Embed presentation
Downloaded 69 times




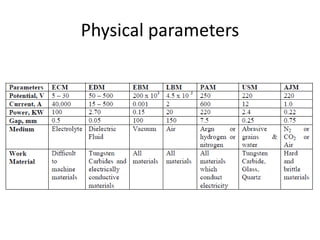
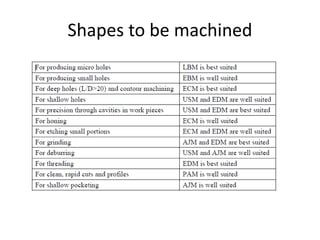
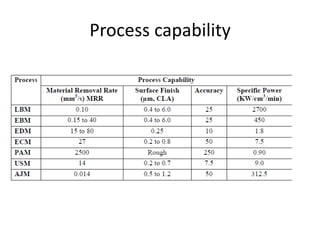
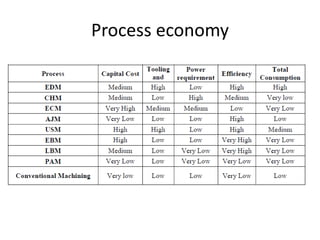


This document discusses unconventional machining processes as an alternative to conventional machining. Unconventional machining is needed to machine harder materials and allows for closer tolerances and less residual stress than conventional methods. Unconventional machining processes are classified based on the type of energy used, such as thermal, electrical, electrochemical, chemical, or mechanical energy, and the mechanism of material removal, such as erosion, ionic dissolution, or vaporization. Selection of the appropriate unconventional machining process depends on factors like the physical properties of the material, the desired shape, the process capabilities, and economic considerations.










