This document discusses potassium management and provides key details about hypokalemia and hyperkalemia. It covers:
- Causes of hypokalemia including redistribution, extrarenal loss, and renal loss. Redistribution can be caused by alkalosis, medications, or increased sympathetic tone. Extrarenal losses include diarrhea, laxative abuse, and sweating. Renal losses are associated with metabolic acidosis or alkalosis.
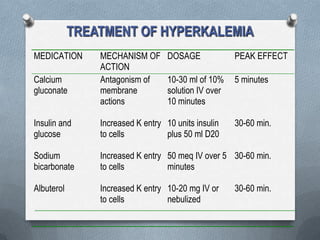
- Treatment of hypokalemia focuses on replacing deficits orally or intravenously, while also treating underlying causes.
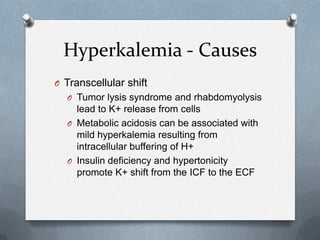
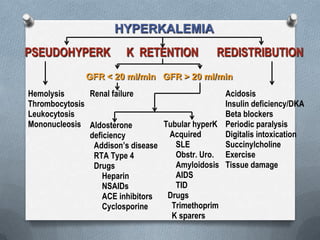
- Causes of hyperkalemia include increased intake, pseudohyperkalemia, transcellular shifts during conditions like tumor l