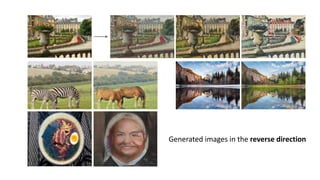
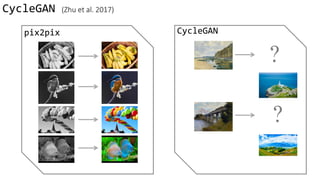
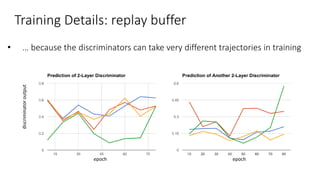
The document discusses the CycleGAN framework and its connection to image generation techniques, particularly focusing on its loss functions and comparison to pix2pix models. It highlights how CycleGAN uses generative adversarial networks (GANs) to synthesize photorealistic images while also allowing for image reconstruction. Additionally, the document presents training details and performance metrics, emphasizing the effectiveness of using CycleGAN for domain adaptation in image classification tasks.








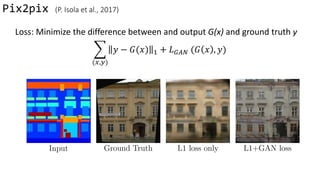
![pix2pix (Isola et al., 2017)
?
train
test
G
• Supervised
• loss: Minimize the difference
between output G(x) and
ground truth y
Data from [Tylecek, 2013]
x y](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cycleganinriasecretsofganallslides-171024050833/85/Finding-connections-among-images-using-CycleGAN-11-320.jpg)
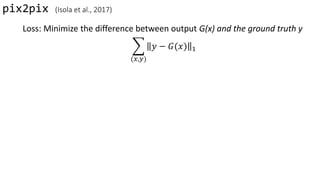





](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cycleganinriasecretsofganallslides-171024050833/85/Finding-connections-among-images-using-CycleGAN-19-320.jpg)
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cycleganinriasecretsofganallslides-171024050833/85/Finding-connections-among-images-using-CycleGAN-20-320.jpg)
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cycleganinriasecretsofganallslides-171024050833/85/Finding-connections-among-images-using-CycleGAN-21-320.jpg)
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cycleganinriasecretsofganallslides-171024050833/85/Finding-connections-among-images-using-CycleGAN-22-320.jpg)
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cycleganinriasecretsofganallslides-171024050833/85/Finding-connections-among-images-using-CycleGAN-23-320.jpg)
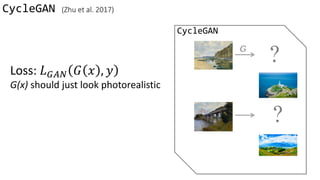
![Loss Function
G’s perspective: D is a loss function.
Rather than being hand-designed, it is learned.
G and D grow together via competition
[Isola et al., 2017]
[Goodfellow et al., 2014]
(slides credit: Phillip Isola)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cycleganinriasecretsofganallslides-171024050833/85/Finding-connections-among-images-using-CycleGAN-24-320.jpg)
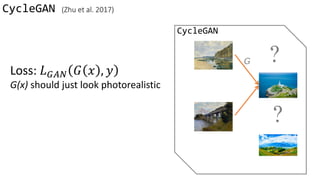
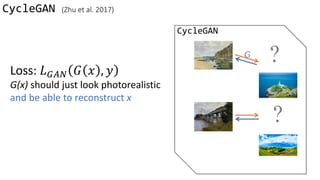
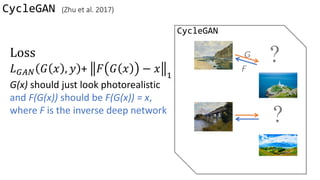
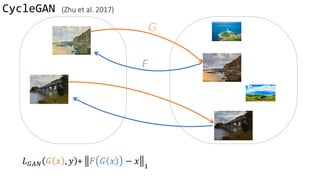
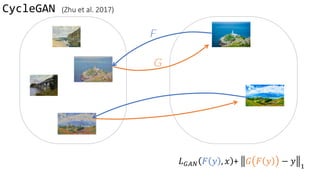
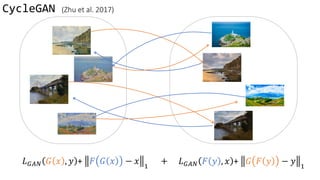
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cycleganinriasecretsofganallslides-171024050833/85/Finding-connections-among-images-using-CycleGAN-35-320.jpg)


![Training Details: Generator 𝐺
Encoder-decoderU-Net
[Ronneberger et al.]
ResNet [He et al.] [Johnson et al.]
• Both have skip connections
• ResNet: fewer parameters
better for ill-posed problems](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cycleganinriasecretsofganallslides-171024050833/85/Finding-connections-among-images-using-CycleGAN-40-320.jpg)
![Training Details: Objective
• GANs with cross-entropy loss
• Least square GANs [Mao et al. 2016]
Stable training + better results
Vanishing gradients](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cycleganinriasecretsofganallslides-171024050833/85/Finding-connections-among-images-using-CycleGAN-41-320.jpg)








![Inspired by [Johnson et al. 2011], Slides from Junyan Zhu
GTA5 CG Input Output
CG2Real: GTA5 → real streetview](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cycleganinriasecretsofganallslides-171024050833/85/Finding-connections-among-images-using-CycleGAN-51-320.jpg)


![[Richter*, Vineet* et al. 2016]
GTA5 images Segmentation labels
Slides from Junyan Zhu](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cycleganinriasecretsofganallslides-171024050833/85/Finding-connections-among-images-using-CycleGAN-54-320.jpg)
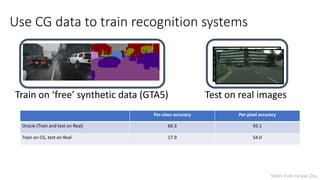
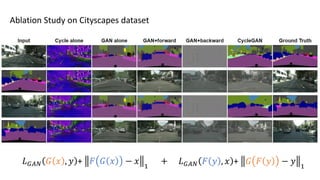
![State-of-the-art domain adaption method
Per-class accuracy Per-pixel accuracy
Oracle (Train and test on Real) 60.3 93.1
Train on CG, test on Real 17.9 54.0
FCN in the wild [Hoffman et al.] 27.1 (+6.0) -
VGG-FCN: 17.9 [Long et al. 2015]; Dilated-VGG-FCN: 21.1 [Fisher and Koltun 2015’]
Train on ‘free’ synthetic data (GTA5) Test on real images
adapt
Slides from Junyan Zhu](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cycleganinriasecretsofganallslides-171024050833/85/Finding-connections-among-images-using-CycleGAN-56-320.jpg)
![Domain Adaption with CycleGAN
Per-class accuracy Per-pixel accuracy
Oracle (Train and test on Real) 60.3 93.1
Train on CG, test on Real 17.9 54.0
FCN in the wild [Hoffman et al.] 27.1 (+6.0) -
Train on CycleGAN, test on Real 34.8 (+16.9) 82.8
Train on CycleGAN data Test on real images
[Tzeng et al. ] In submission, Slides from Junyan Zhu](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cycleganinriasecretsofganallslides-171024050833/85/Finding-connections-among-images-using-CycleGAN-57-320.jpg)
