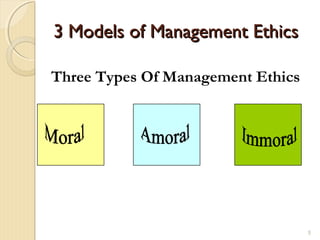
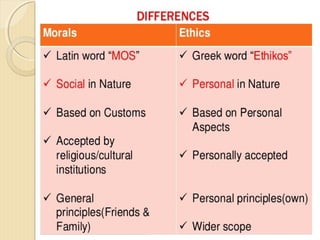
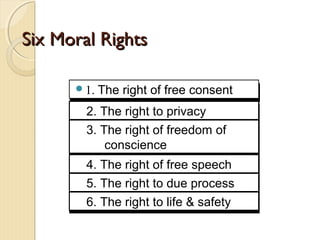
This document provides an introduction to business ethics. It defines ethics as a set of moral standards or values to determine what is right or wrong. Business ethics applies ethical standards to business decisions and actions. There are two types of ethical problems in business - overt issues like bribery and theft, and more complex covert issues. The document outlines three models of management ethics and six stages of ethical consciousness that businesses may progress through. It also discusses factors like an individual manager's moral development and a company's culture and systems that can influence ethical choices. The benefits of practicing business ethics and approaches to ethical decision making are presented.