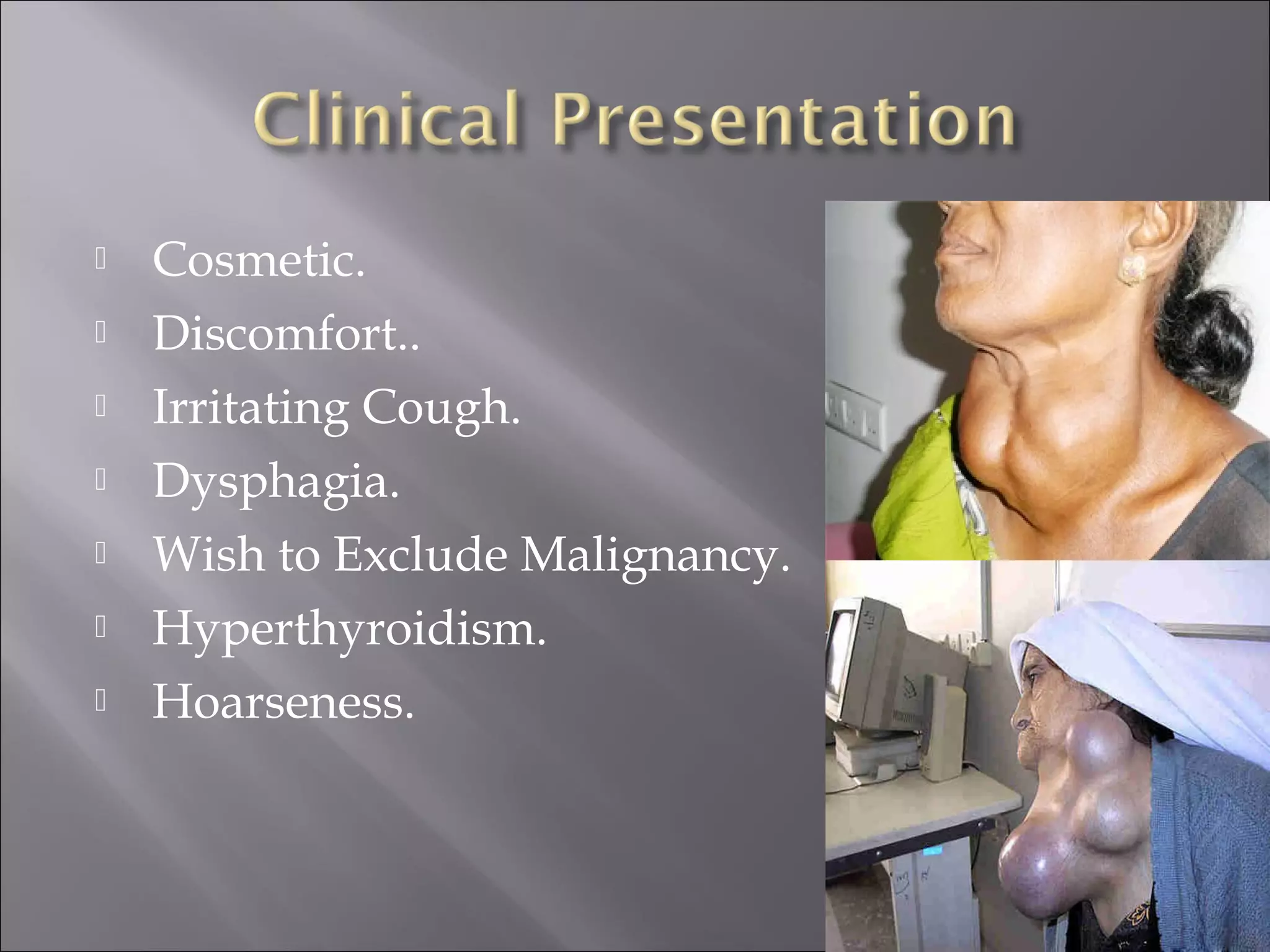
Diffuse toxic goiter, also known as endemic goiter, is an autoimmune disease characterized by overproduction of thyroid hormones causing damage to organs like the nervous and cardiovascular systems. It is caused by iodine deficiency in the environment, especially in soil and water. People in iodine-deficient areas can develop an enlarged thyroid gland with a reduction in its function over time, along with symptoms like difficulty swallowing and changes to heart function. Treatment options include thyroid drugs, surgery to remove part of the thyroid gland, and preventing future cases by providing iodized salt and foods to populations.