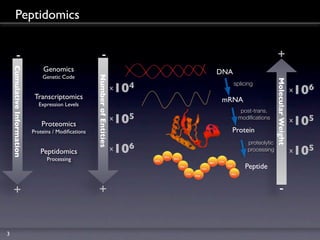
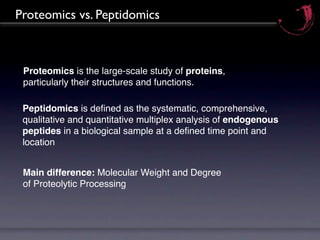
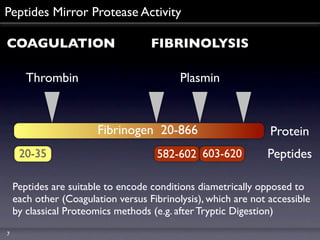
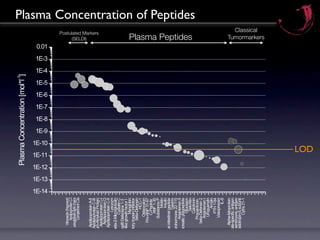
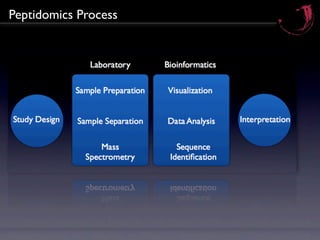
Peptidomics is the study of endogenous peptides in biological samples. It analyzes peptides on a larger scale than proteomics due to peptides' lower molecular weight and higher numbers produced through proteolytic processing. Peptidomics can detect markers not accessible by proteomics as peptides reflect protease activity. The process involves fractionating samples, analyzing peptides by mass spectrometry, and correlating peptide signals to variables like disease markers. Key factors for successful peptidomics studies include design, quality control, technology integration, and a holistic biological and technical approach.


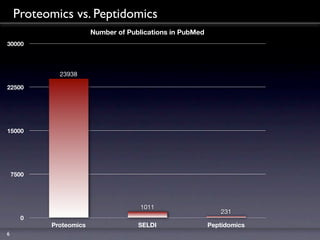
![NCBI-PubMed Search
Proteomics Genomics
0.700
0.525
% of Publications [normalized]
0.350
0.175
0
1980 1986 1992 1998 2004 2010
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/peptidomicsbasics1109-1315400508042-phpapp02-110907080410-phpapp02/85/Peptidomics-Basics-4-320.jpg)
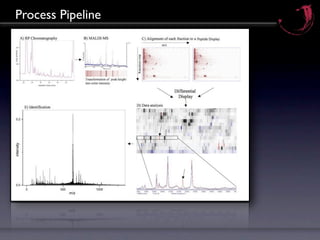
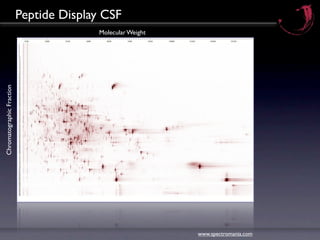
![Correlation Analysis
m/z
Each datapoint (1-3 Mill./Display) is [INS_human 57-87]
correlated to a corresponding
variable (e.g. plasma level insulin).
Fraction
[INS_human 25-54]
By applying a threshold value only
correlating datapoints are shown.
In contrast to „conventional“
methods no export of signals is
required:
The full information content of each
mass spectrum is used for analysis.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/peptidomicsbasics1109-1315400508042-phpapp02-110907080410-phpapp02/85/Peptidomics-Basics-12-320.jpg)

