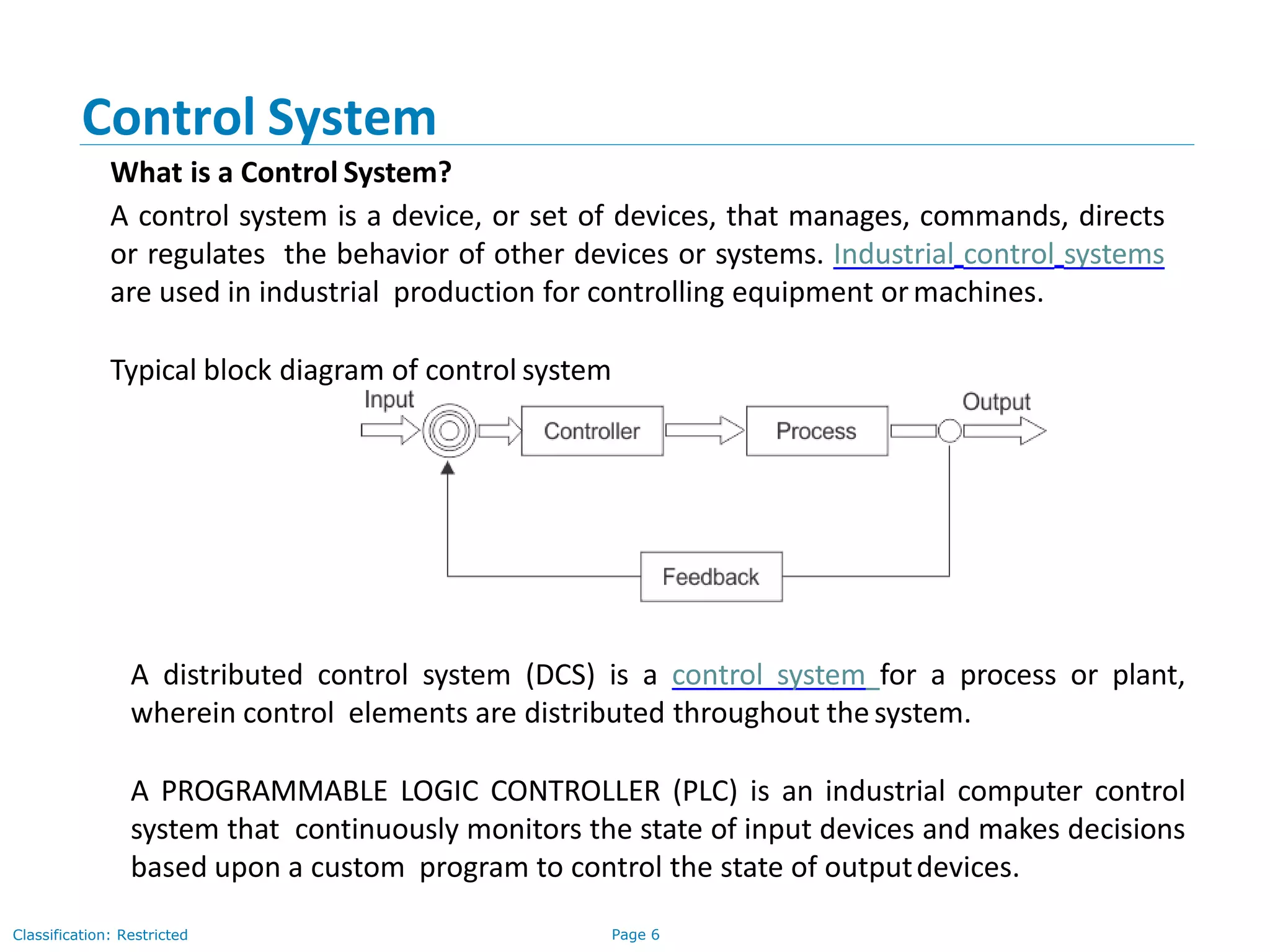
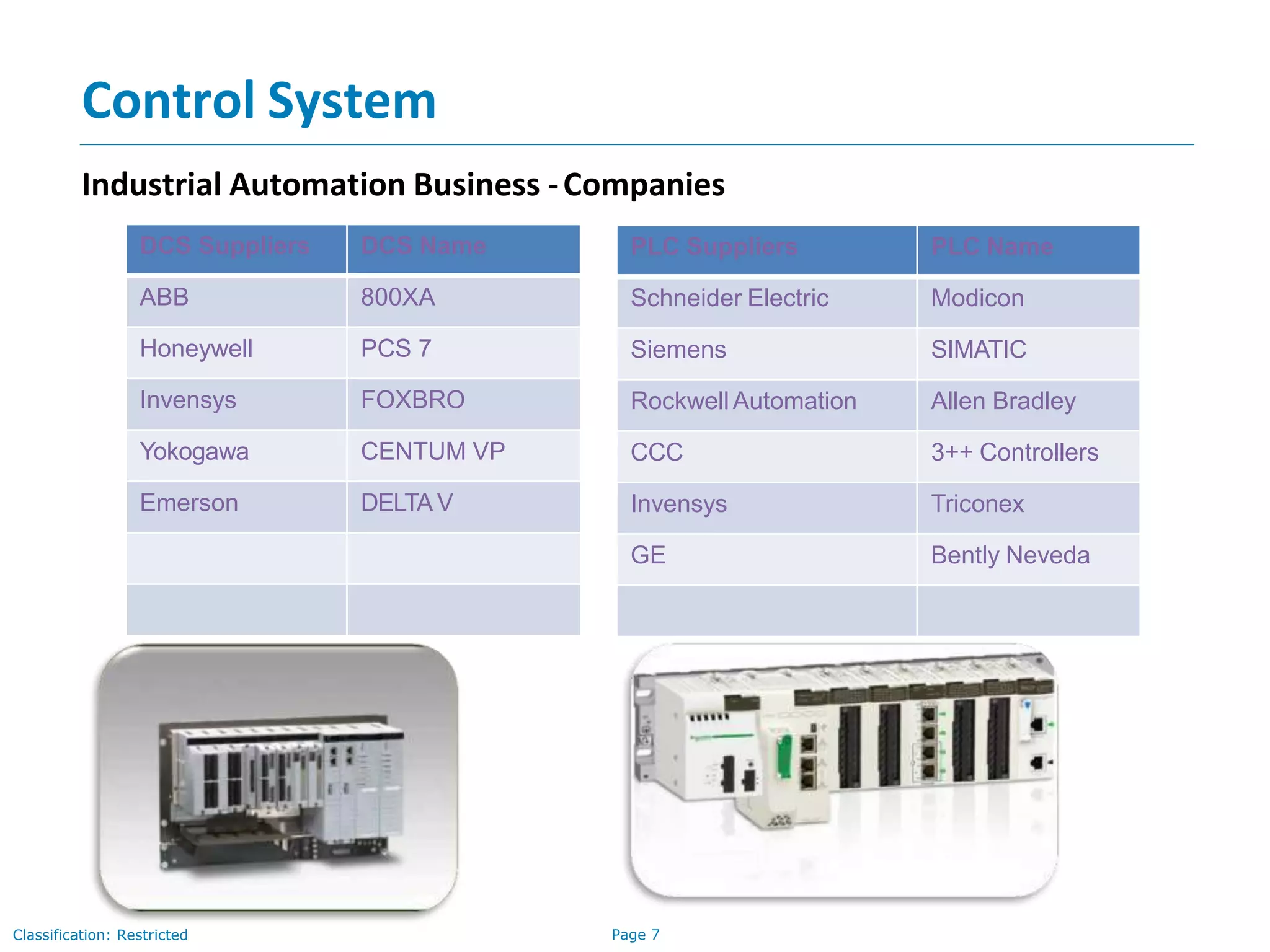
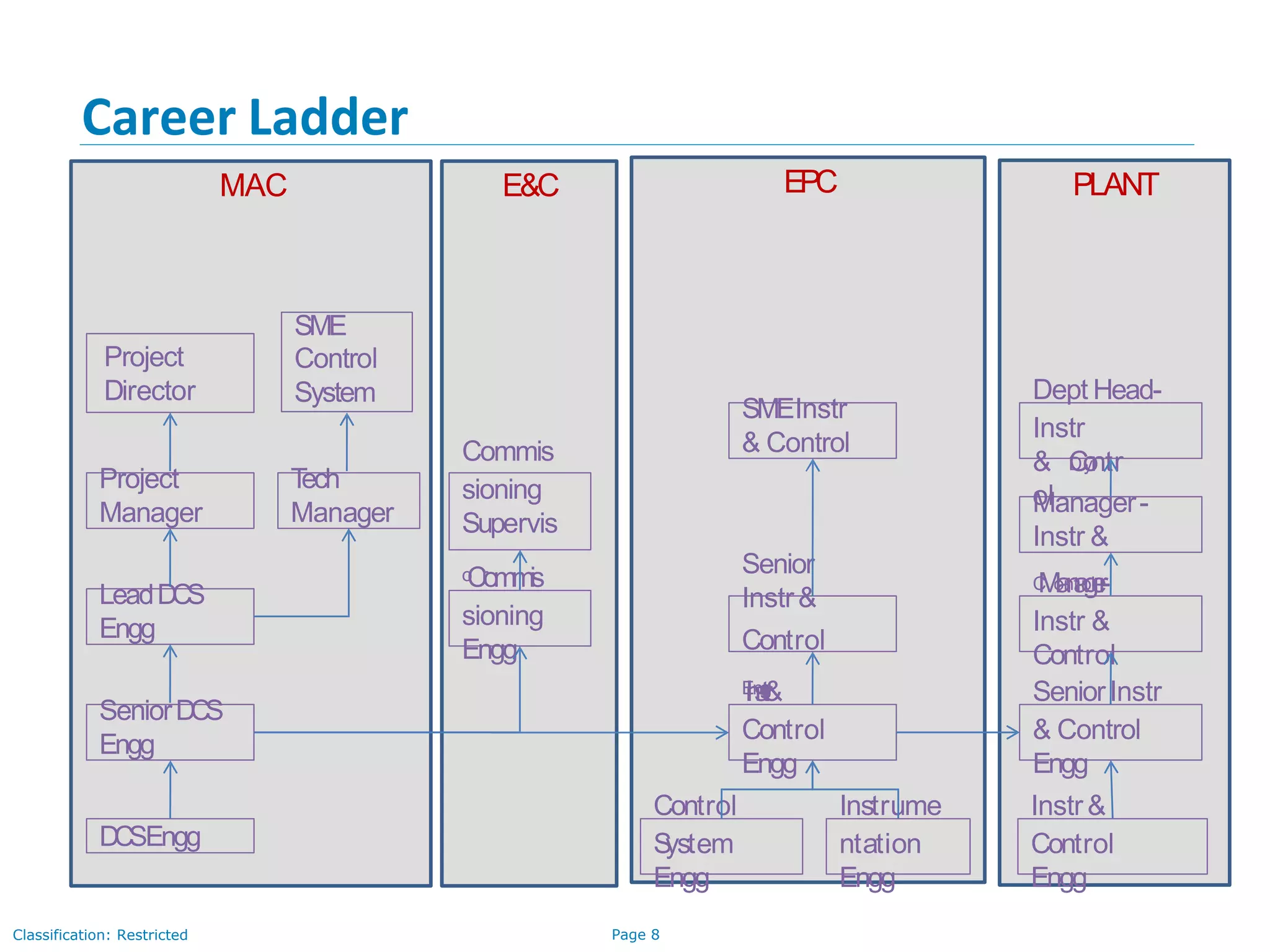
The document provides an overview of industrial automation and its significance in process industries, focusing on enhancing productivity, reducing costs, and improving safety and product quality. It outlines key concepts such as process control, the functionality of control systems, and the technical skills required for a control system engineer, along with a curriculum for training in these areas. Additionally, it lists examples of process industries and relevant suppliers of Distributed Control Systems (DCS) and Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC).