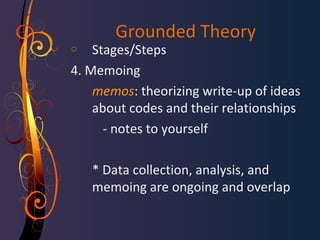
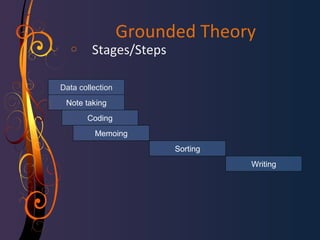
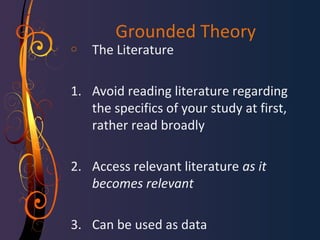
Grounded theory is a qualitative research method introduced in 1967 by Glaser and Strauss. It involves developing a theory grounded in data that is systematically gathered and analyzed through the constant comparative method. This iterative process involves collecting data, analyzing through coding and memo writing, and sorting memos to develop conceptual categories to generate an emergent theory. The theory should fit and work to explain the phenomenon under study. Grounded theory challenges assumptions that qualitative research is not systematic or rigorous and aims to develop conceptual theories rather than just descriptive case studies.