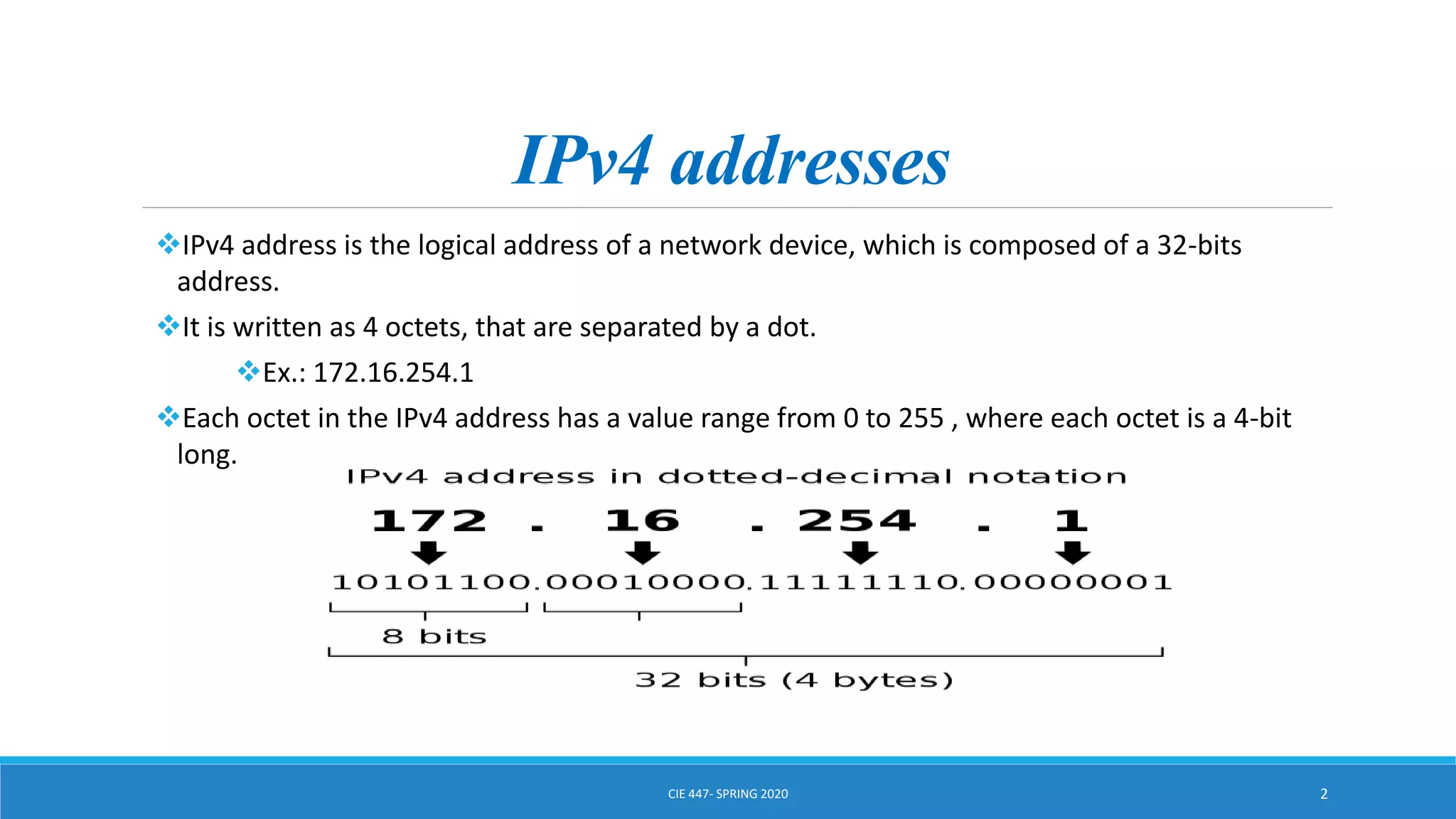
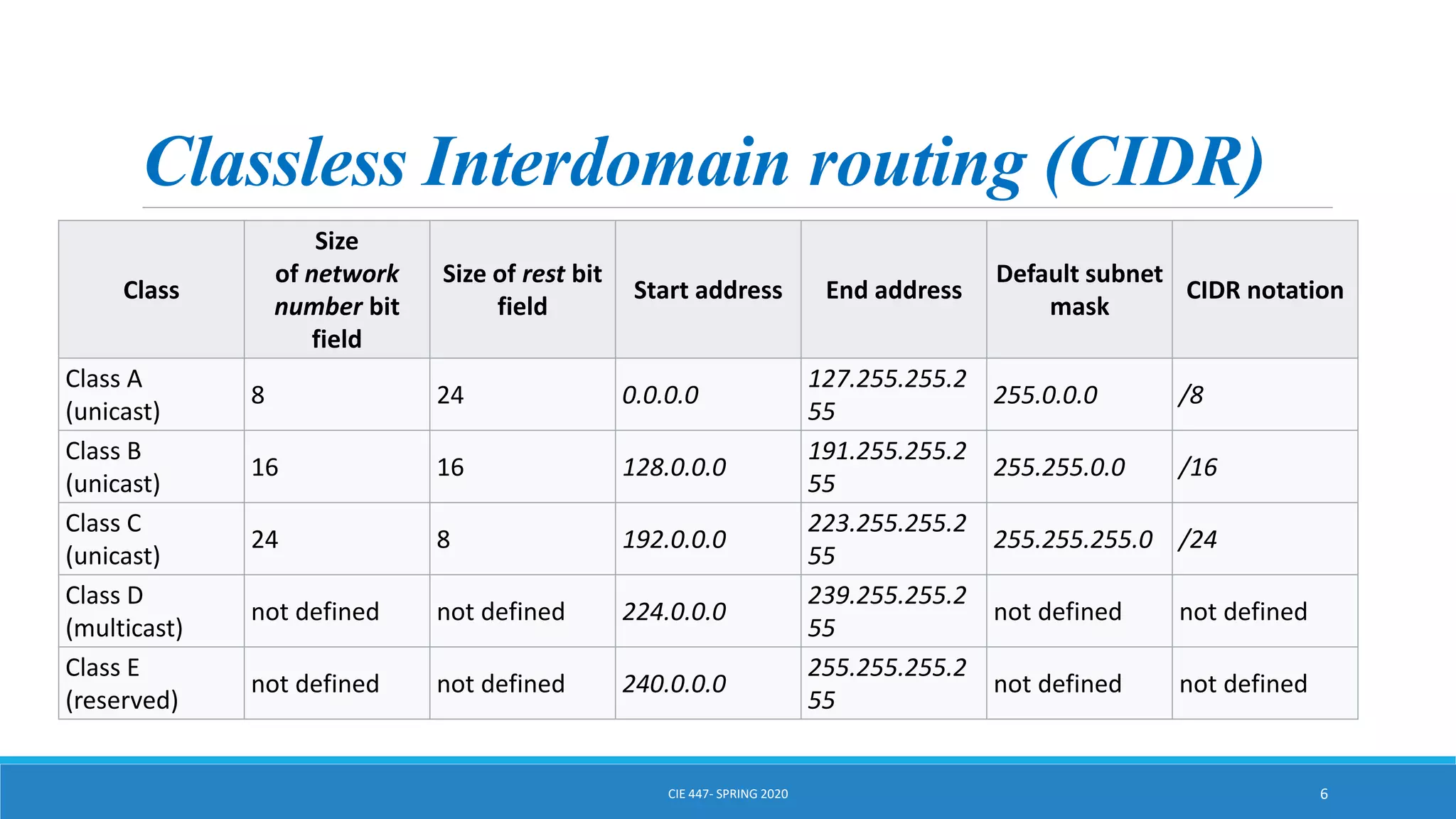
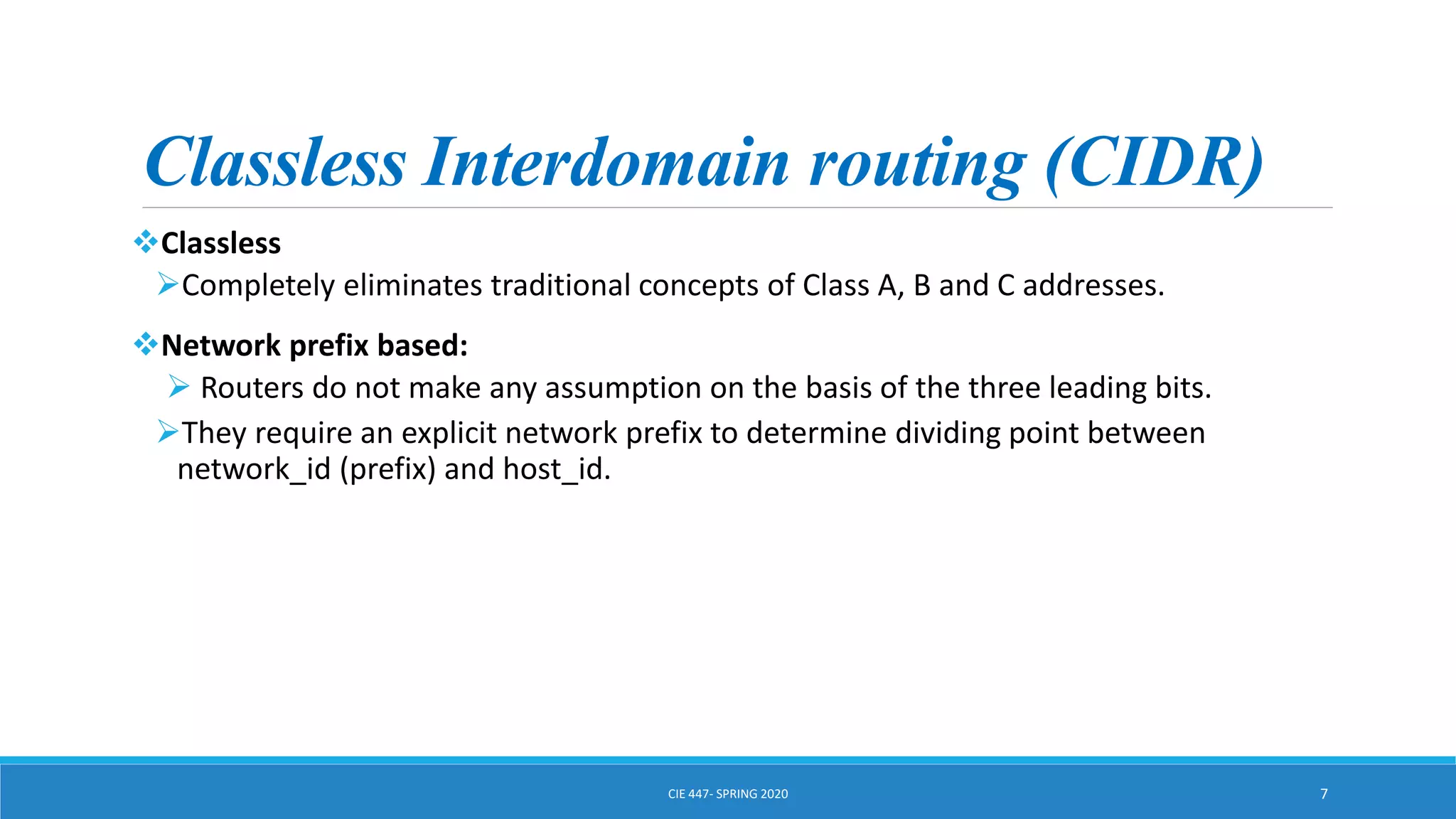
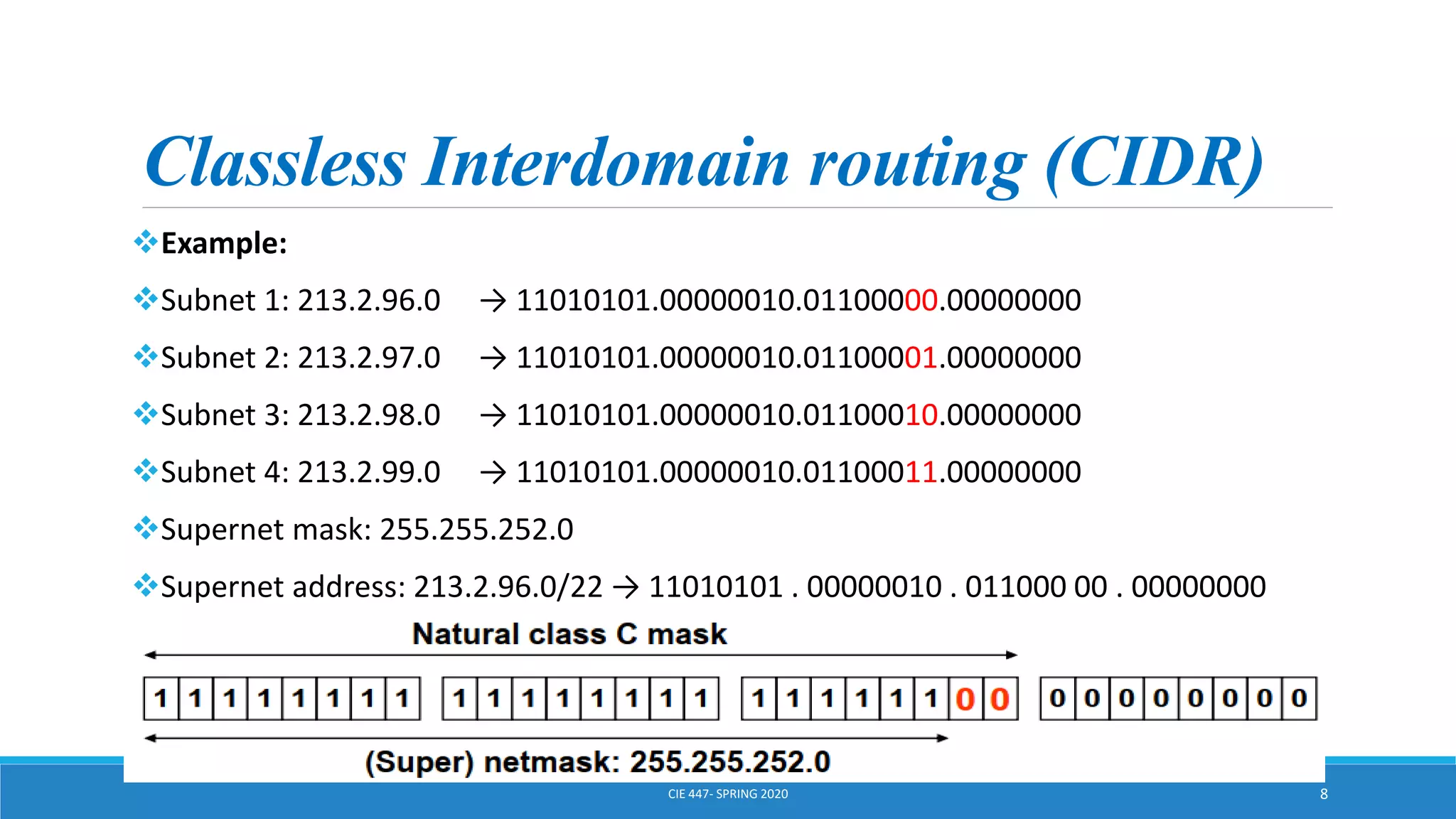
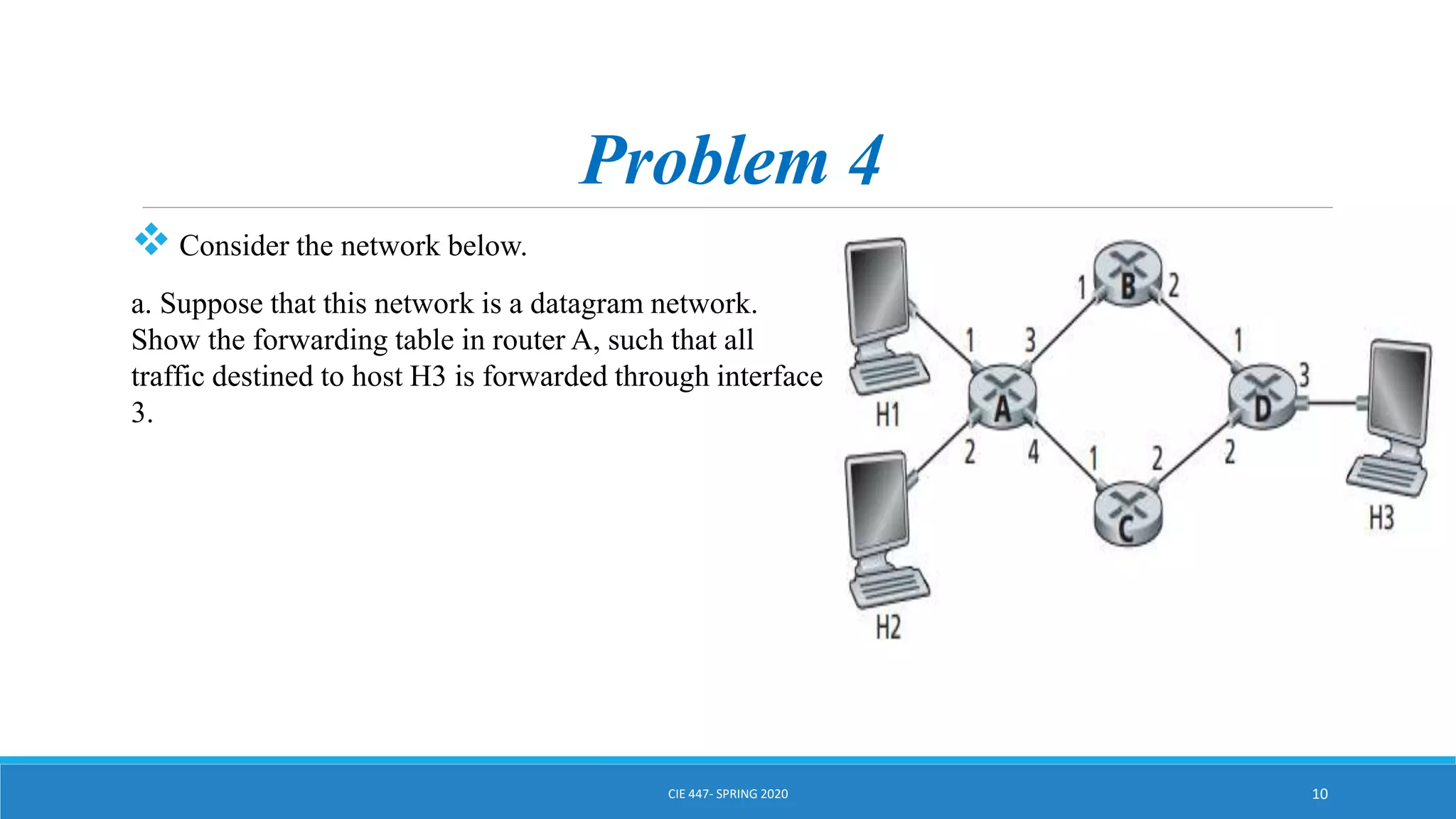
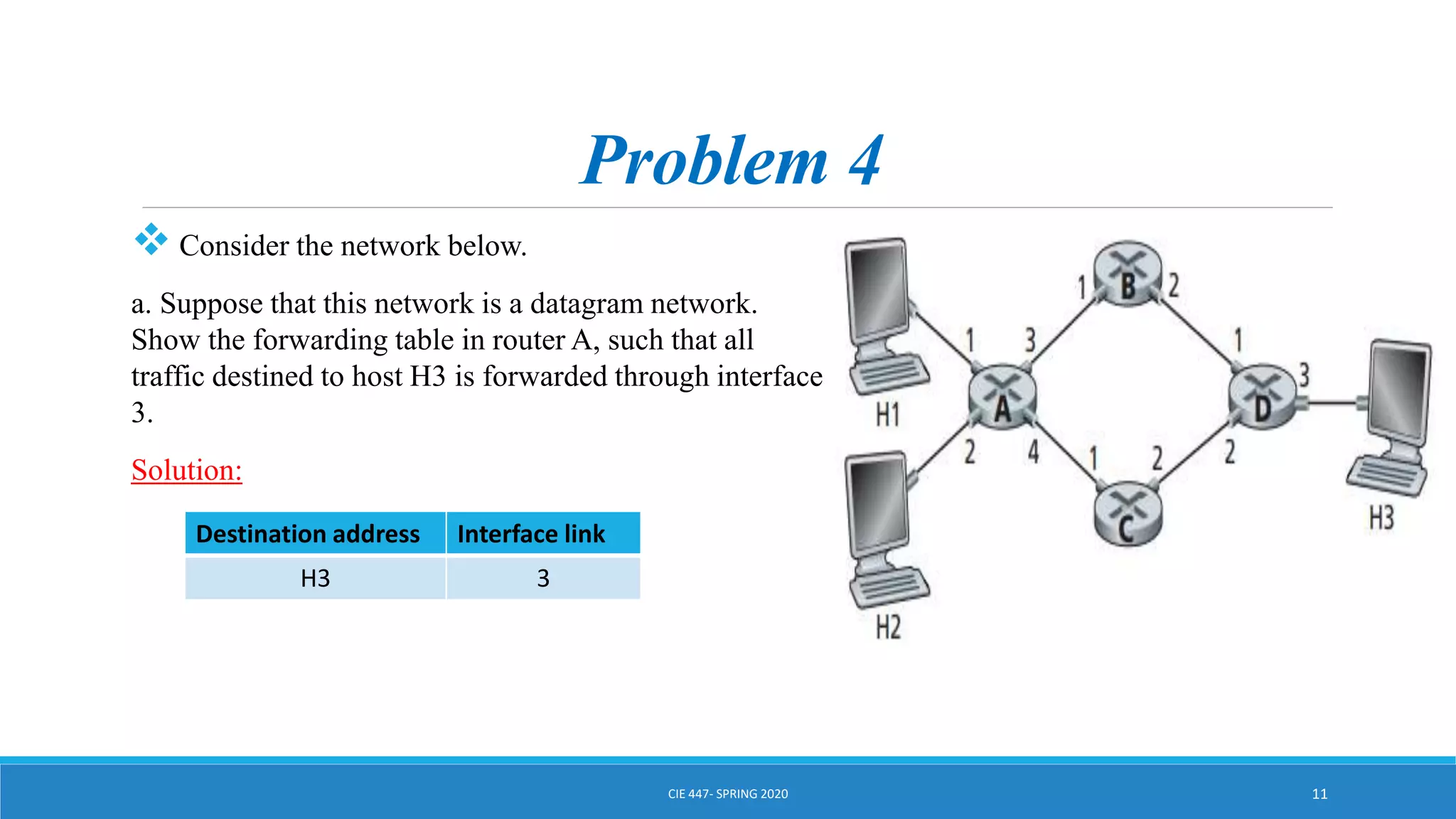
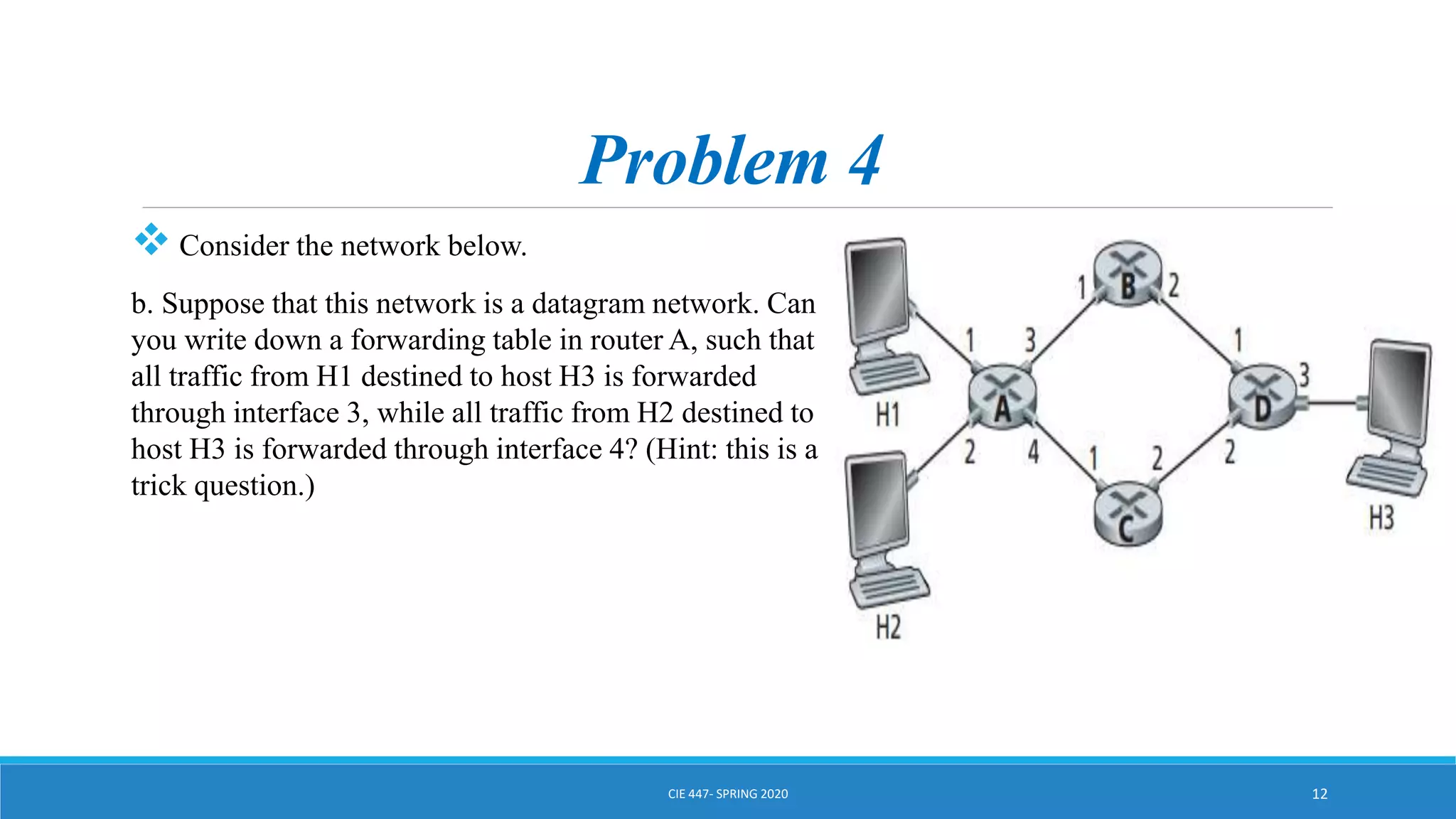
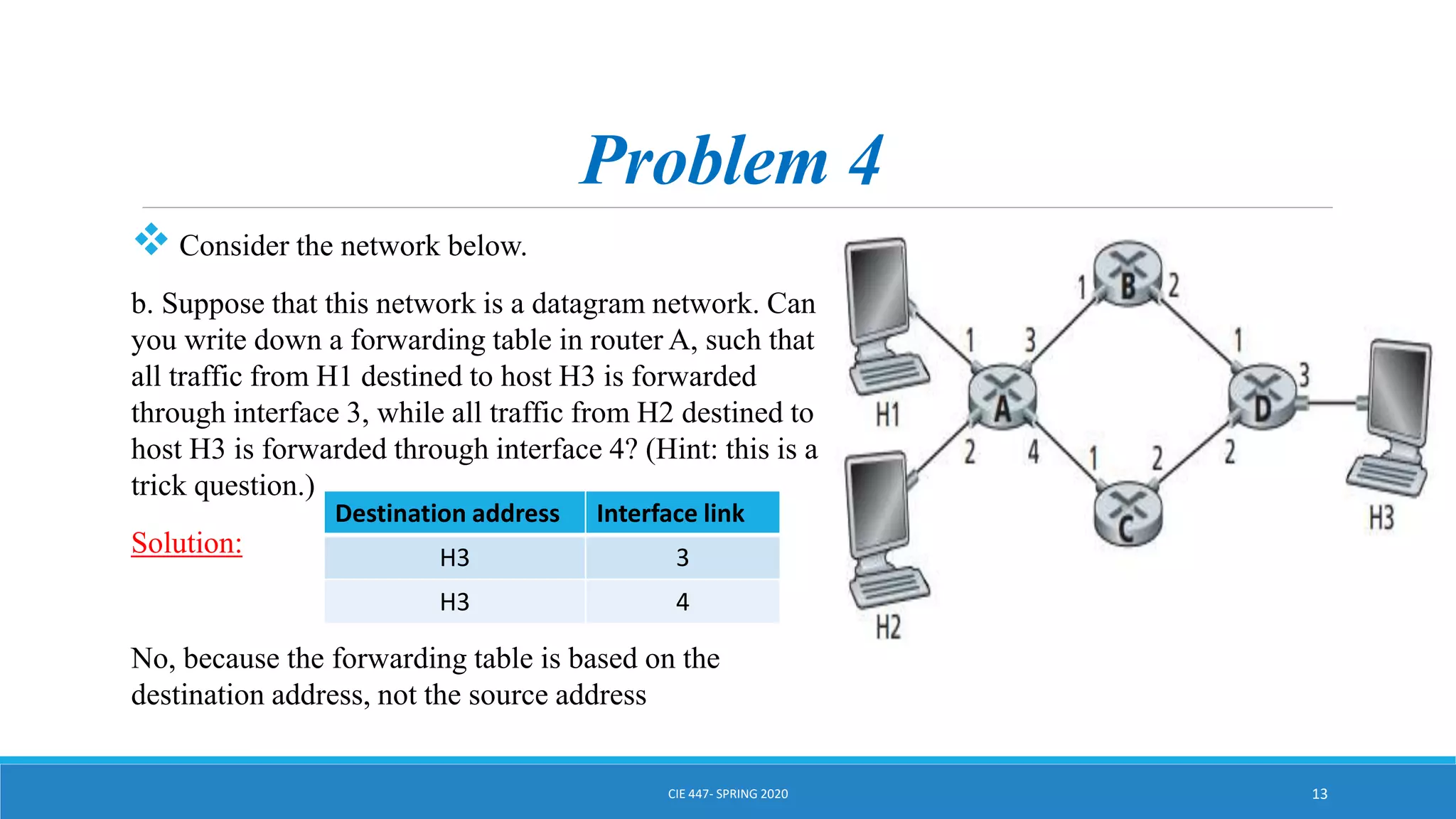
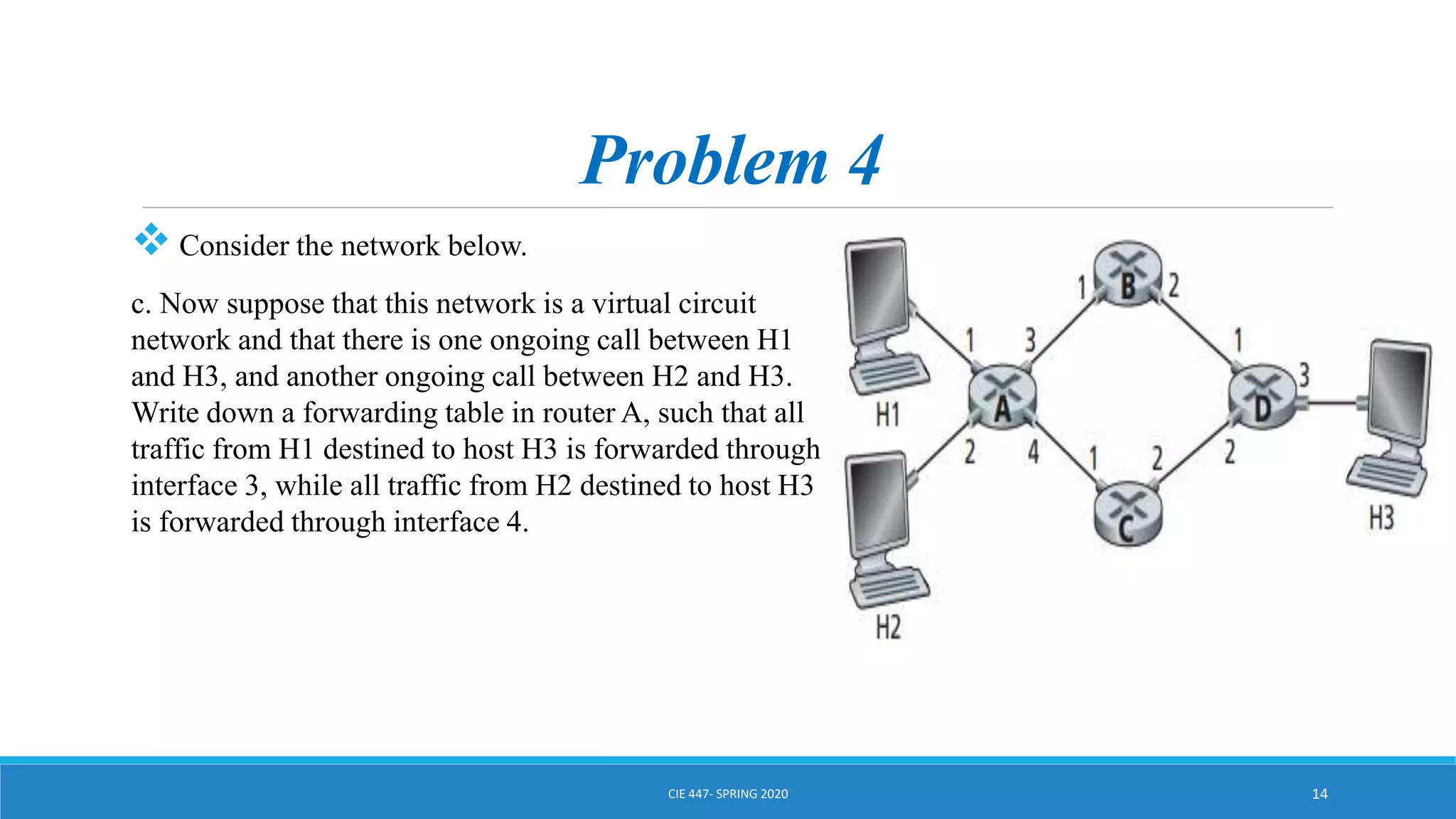
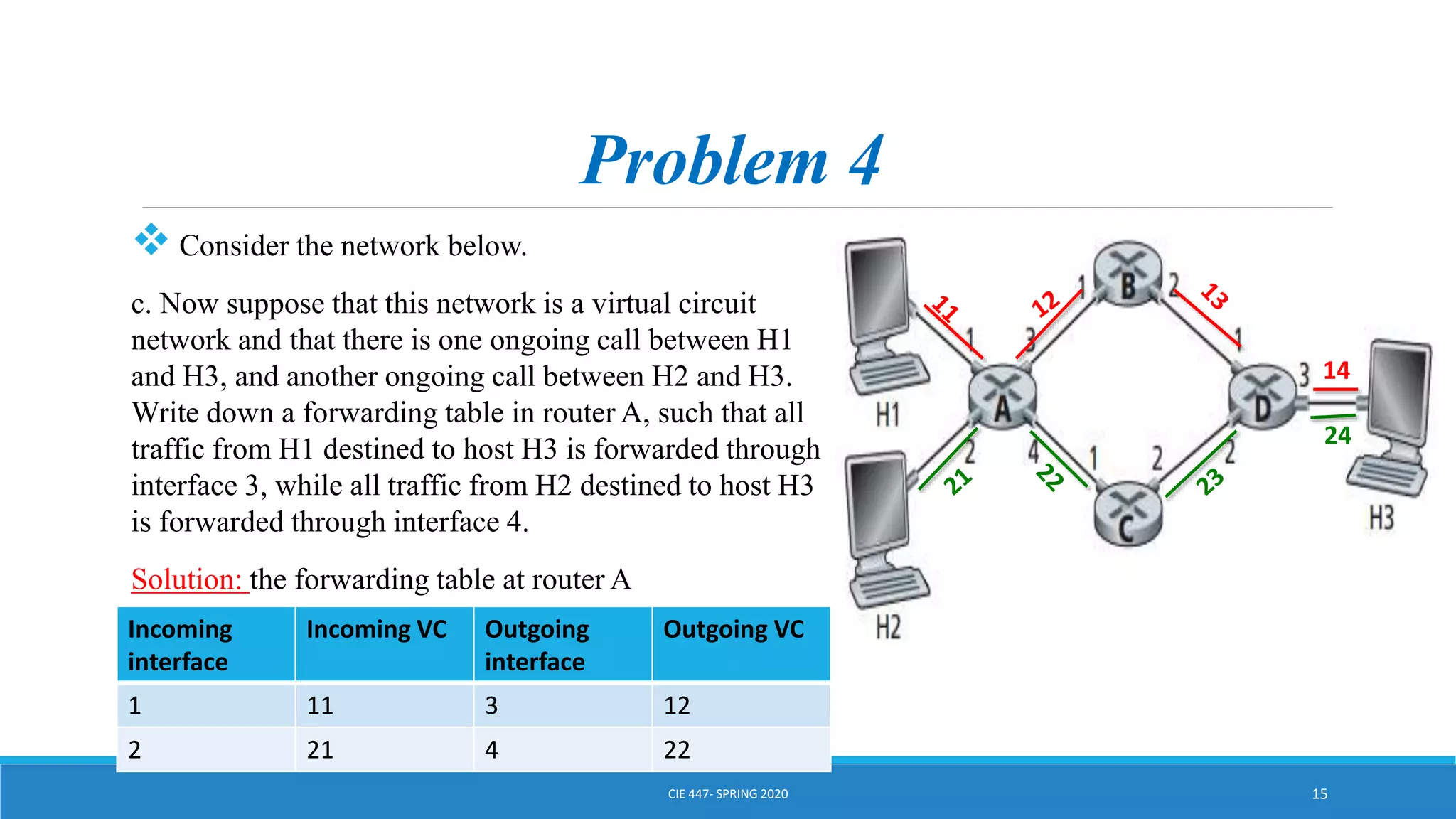
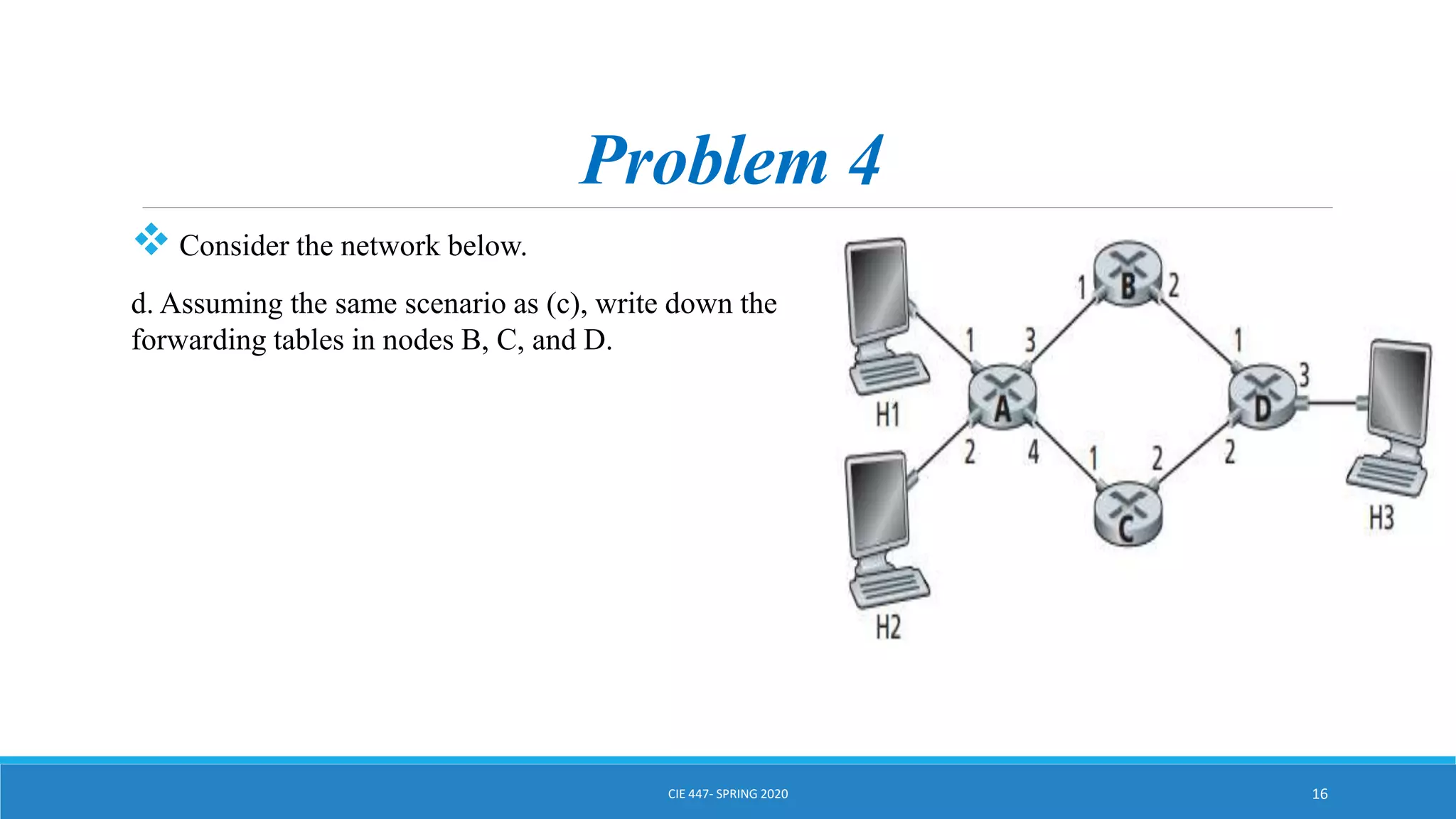
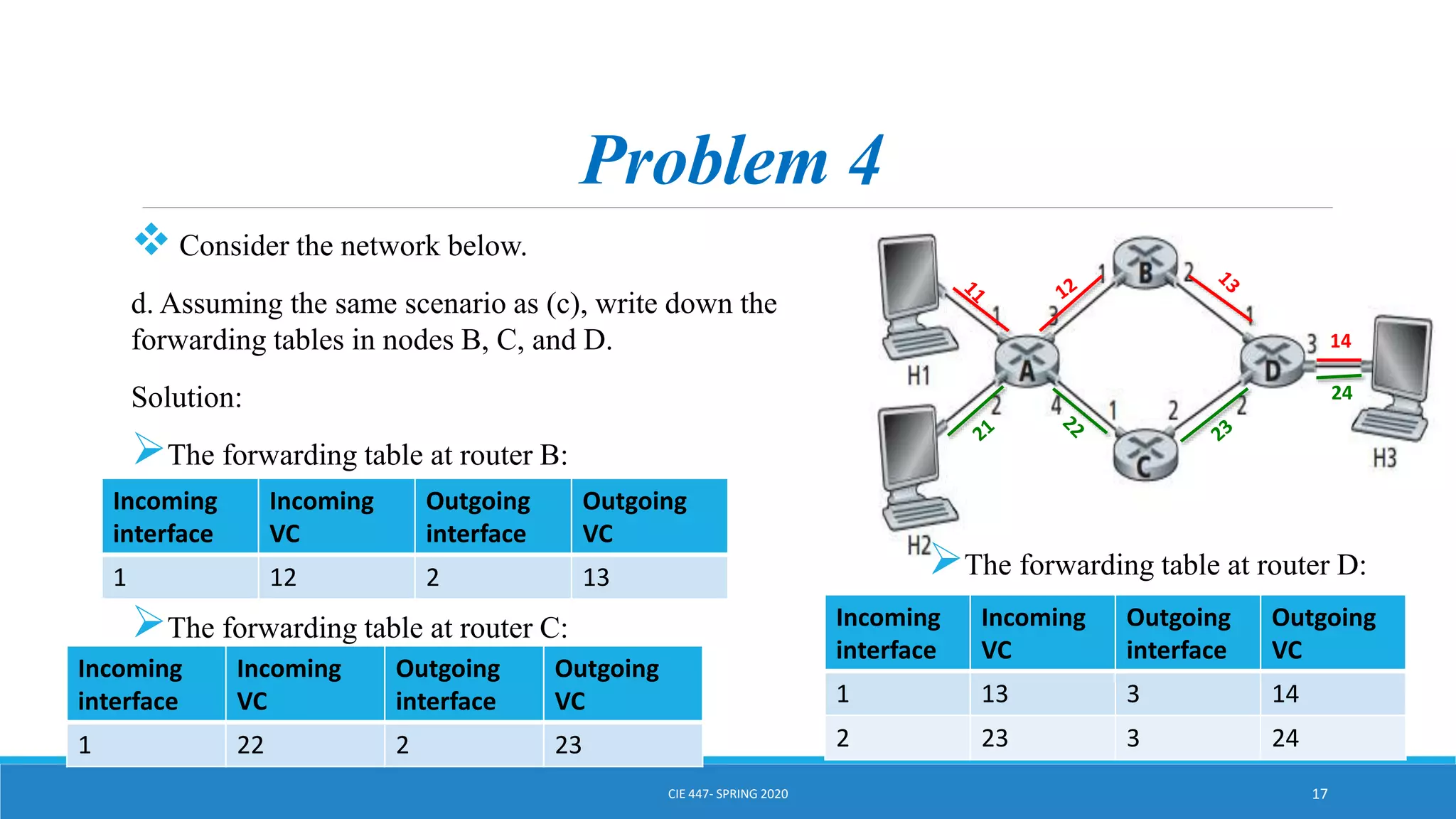
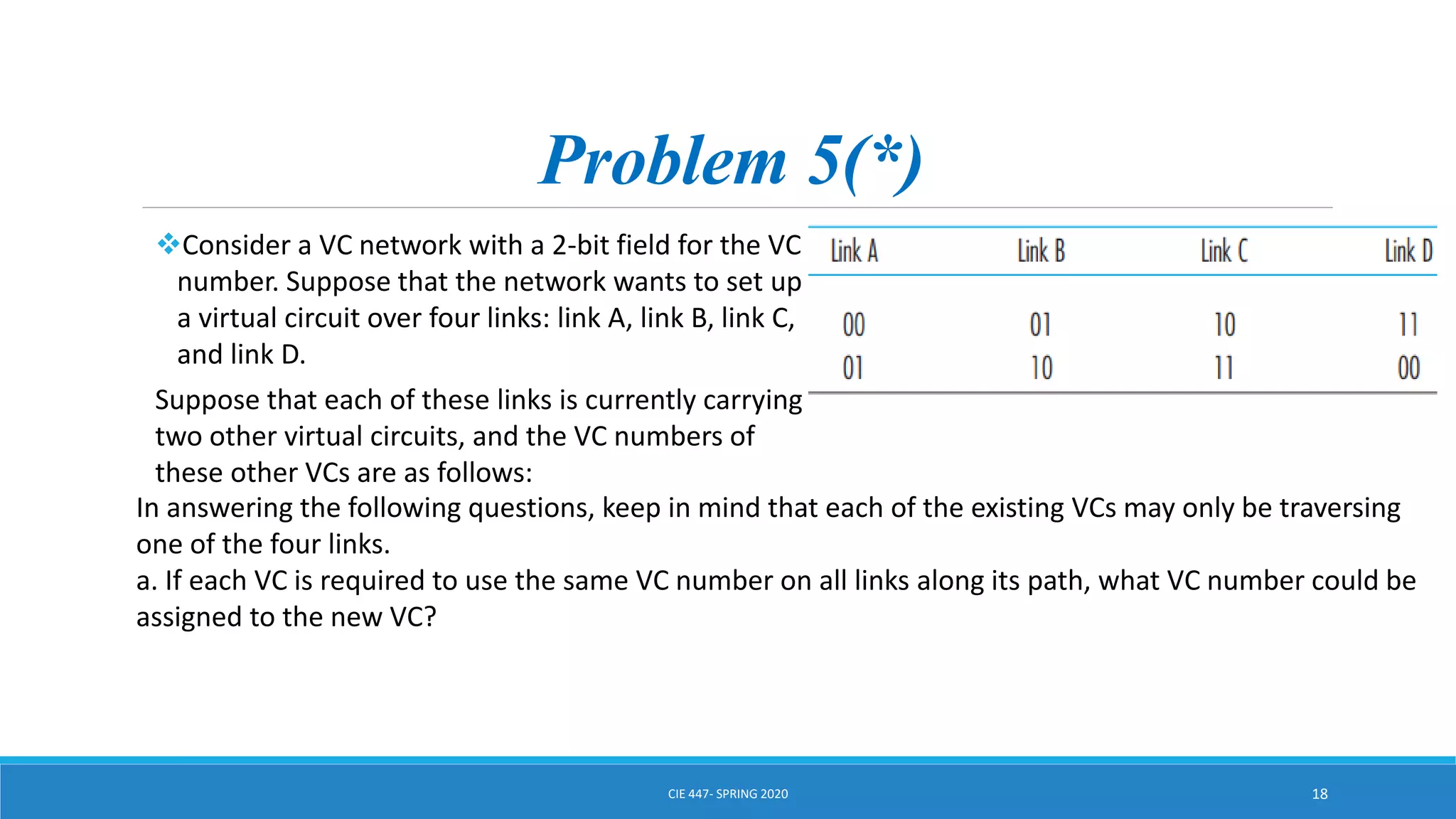
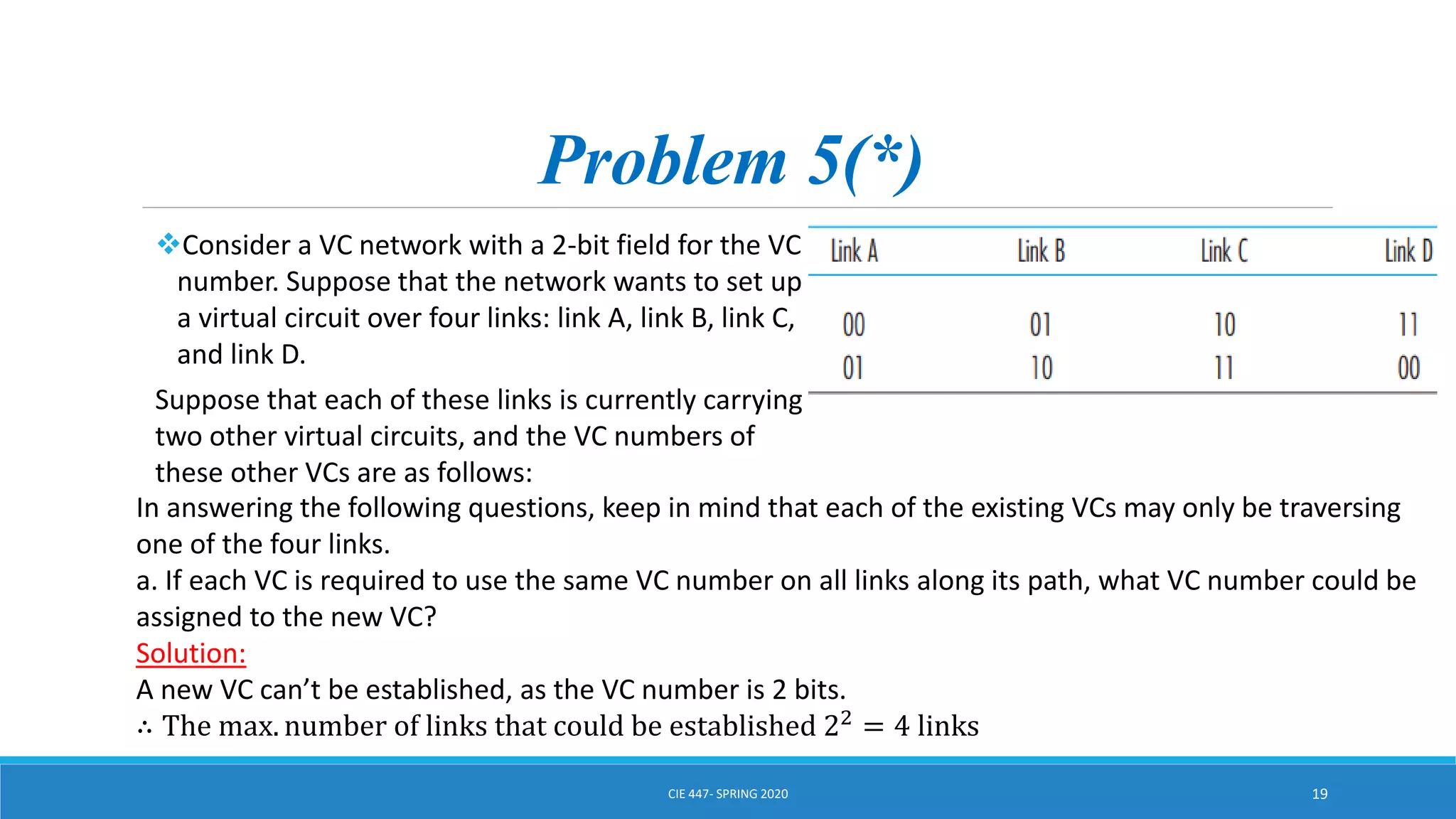
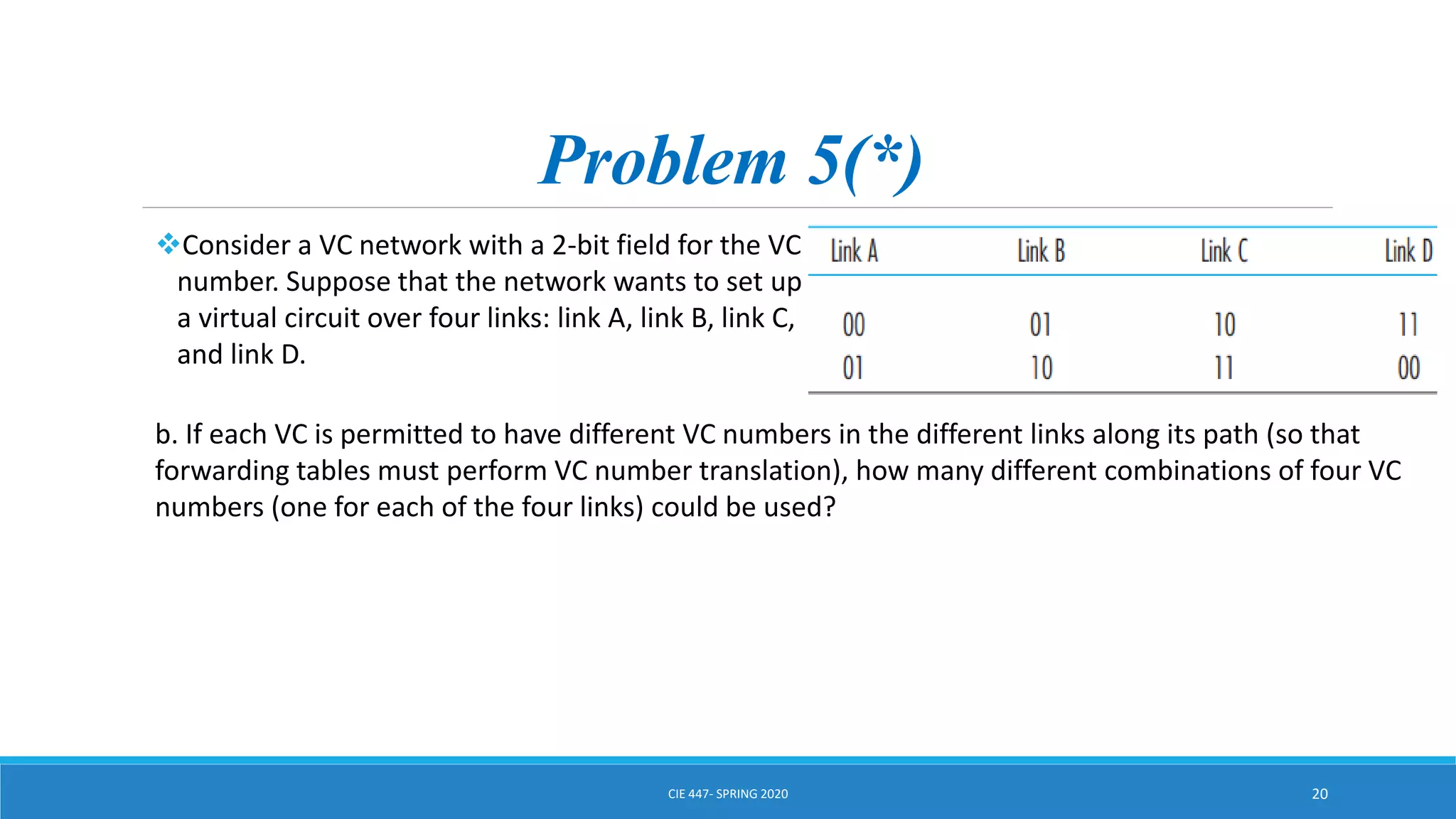
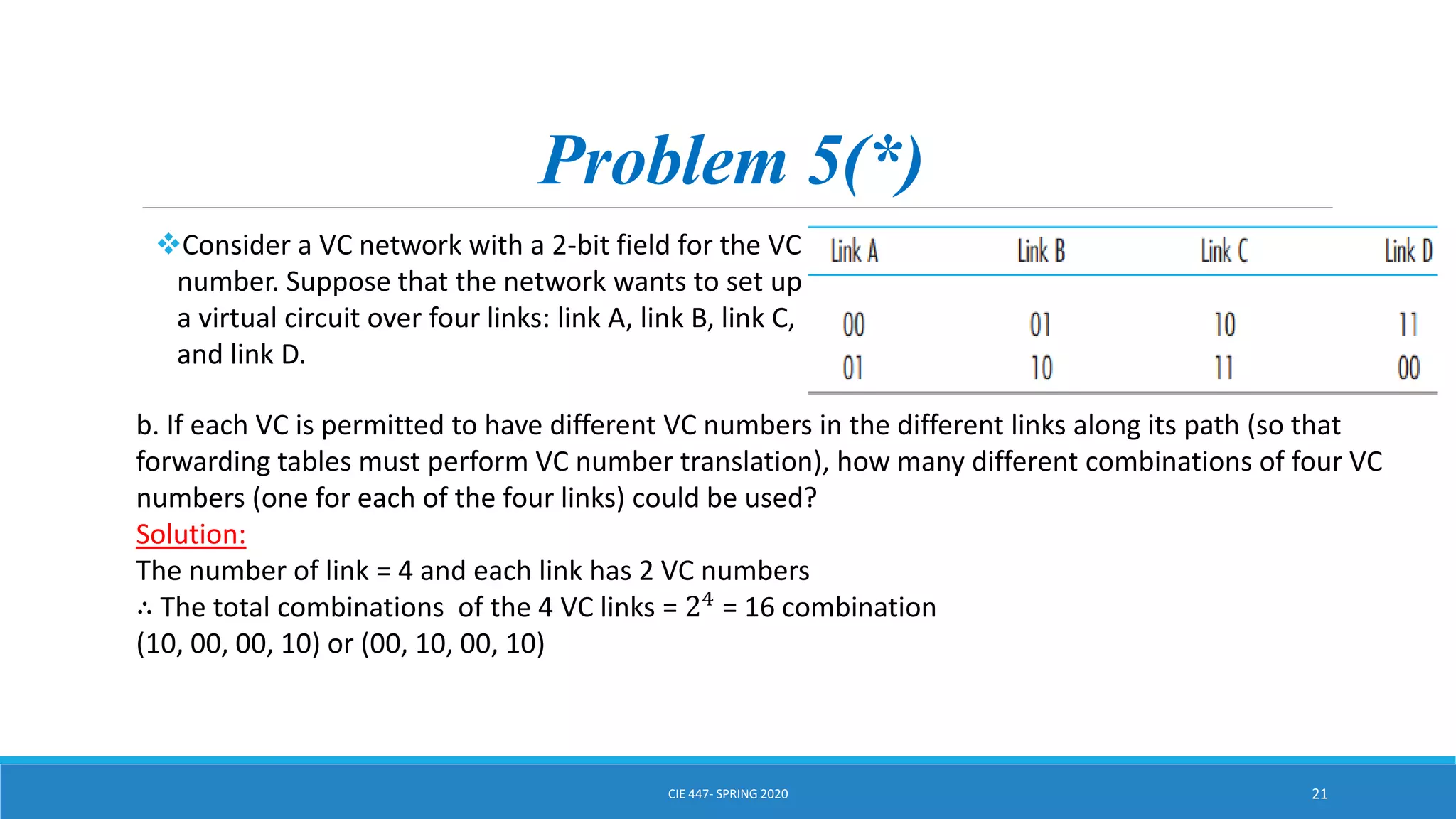
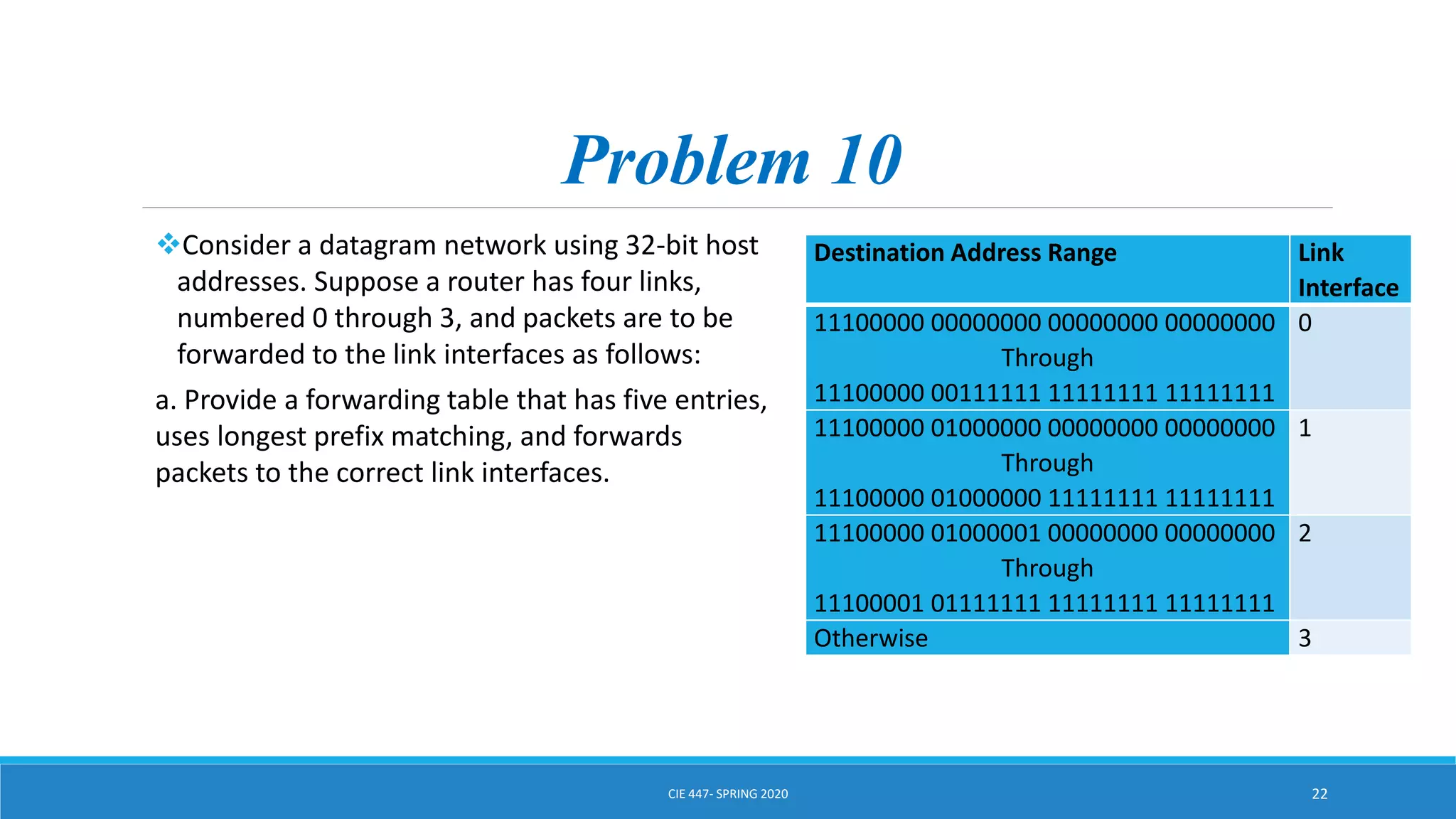
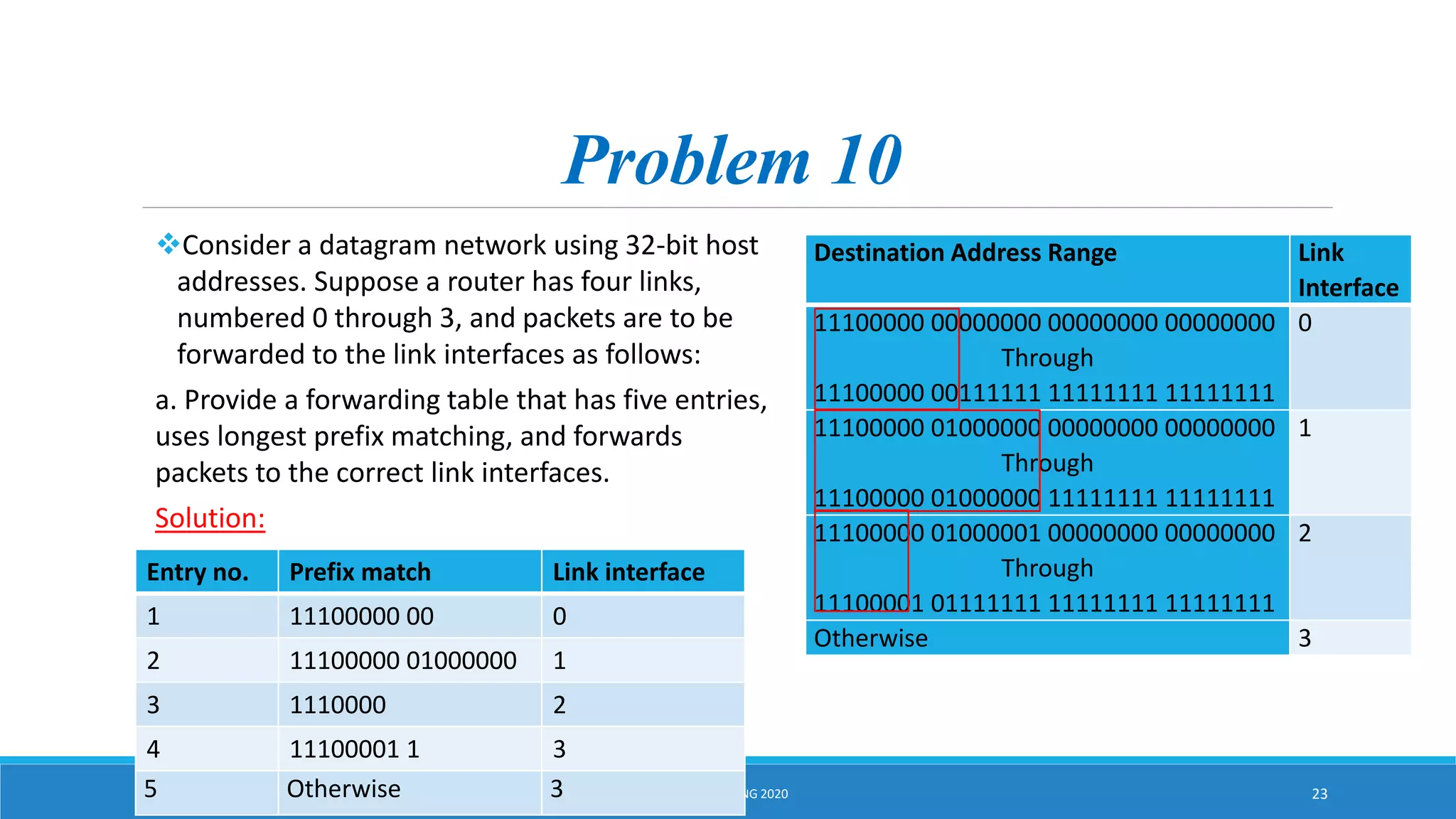
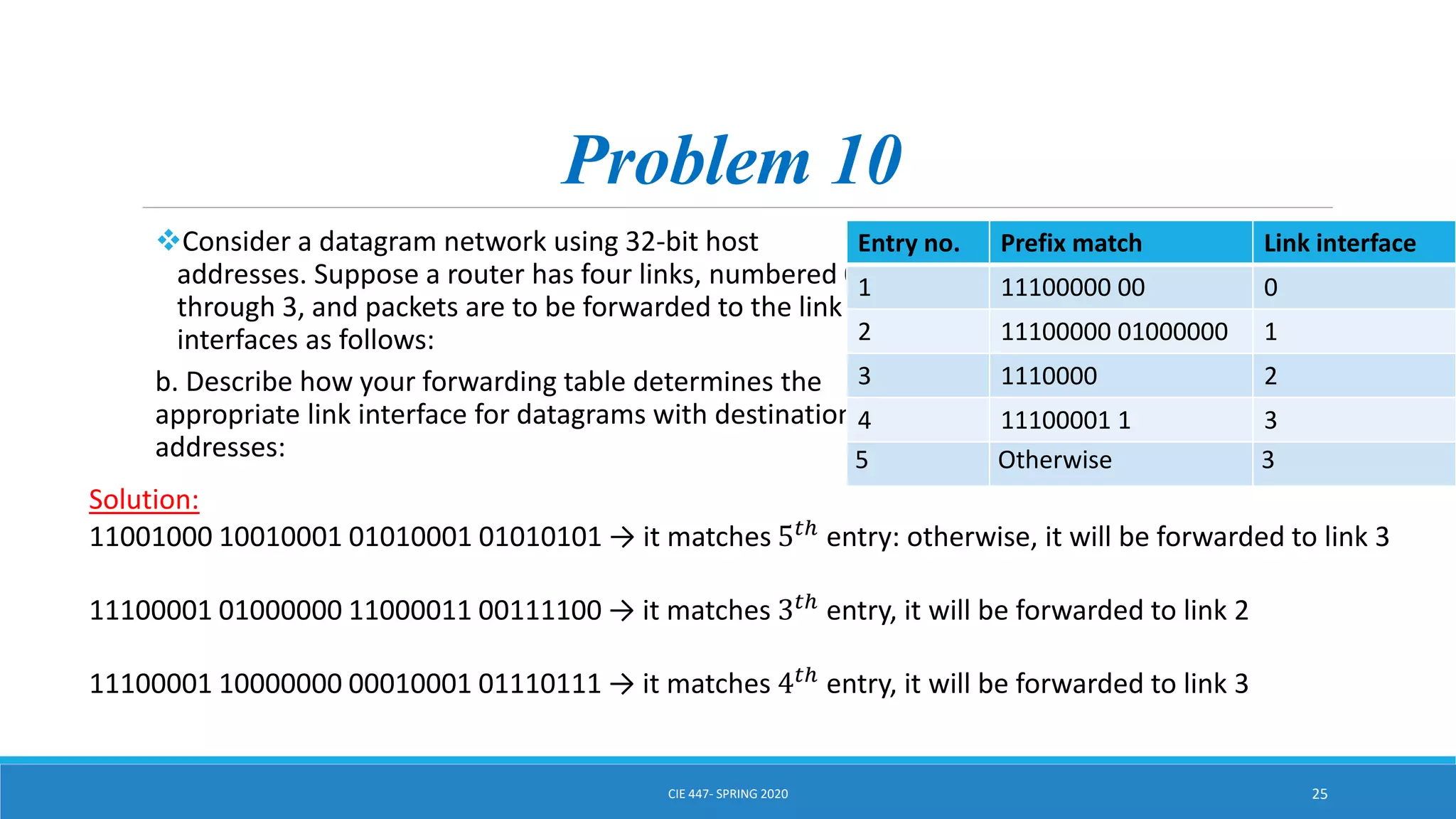
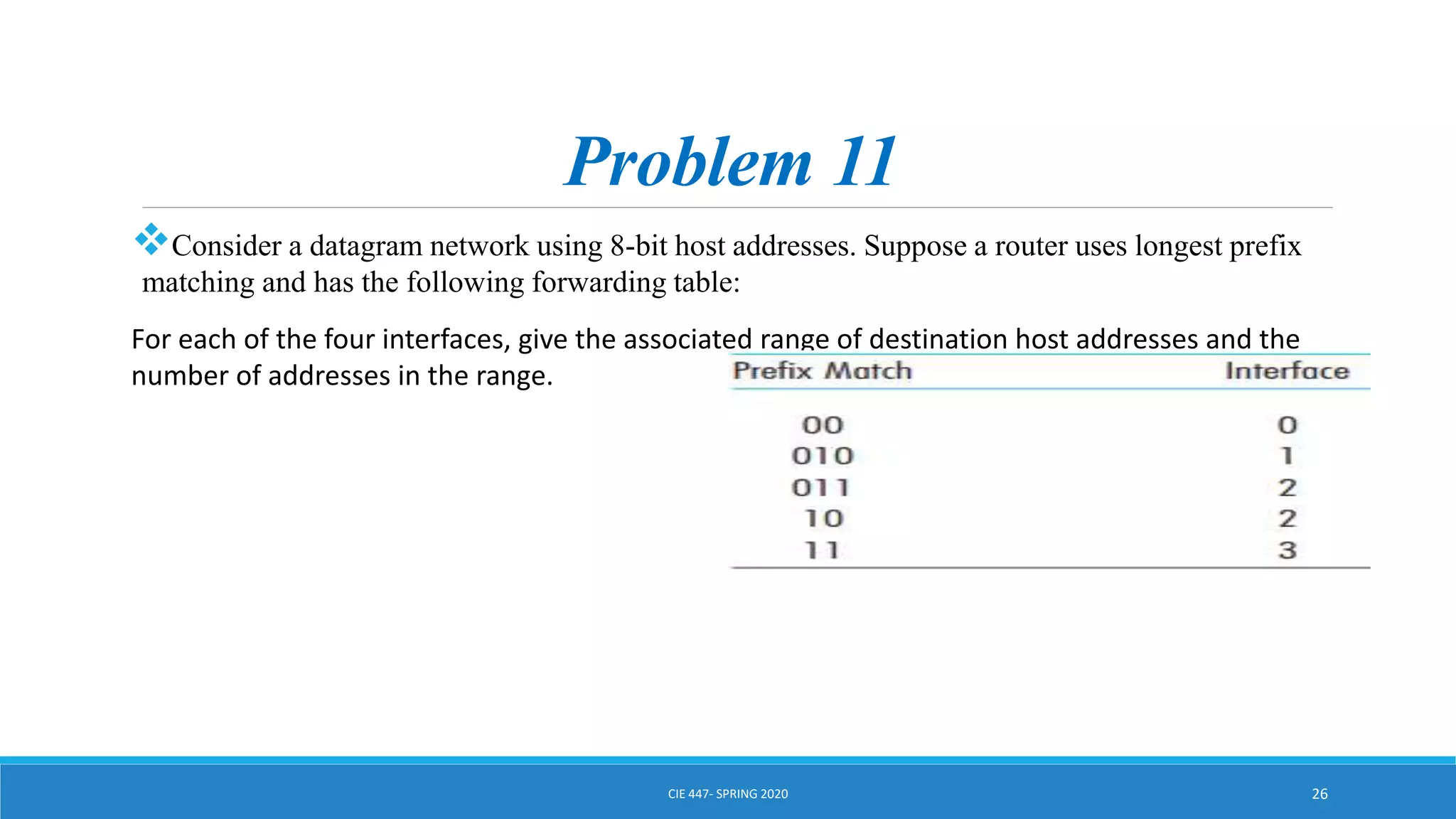
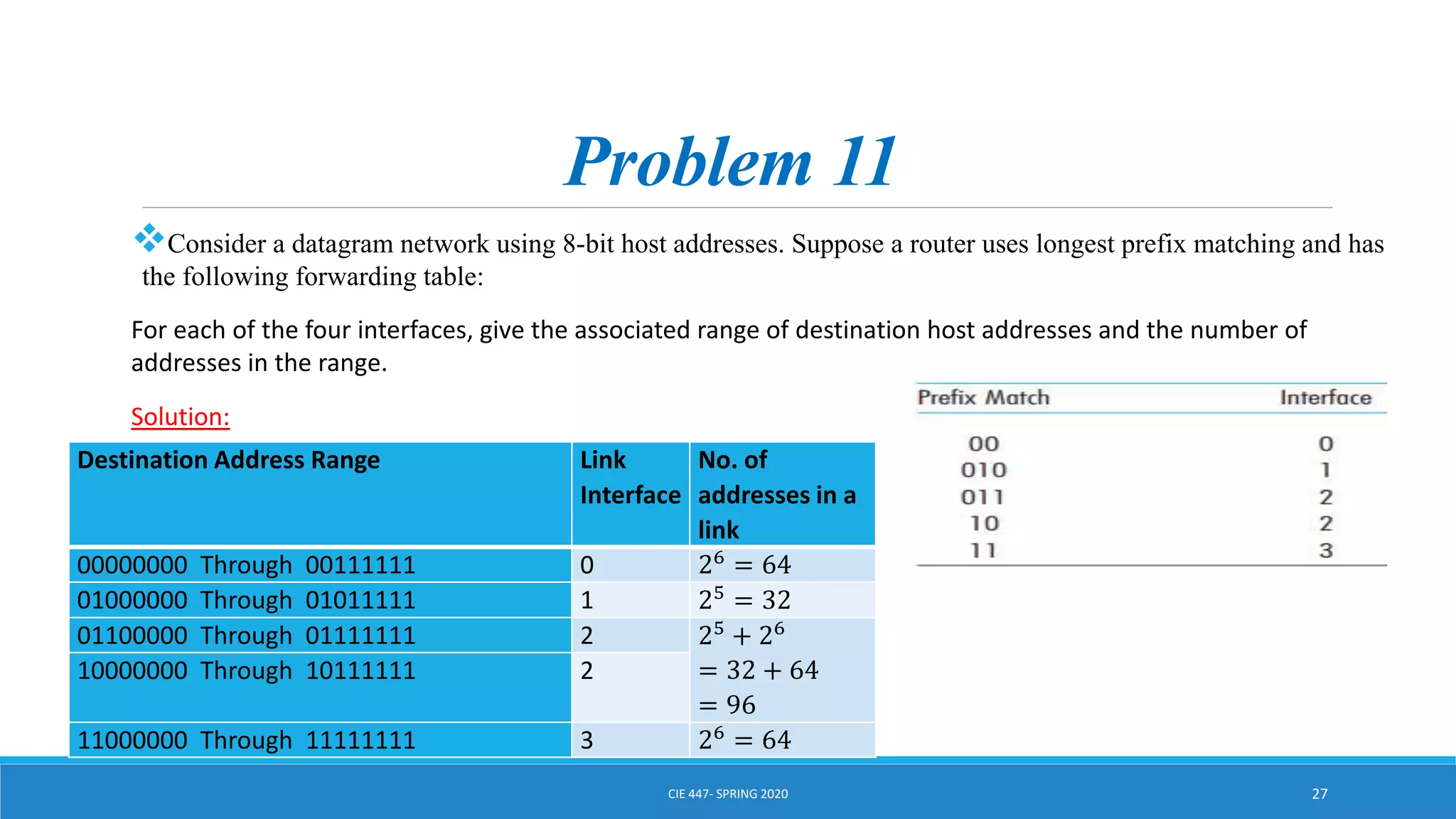
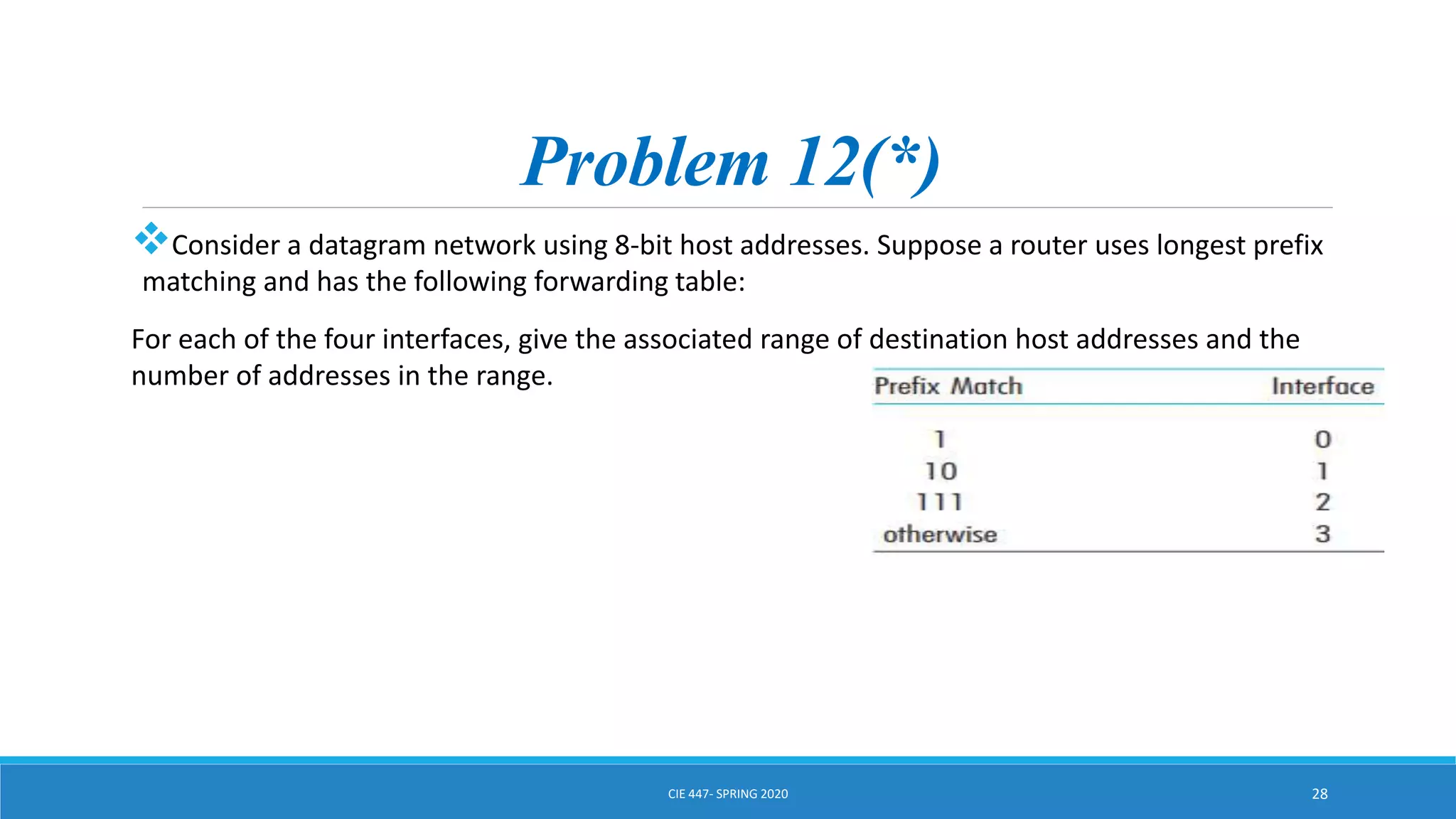
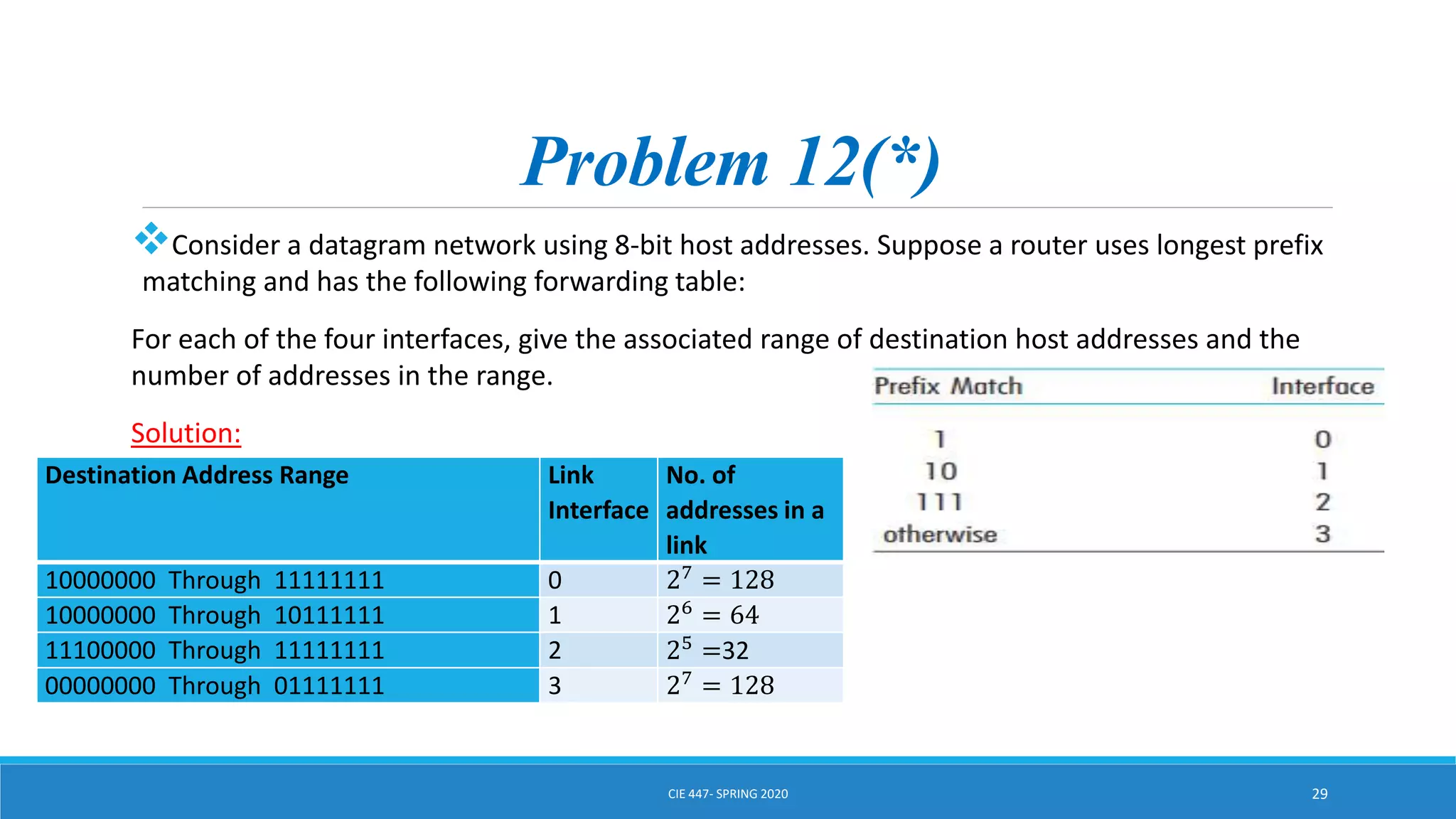
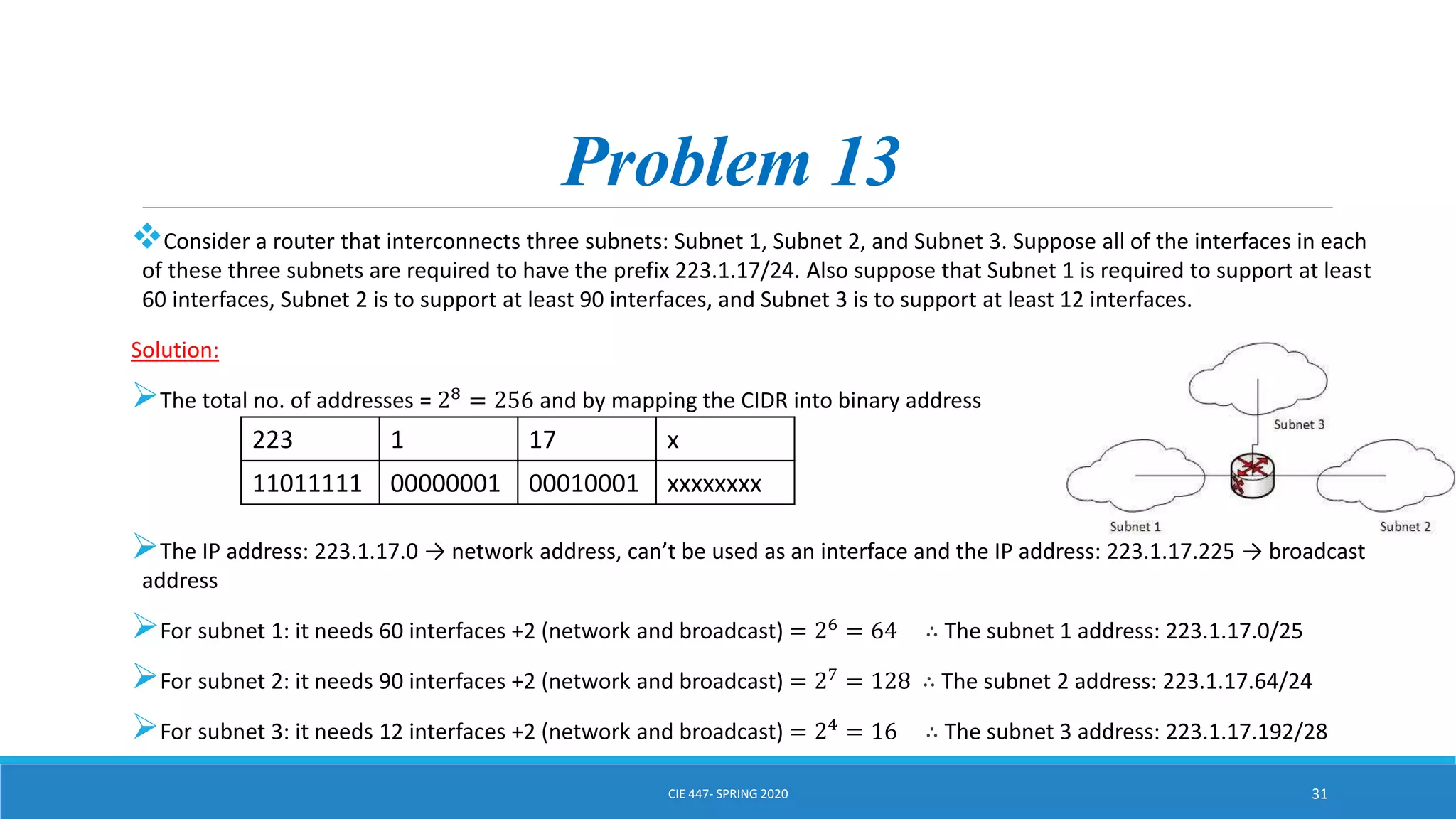
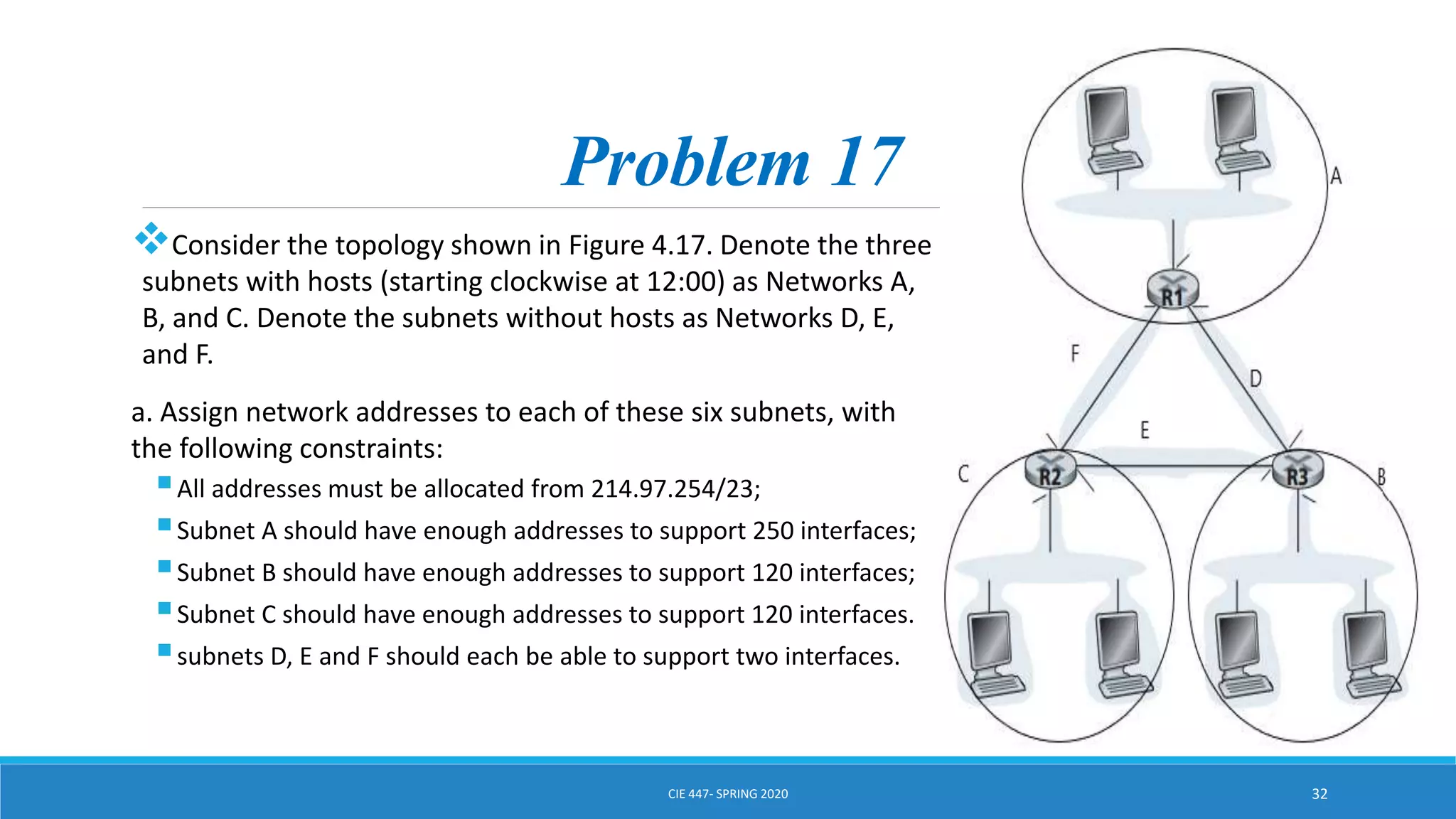
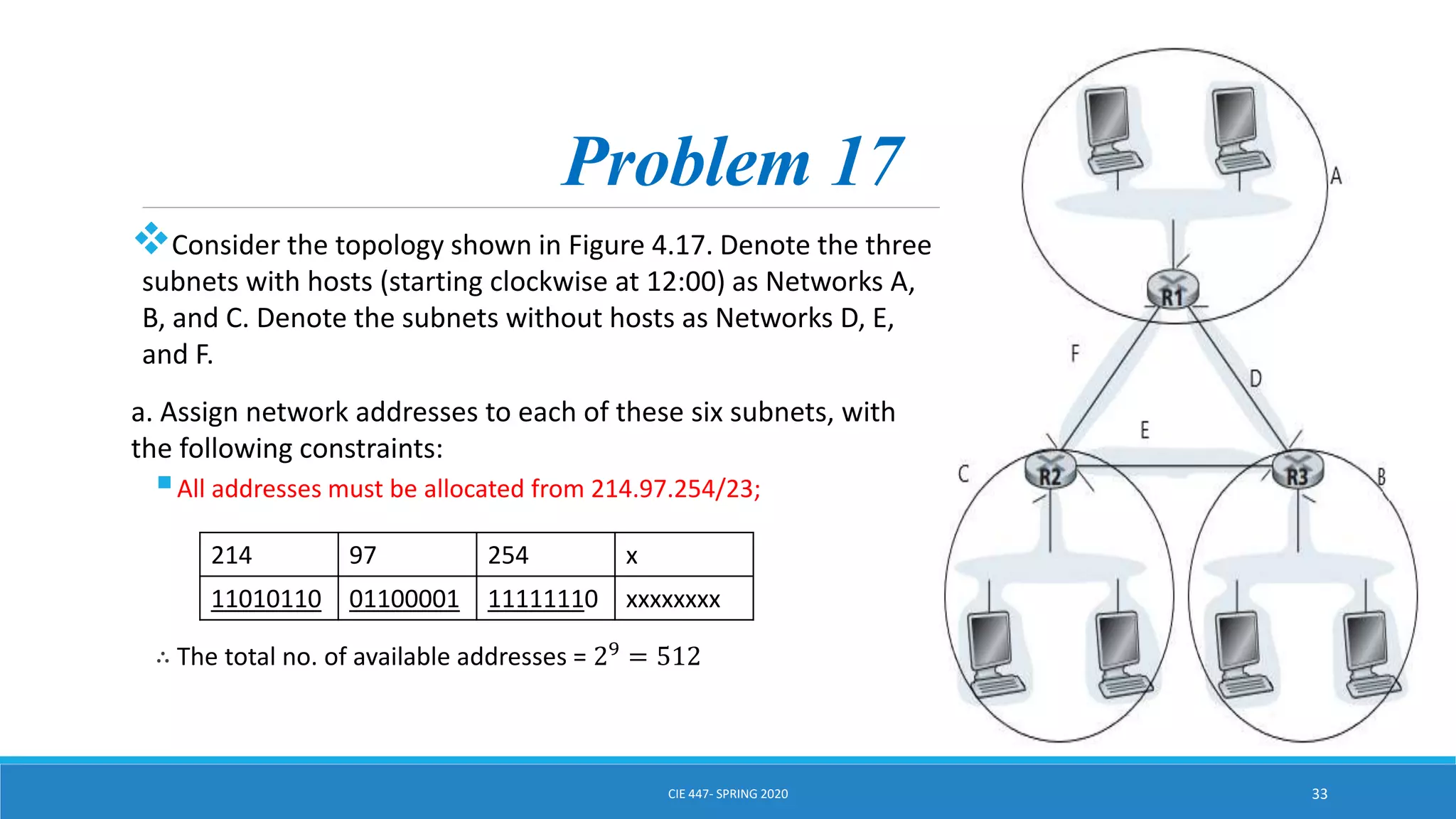
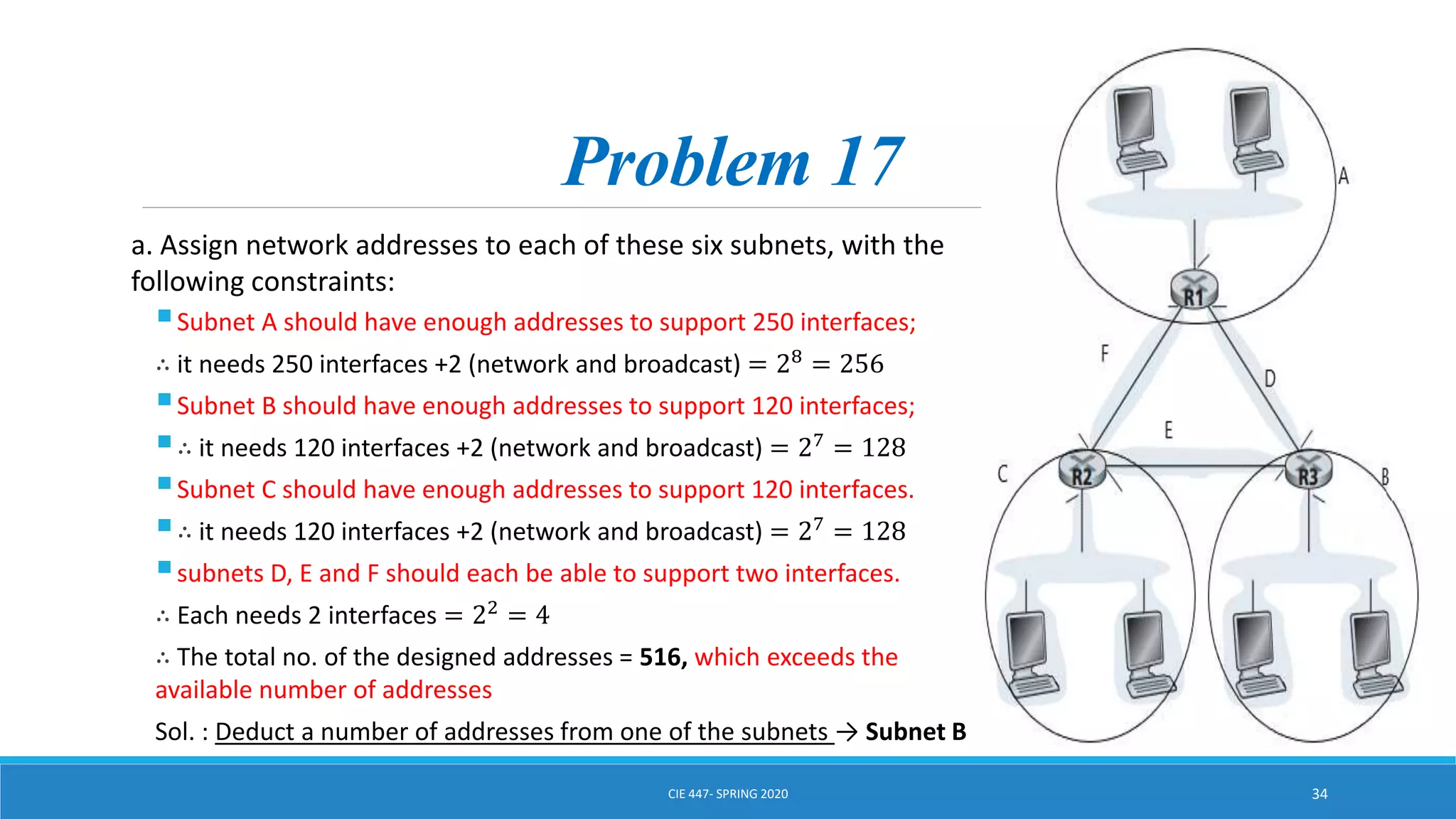
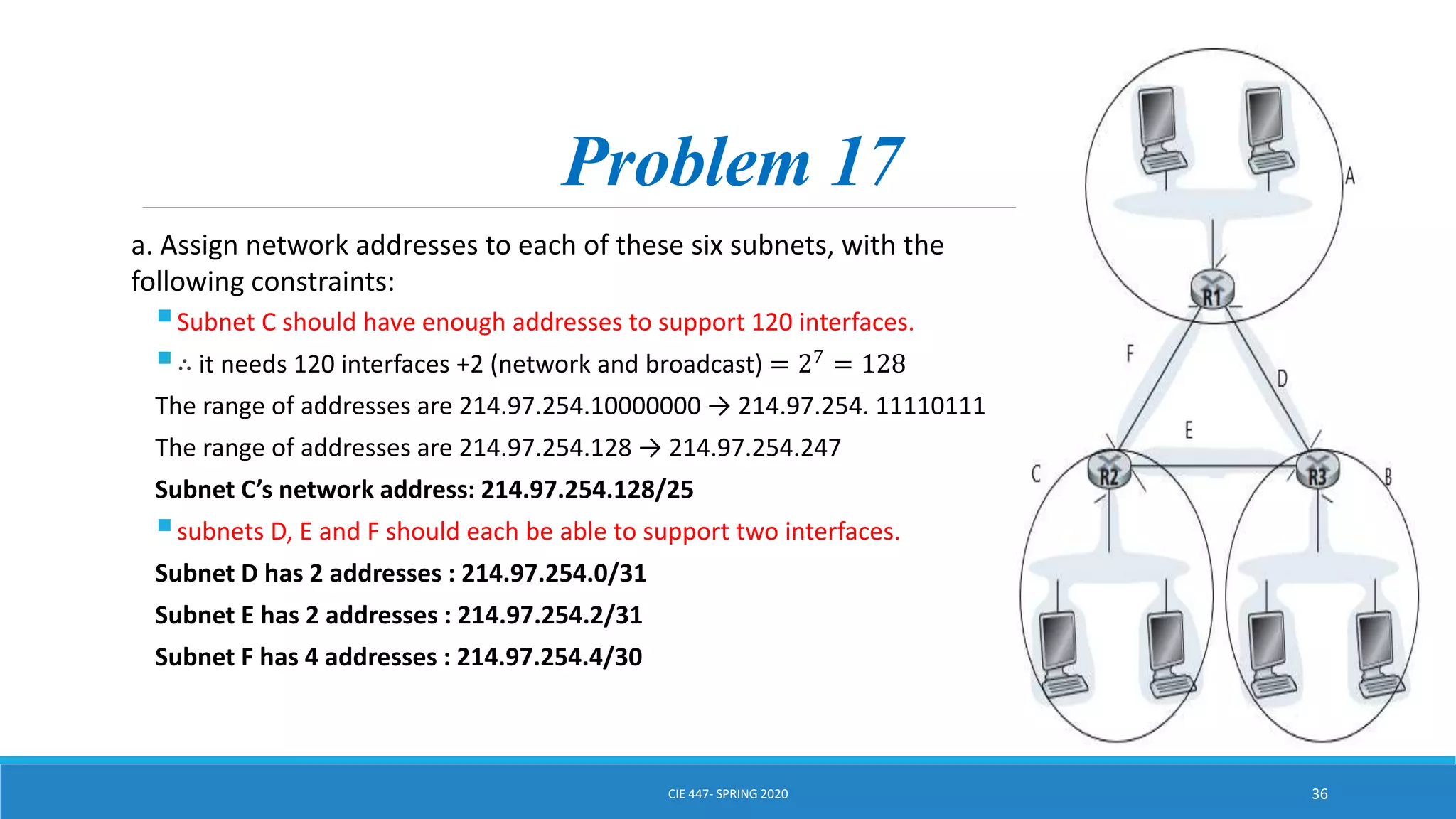
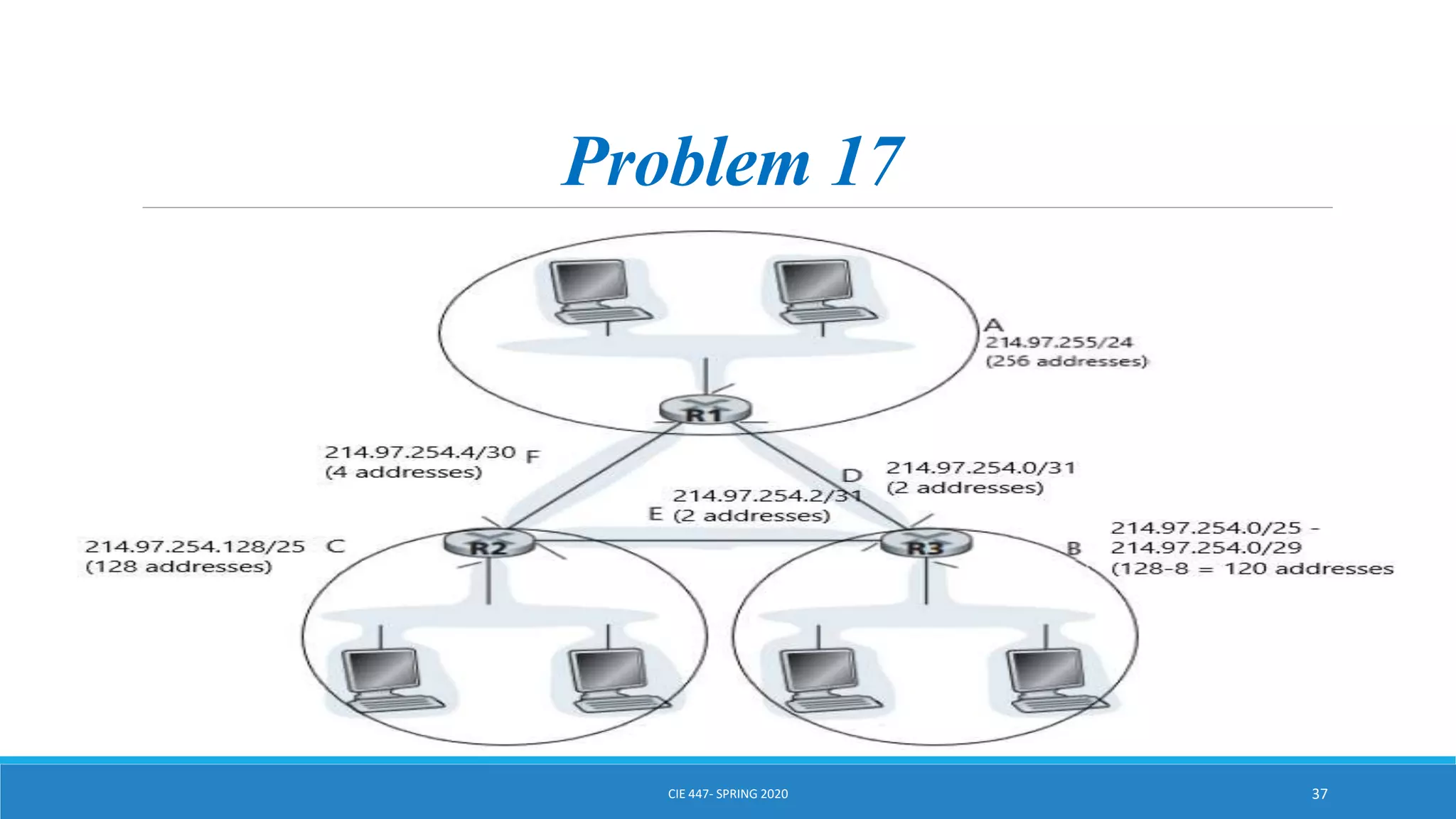
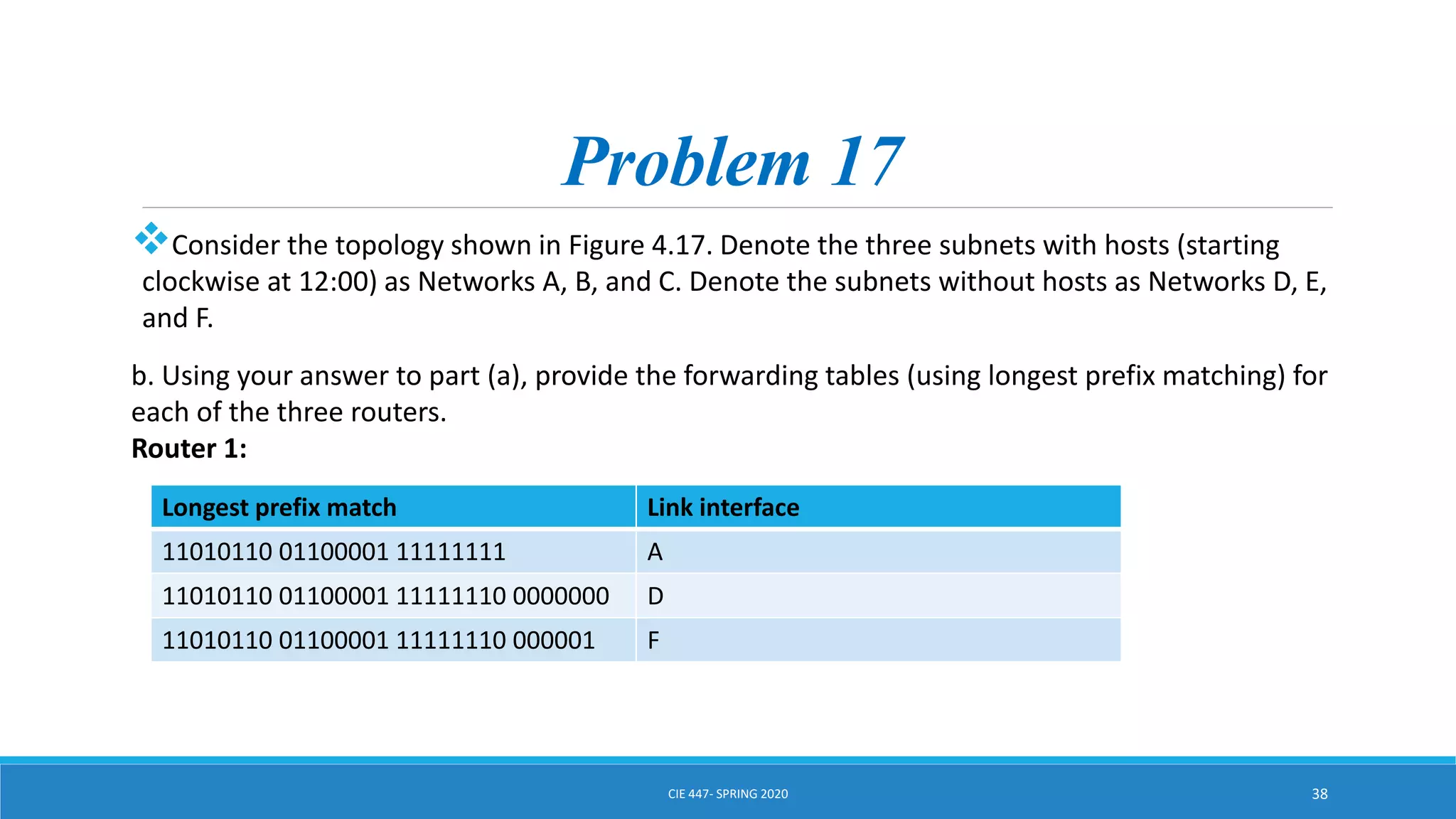
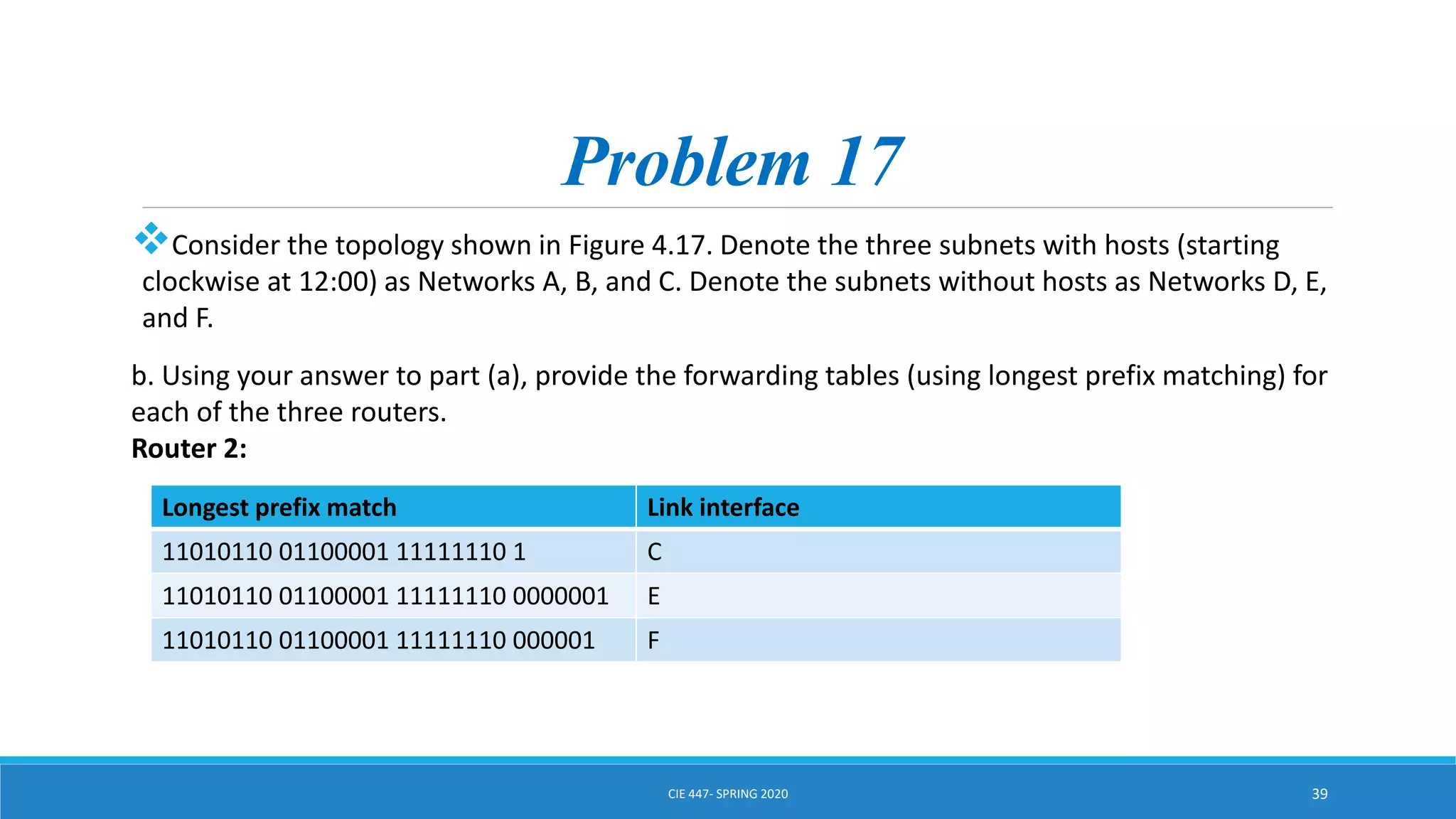
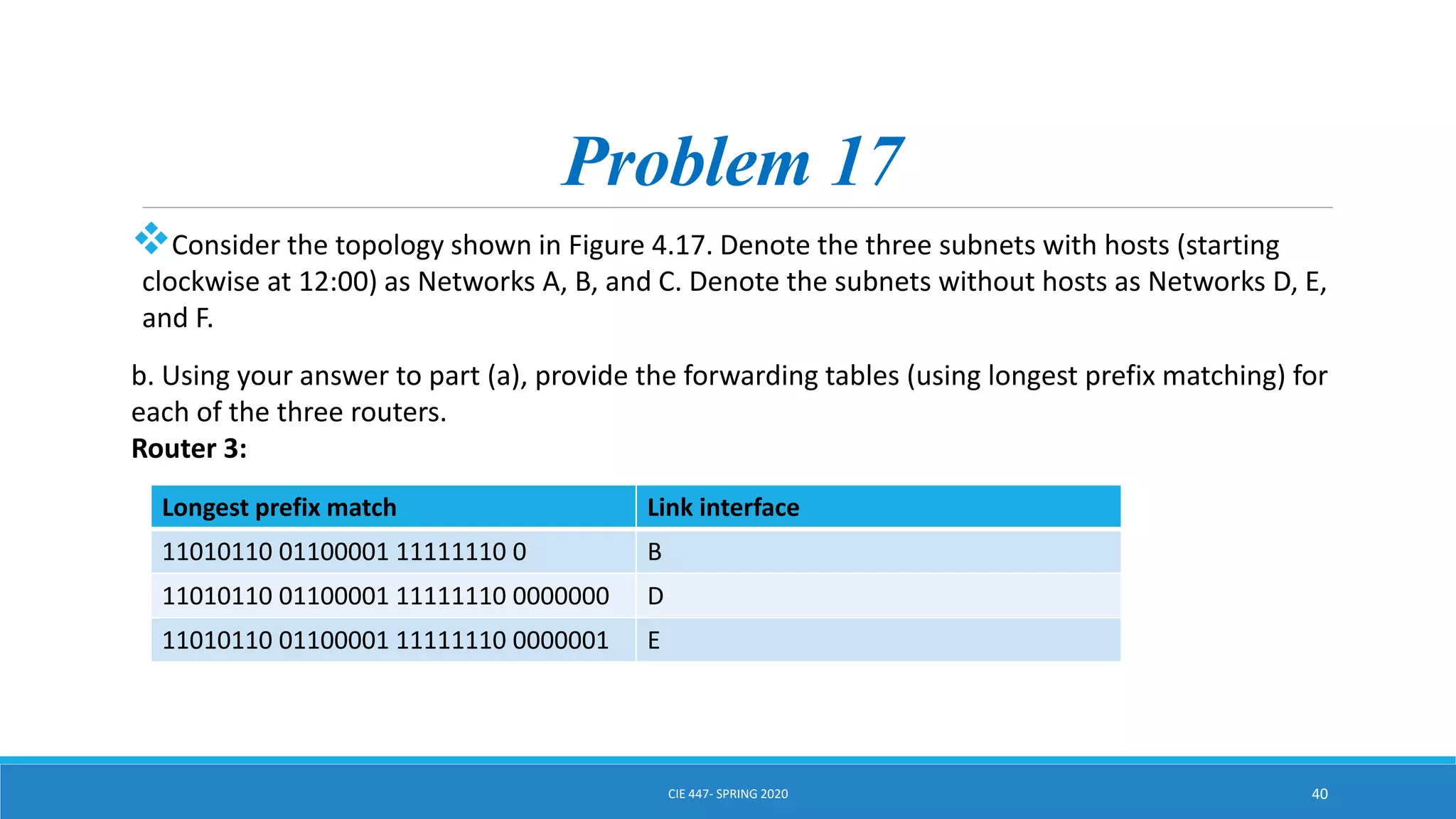
This document discusses IPv4 addressing and subnetting. It begins by explaining that an IPv4 address is a 32-bit logical address written in dotted decimal notation, with each octet ranging from 0-255. It then covers the different IPv4 address classes (A, B, C, D, E), their subnet masks, and address ranges. Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) is introduced as eliminating classful networking. The document also includes problems about configuring forwarding tables and longest prefix matching.