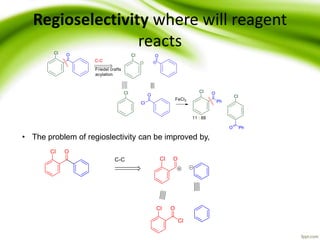
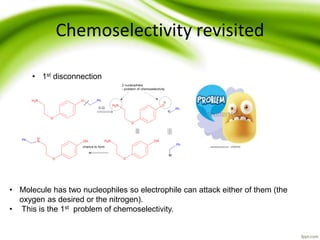
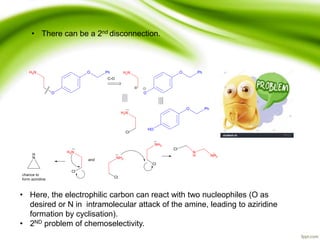
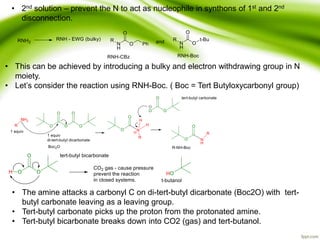
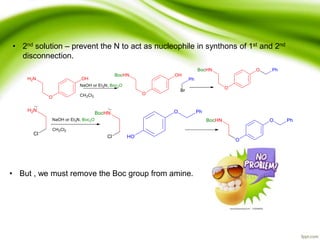
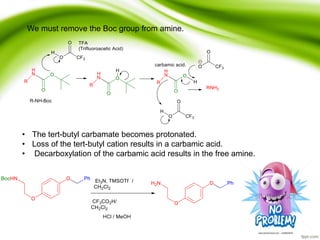
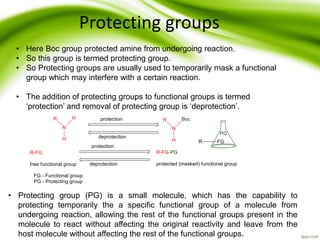
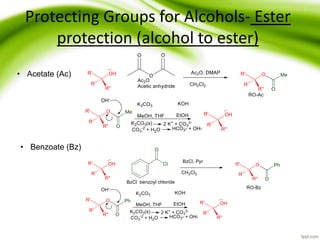
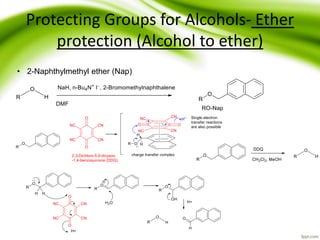
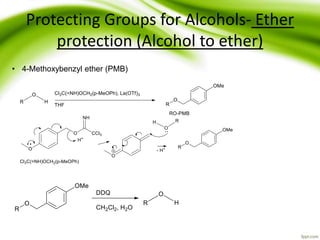
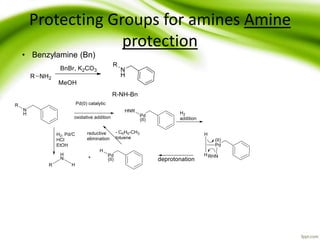
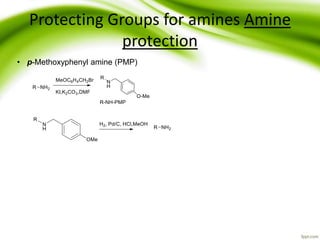
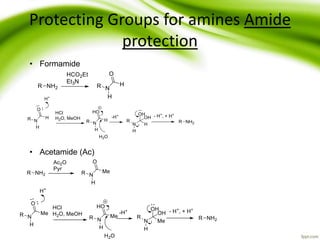
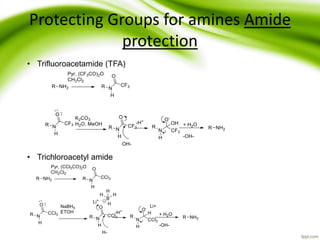
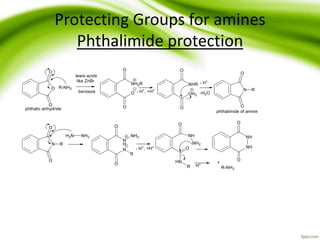
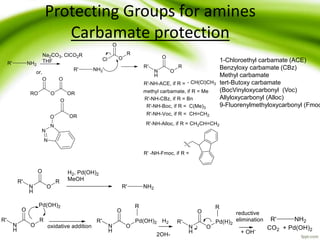
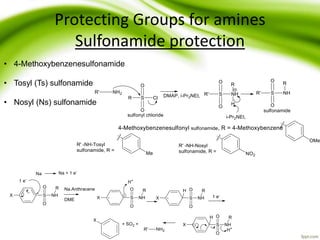
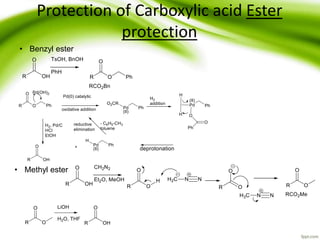
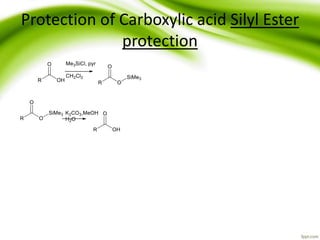
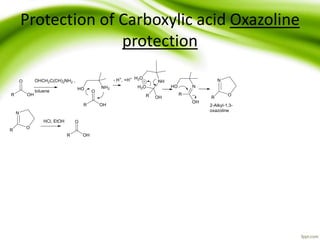
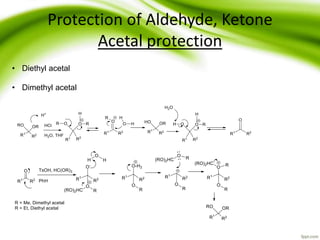
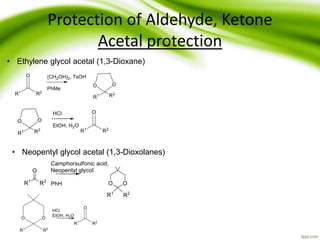
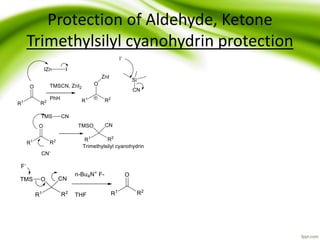
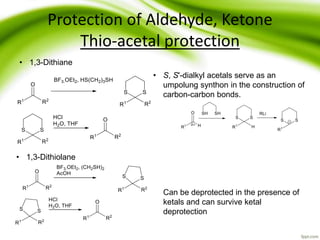
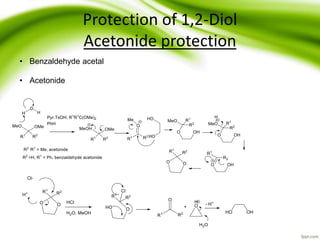
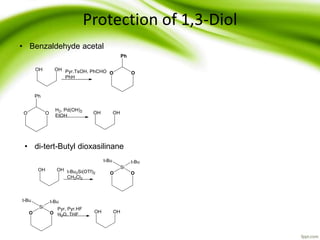
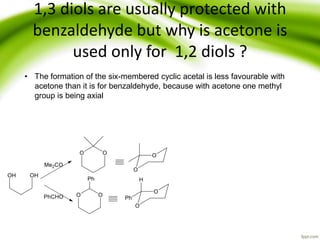
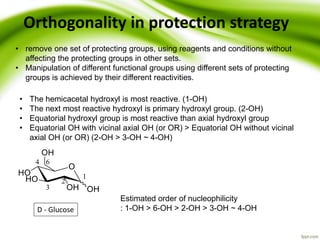
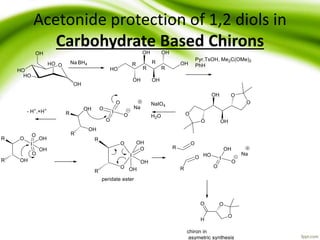
The document discusses the significance of protecting groups in organic synthesis, emphasizing their role in enhancing selectivity during chemical reactions. It outlines different types of protecting groups, their applications, and strategies for both protection and deprotection of functional groups. The document also explores various examples and conditions for using specific protecting groups for alcohols, amines, and carboxylic acids.