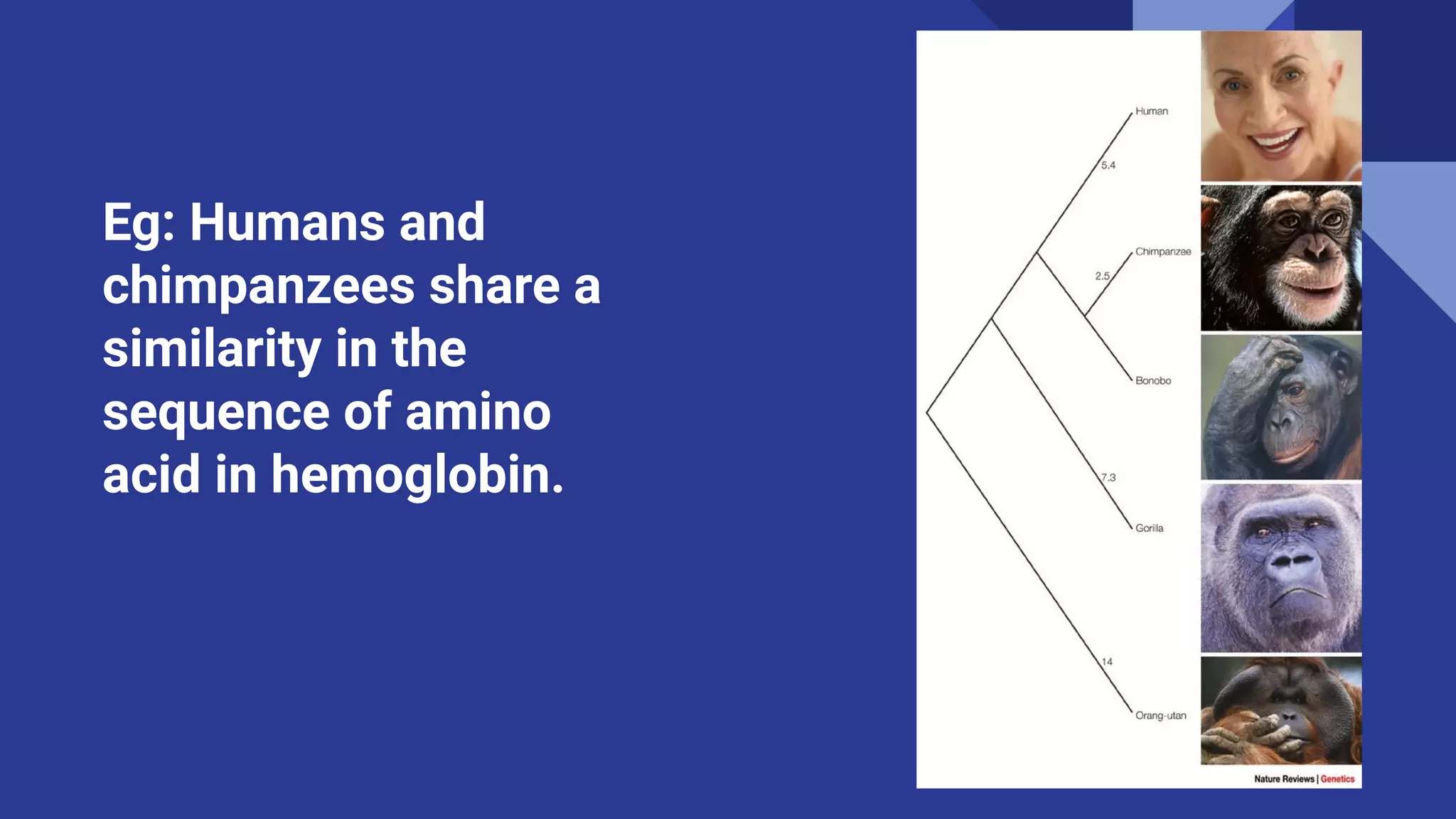
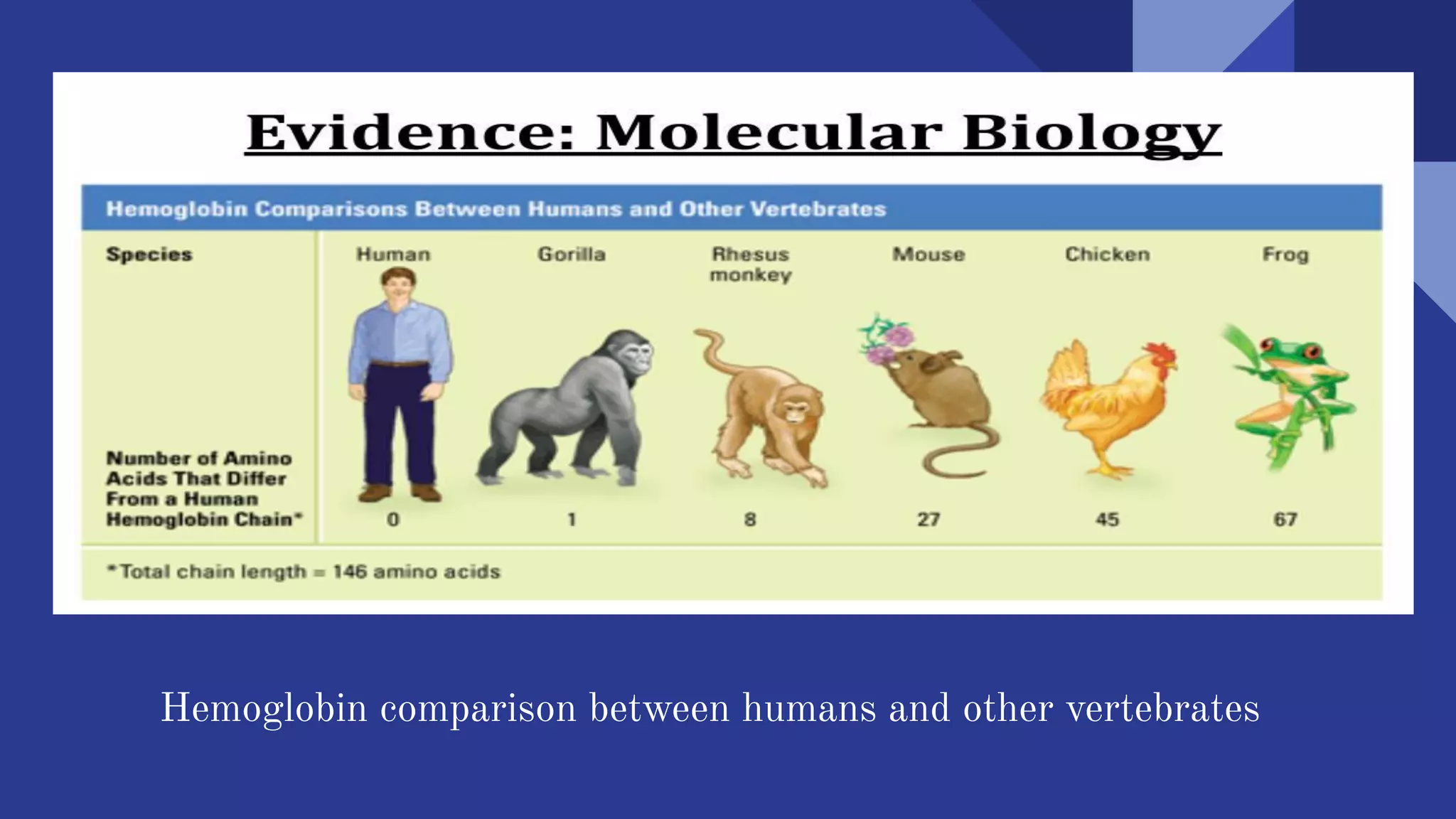
This document discusses molecular evolution and phylogenetic relationships as seen through molecular homology and comparisons of DNA, RNA, and protein sequences. It defines key terms like homology, orthologs, and paralogs. Orthologs are homologous sequences that result from speciation events, retaining similar functions in different species. Paralogs arise from gene duplication events and may develop new functions. Comparing sequences allows scientists to construct phylogenetic trees and study how genes and genomes have evolved over time.














![PARALOGS
● They are sequences that arose due to gene duplication
event
● Similar sequences within same species
● Two types :::
1 ] In paralog -Genes that have duplicated after a
speciation event
2 ]Out paralog-Genes that have duplicated before
speciation event](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/homologyhomologoussequenceorthologusparalogous-220531132640-f6808c1c/75/Phylogenetic-relationships-Homology-Homologous-sequences-of-proteins-and-DNA-orthologous-and-paralogous-17-2048.jpg)




