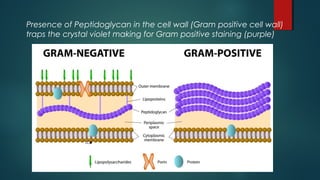
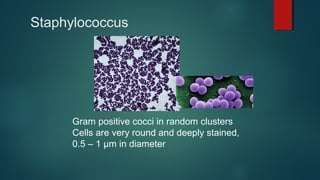
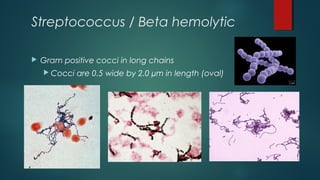
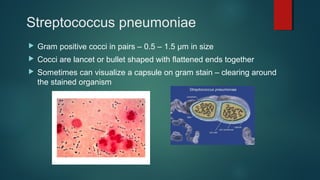
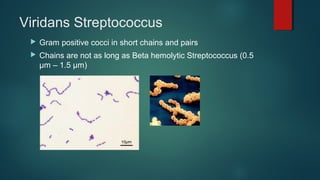
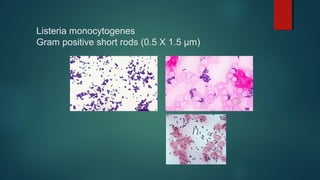
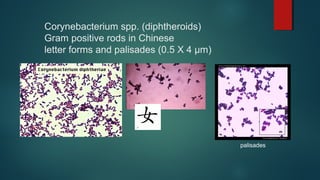
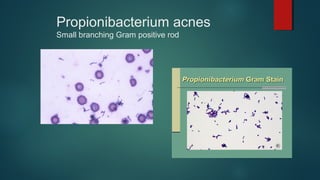
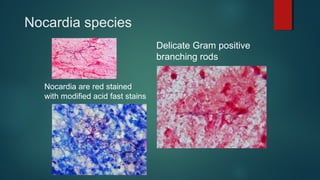
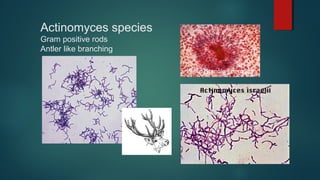
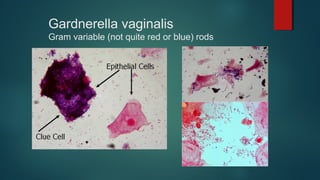
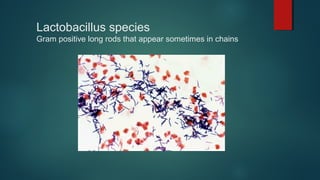
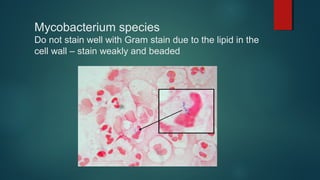
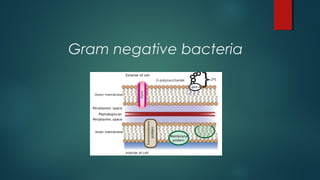
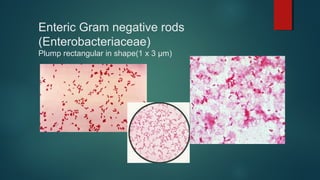
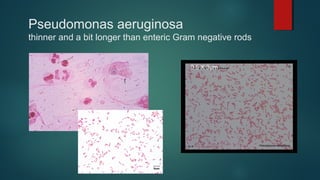
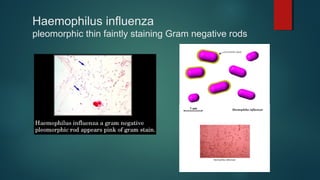
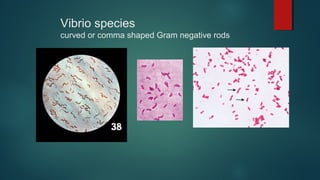
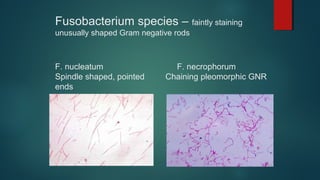
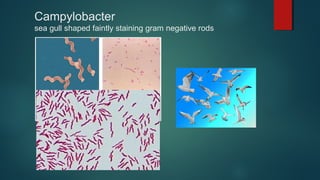
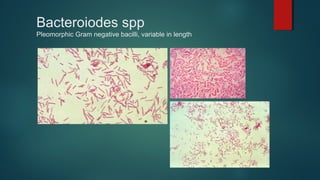
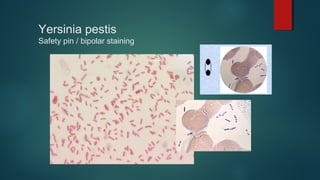
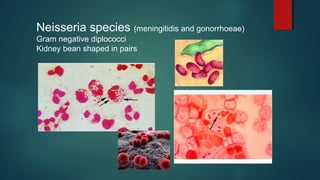
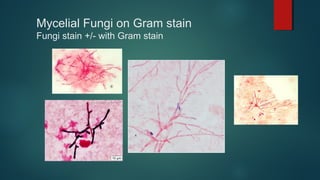
The document provides information on performing and interpreting Gram stains. Gram stains work by using crystal violet, iodine, decolorizer and safranin to differentiate bacteria based on their cell wall structure as either Gram positive (purple) or Gram negative (red). Key morphological characteristics are described for common Gram positive bacteria like Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, and Bacillus as well as Gram negative bacteria like Pseudomonas, Haemophilus, and Neisseria. Potential artifacts and non-bacterial organisms that may be seen on Gram stains are also outlined.