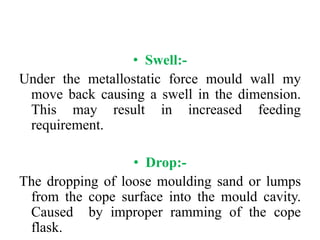
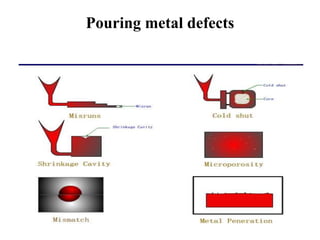
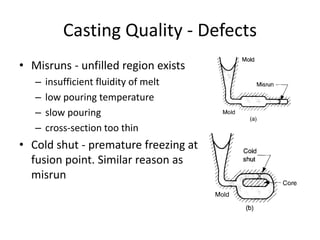
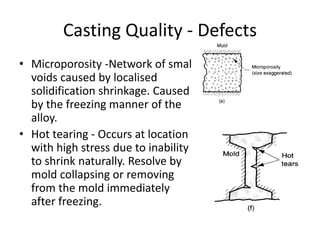
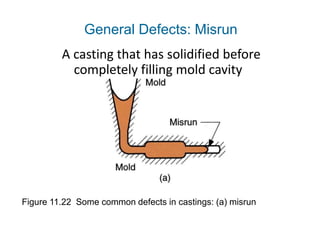
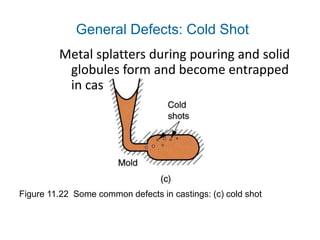
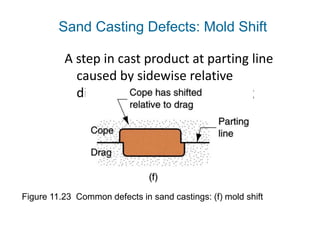
Casting defects can be classified into general defects common to all casting processes and defects related specifically to sand casting. General defects include misruns where the mold is not fully filled, cold shuts where two metal flows fail to fuse, cold shots where metal splatters during pouring, and shrinkage cavities caused by solidification shrinkage. Sand casting defects include sand blows caused by trapped gases, pin holes of small gas cavities, and penetration where molten metal enters the sand mold. Proper design and production processes seek to eliminate defects and ensure casting quality.