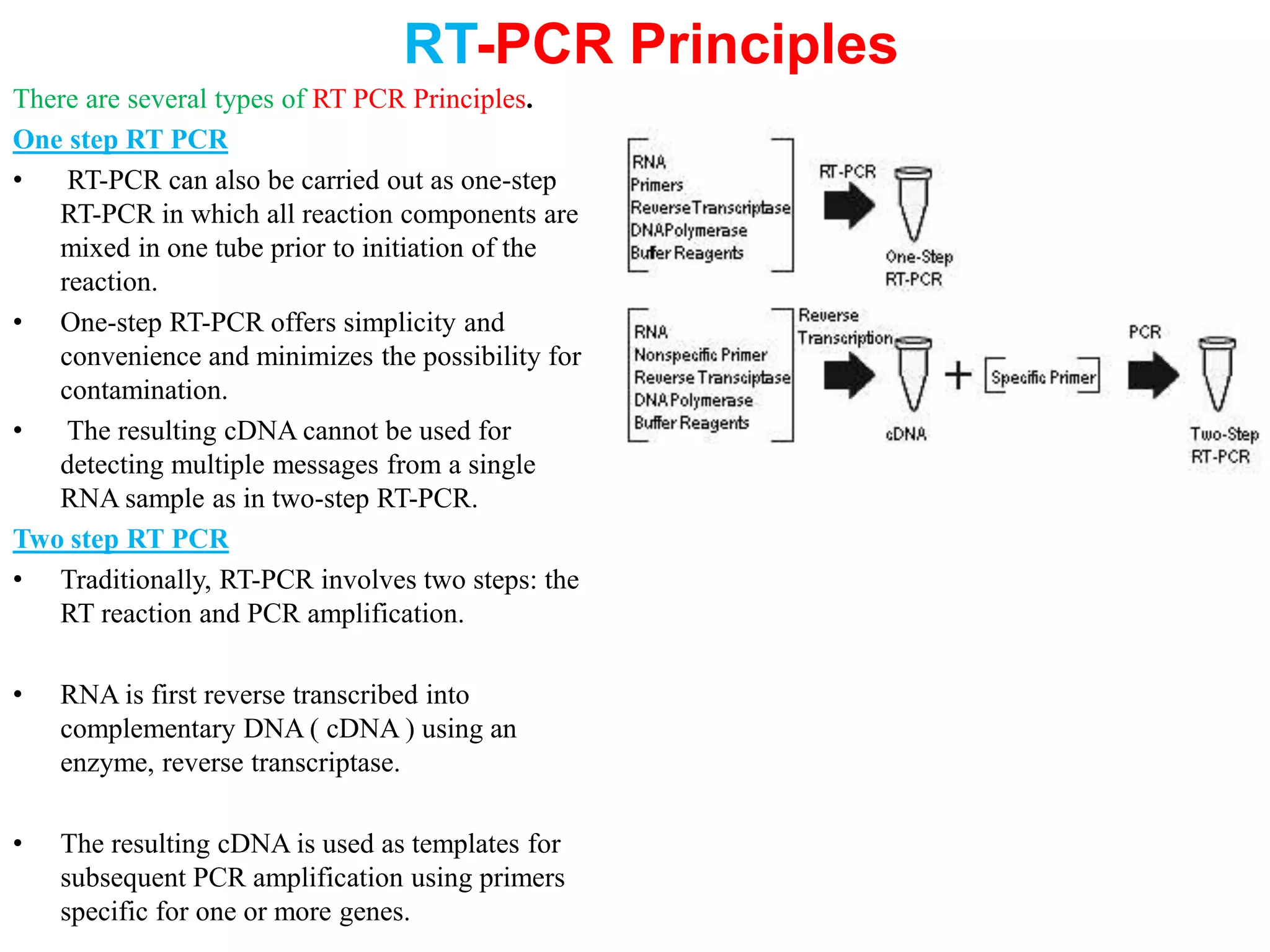
RT-PCR is a technique that uses reverse transcription to transcribe RNA into cDNA, which is then amplified using PCR. It allows for the detection and quantification of RNA. There are two main types: one-step RT-PCR, which performs reverse transcription and PCR in a single step, and two-step RT-PCR, which performs them as separate steps. RT-PCR is widely used in research, disease diagnosis, and detection of gene expression levels.