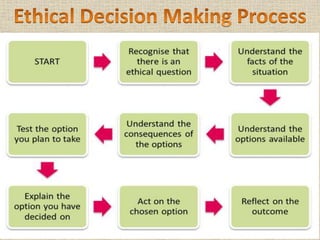
Managerial ethics refers to ethical standards and principles that guide managers' decisions and behavior in an organization. There are three main types of managerial ethics: immoral management which lacks ethics; moral management which adheres to high ethical standards; and amoral management which either does not consider ethics or is careless about them. To improve ethical behavior, managers should hire ethically, establish codes of ethics, lead by ethical example, provide ethics training, conduct audits, and support those facing dilemmas. Ethical decision making involves evaluating options based on ethical principles to select the most ethical alternative.