1. The document outlines the key initial management steps for several acute medical emergencies including rapid assessment, timely management, asking for help, liaising with consultants, and avoiding harm.
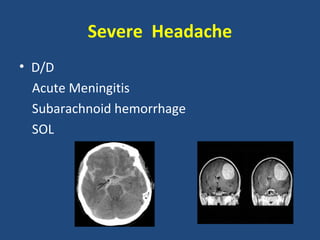
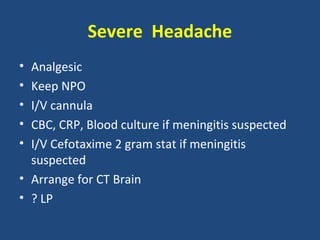
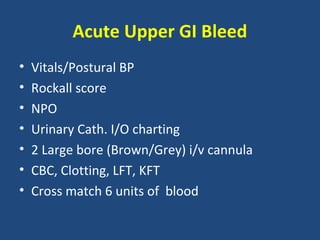
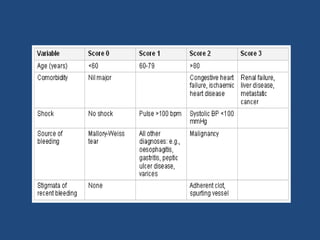
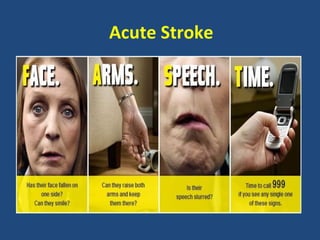
2. For each condition, it provides guidance on important investigations, treatments, and management decisions. The conditions covered include acute coronary syndrome, acute heart failure, acute kidney injury, severe asthma, diabetic ketoacidosis, sepsis, headache, gastrointestinal bleed, stroke, and pulmonary embolism.
3. The overall objective is to provide concise guidance to support rapid evaluation and treatment of acute medical emergencies to optimize patient outcomes.