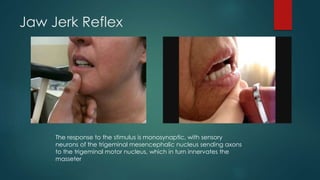
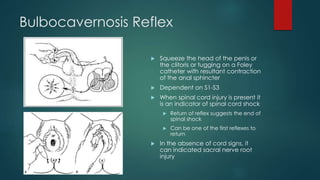
This document discusses several forgotten reflex tests including:
- The ciliospinal reflex which evaluates C8-T2 nerve roots and sympathetic outflow.
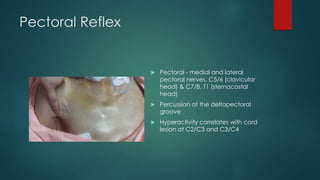
- The pectoral reflex which assesses C5/6 and C7/8 nerve roots via percussion of the deltopectoral groove. Hyperactivity correlates with cord lesions at C2/C3 and C3/C4.
- The Hoffman reflex which assesses the C8-T1 reflex arc and is an upper motor neuron sign.
- The superficial abdominal cutaneous reflex which evaluates T8-T12 nerve roots with loss indicating a loss of reflex arc.
- The mesial hamstring reflex which