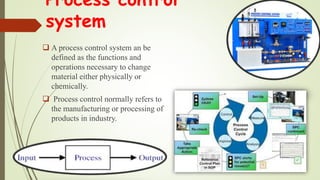
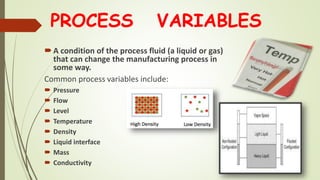
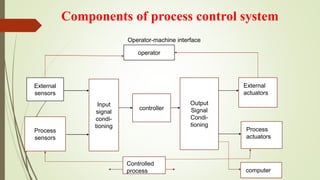
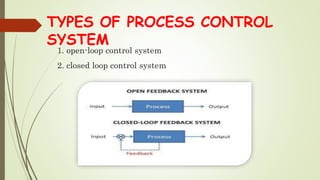
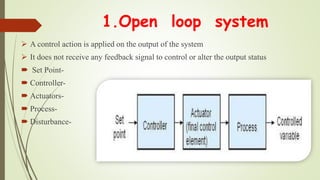
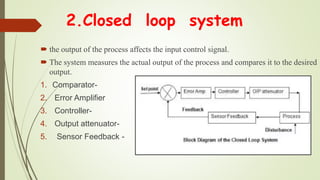
This document discusses process control systems. It defines a process as a sequence of interdependent procedures that transforms inputs into outputs. Control involves regulating all aspects of a process. There are three main types of processes: continuous, batch, and discrete. A process control system uses controllers and feedback to maintain process variables like pressure, temperature and flow within desired ranges. It consists of sensors, actuators and an operator interface. The two main types are open-loop and closed-loop systems. Process control has applications in industries like food production, manufacturing, and waste water treatment. Future areas of development include smart cities and transportation.