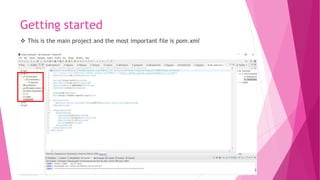
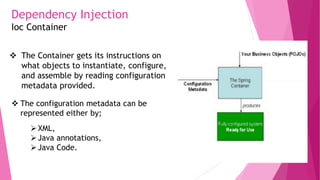
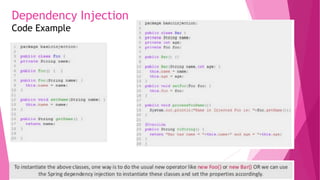
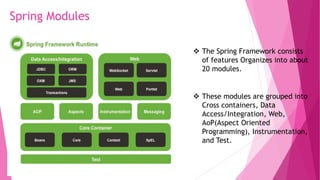
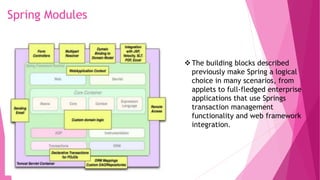
The document provides an introduction to the Spring Framework. It discusses what Spring is, its key features including dependency injection, aspect-oriented programming, and modules. It also covers Spring concepts such as the IoC container, bean scopes, and the ApplicationContext. The advantages of using Spring include its lightweight and modular nature, low coupling through dependency injection, and support for aspects and security through related Spring projects. Setting up a development environment with Maven and Eclipse IDE is also briefly outlined.














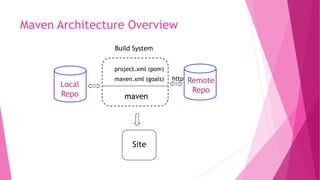
![Maven Artifact Repository
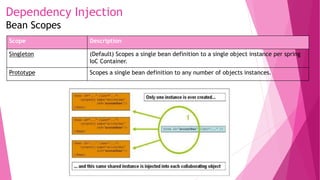
The Most Important Feature
Remote Repository
…
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>xalan</groupId>
<artifactId>xalan</artifactId>
<version>2.5.1</version>
<type>jar</type>
</dependency>
…
</dependencies>
…
${mave.repo.remote}/<groupId>/<type>s/<artifactId>-<version>.<type>
- repository
- […]
- xalan
- jars
- xalan-2.5.0.jar
- xalan-2.5.1.jar
- […]
- […]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontospringsec1-230310215135-1d4c5e72/85/Introduction-to-Spring-sec1-pptx-21-320.jpg)