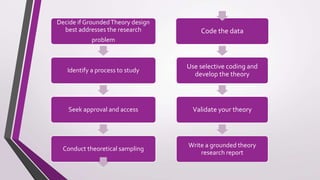
The document provides an overview of grounded theory, including its definition, history, uses, and evaluation. Grounded theory was developed in the 1960s by Glaser and Strauss as a qualitative research methodology to build theories inductively from data rather than testing existing hypotheses. The key steps include collecting data through methods like interviews, coding the data to identify concepts and categories, and developing a theory grounded in the data to explain a process. The theory is evaluated based on its connection to the raw data and usefulness in explaining the phenomenon under study.