1) The document discusses power steering systems, including hydraulic power steering (HPS) and electric power steering (EPS).
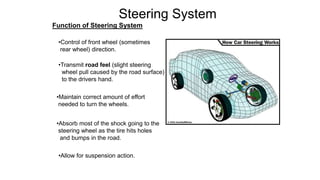
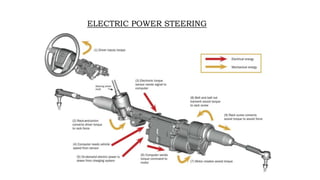
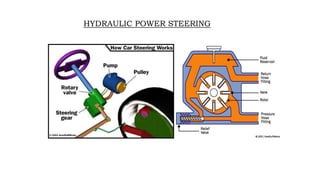
2) HPS uses a hydraulic system and pump driven by the engine to reduce steering effort. EPS uses an electric motor and sensors to detect steering torque and apply assistive torque.
3) Both systems aim to make steering easier while maintaining feedback and stability, and allow for a mechanical linkage backup in failures.
![Gandhinagar Institute of Technology
Subject :- Control Engineering
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
5th - B : 2
Presentation
on
Power steering
– Pavan Narkhede [130120119111]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/powersteeringsystem-151231104423/75/Power-steering-system-1-2048.jpg)