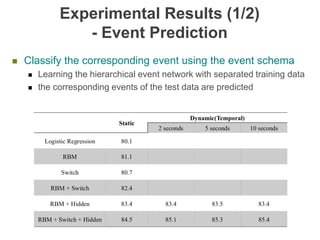
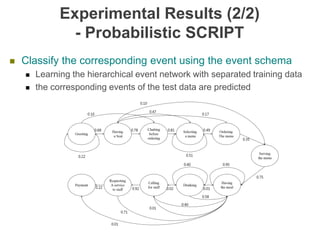
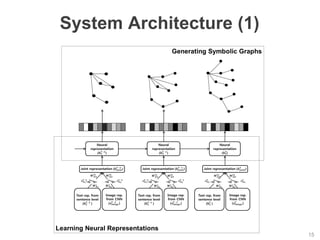
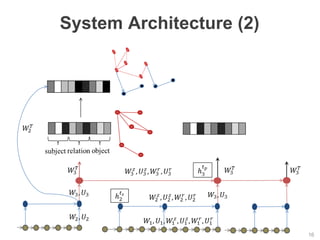
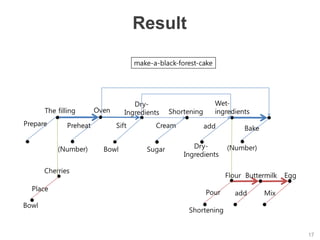
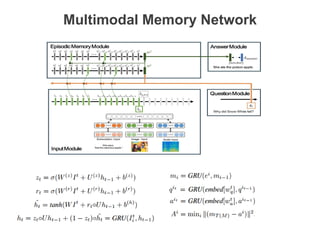
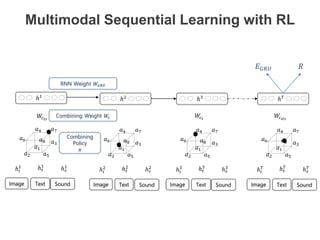
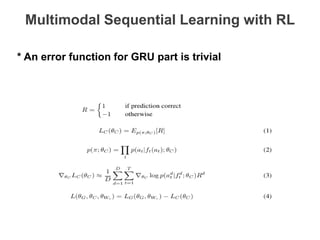
The document discusses multimodal sequential learning, focusing on automatic schema construction and deep learning methods applied to restaurant environments using wearable sensor data. It presents the development of a hierarchical event network and experiments involving event prediction and probabilistic scripts based on collected datasets. Additionally, it explores video question answering systems trained on animated content, integrating various modalities such as text, sound, and images.