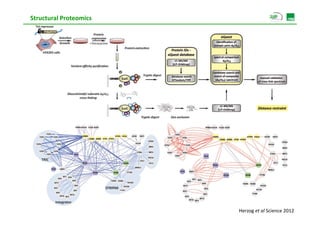
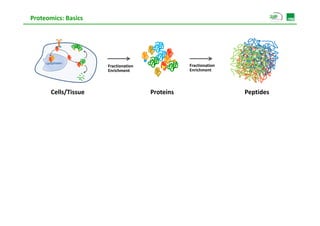
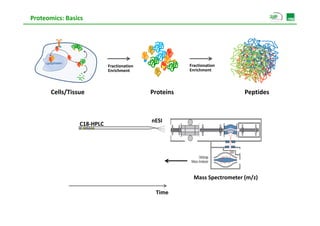
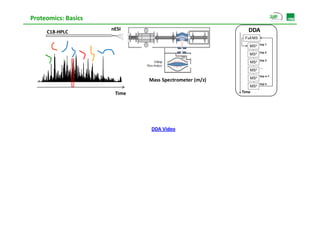
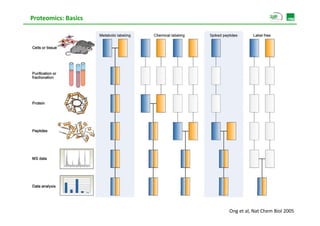
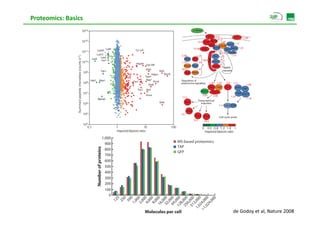
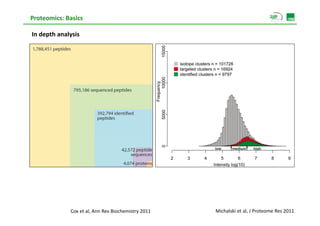
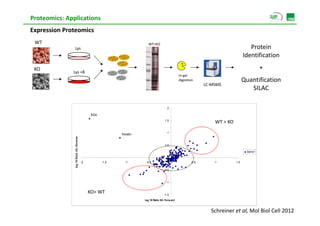
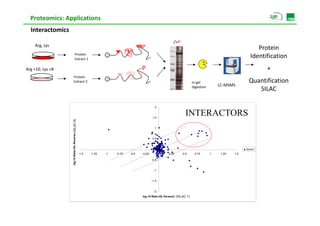
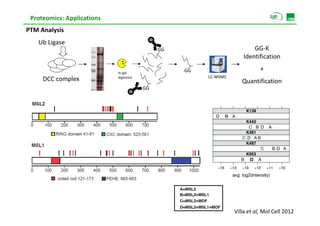
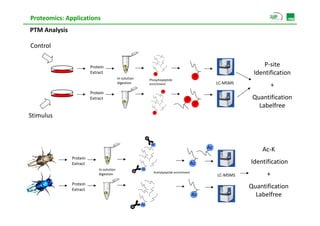
Proteomic analysis involves fractionating and enriching cells or tissue to isolate proteins, then further breaking the proteins into peptides. The peptides are separated using chromatography and introduced into a mass spectrometer to determine their mass-to-charge ratios. Data-dependent acquisition is used to automatically select peptides for fragmentation and sequencing to identify the proteins present. Proteomics provides information about protein expression levels, post-translational modifications, interactions, and dynamics that complement genomics and transcriptomics data.

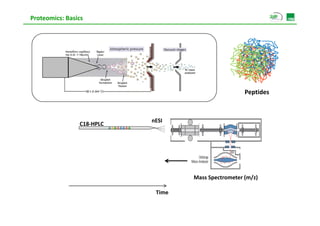
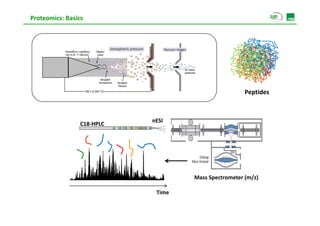
![Proteomics: Basics
nESI DDA
C18‐HPLC
Full MS
top 1
MS2
top 2
MS2
top 3
p
MS2
....
MS2
top n-1
MS2
Mass Spectrometer (m/z)
top n
MS2
Time Time
Full MS
p [ ] MS2 MS2 MS2 MS2
T: FTMS + p NSI Full ms [300.00-2000.00] 472.7700
472.7700 100 _ _ _ top 1 top 2 top 3 top n
100
F: ITMS + c NSI d w Full ms2 472.77@cid35.00
90
575.30
90 100
80 428.25
90
ce
80 70
Relative Abundanc
60 80
70
473.2710
Relative Abundance
50 70
Relativ Abundance
60
40 60
50 944.5325
513.2991 30 50
ve
769.4453
769 4453
40 691.3953 20 40
473.7723
10 472.3233 30 703.36
30
471.8120 474.2738 517.17
0 20 242.05 343.35
20 472 473 474
1046.2464 232.18
/ 10
0 686 31 713.30
686.31
10 1106.5581 1381.7826
1844.3618
873.53
1306.7396 1537.8872
0
1890.9115
0 200 400 600 800
400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800 2000 m/z
m/z
Time](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day2s3forneferrer-130308090111-phpapp02/85/Proteomics-analysis-Basics-and-Applications-10-320.jpg)
![Proteomics: Basics
nESI DDA
C18‐HPLC
Full MS
top 1
MS2
top 2
MS2
top 3
p
MS2
....
MS2
top n-1
MS2
Mass Spectrometer (m/z)
top n
MS2
Time Time
Full MS
MS2 MS2 MS2 MS2
T: FTMS + p NSI Full ms [300.00-2000.00]
472.7700 944.5324 top 1 top 2 top 3 top n
100 100
F: ITMS + c NSI d w Full ms2 944.53@cid35.00
90 1108.53
90
100
80
80 90
Relative Abundanc e
70
945.0824
810.08
70 60 80
945.5353
Relative Abundance
50 70
Relativ Abundance
60
761.14
40 60
50 944.5325 944.2667
513.2991 30 50
ve
A
769.4453
769 4453
945.7967
40 691.3953 20 621.24
946.5384 40
10
30 9 30 1266.51
943.5265
0
20 944 945 946 947 20 353.26
1046.2464 m/z 493.13
493 13 915.90
1381.7826 10 1469.38
1469 38
10 1106.5581
1844.3618 1714.74
1306.7396 1537.8872 1890.9115 0
0 500 1000 1500
400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800 2000
m/z m/z
Time](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day2s3forneferrer-130308090111-phpapp02/85/Proteomics-analysis-Basics-and-Applications-11-320.jpg)
![Proteomics: Basics
nESI DDA
C18‐HPLC
Full MS
top 1
MS2
top 2
MS2
top 3
p
MS2
....
MS2
top n-1
MS2
Mass Spectrometer (m/z)
top n
MS2
Time Time
Full MS
MS2 MS2 MS2 MS2
513.2990
T: FTMS + p NSI Full ms [300.00-2000.00] 100
472.7700 top 1 top 2 top 3 top n
100
90 F: ITMS + c NSI d w Full ms2 513.30@cid35.00
513.6329
80 534.53
90 100
598.58
dance
70
80 90
60
Relative Abund
80
70 50
Relative Abundance
70
Relativ Abundance
40 513.9668
60
30 60
50 944.5325
513.2991 20 50 655.13
655 13
ve
769.4453
769 4453 514.3010
40 691.3953 10 513.1269
512.7917 514.6352 40
0
30 513.0 513.5 514.0 514.5 30 449.42
m/z
20
20
230.02 717.35
1046.2464 10 343.04
343 04
10 1106.5581 1381.7826
1844.3618
825.52 926.25 1050.54
1306.7396 1537.8872
0
1890.9115
0 200 400 600 800 1000
400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800 2000
m/z
m/z
Time](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day2s3forneferrer-130308090111-phpapp02/85/Proteomics-analysis-Basics-and-Applications-12-320.jpg)
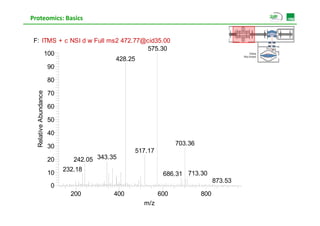
![Proteomics: Basics
Peptide charge and mass
p g
(M+2H)2+ [ The charge
p ]
100
472.7700 (m2-m1)/z= 0.5 z=2
90
[m2-m1 = 1]
80
z=2 m= M+2H+
ance
70
Relativ Abunda
60
473.2710
50 The mass
ve
40
0 m/z= (M+2H+)/2
30 m/z=472.7700
20 473.7723 H+ =1 0073
=1.0073
10 472.3233
471.8120 474.2738
0 M 943.5254
M= 943 5254
472 473 474
m/z /](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day2s3forneferrer-130308090111-phpapp02/85/Proteomics-analysis-Basics-and-Applications-14-320.jpg)
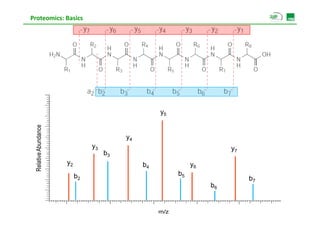
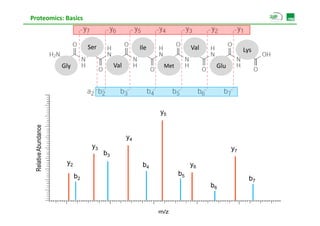
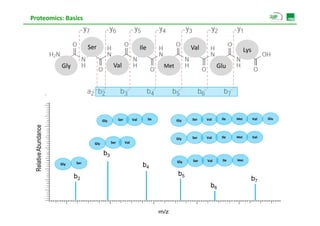
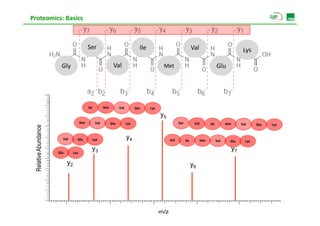
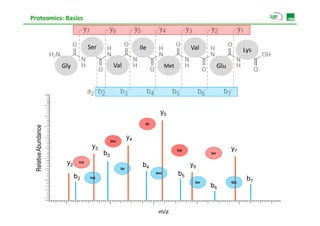
![Proteomics: Basics
nESI
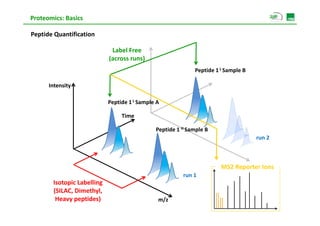
Peptide Quantification
Peptide Quantification C18‐HPLC
p [ ]
472.7700
100
90
80
ance
70
Relative Abunda
60
473.2710
50
40
30
20 473.7723
10 472.3233
Intensity 0
471.8120
472 473 474
474.2738
Mass Spectrometer (m/z)
Mass Spectrometer (m/z)
/
Peptide 1 L Sample A
Time
m/z](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day2s3forneferrer-130308090111-phpapp02/85/Proteomics-analysis-Basics-and-Applications-23-320.jpg)
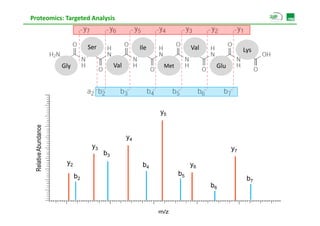
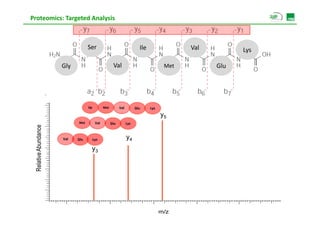
![Proteomics: Targeted Analysis
p [ ]
472.7700
472 7700
100 Ile Met Val Glu Lys
90 y5
Met Val Glu Lys
80
ce
Relativ Abundanc
Relativ Abundance
70
60 Val Glu Lys y4
473.2710
50 y3
ve
ve
40
30
20 473.7723
10 472.3233
472 3233
471.8120 474.2738
0
472 473 474
/
m/z
SRM Video Picotti et al, Nat Methods 2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day2s3forneferrer-130308090111-phpapp02/85/Proteomics-analysis-Basics-and-Applications-38-320.jpg)