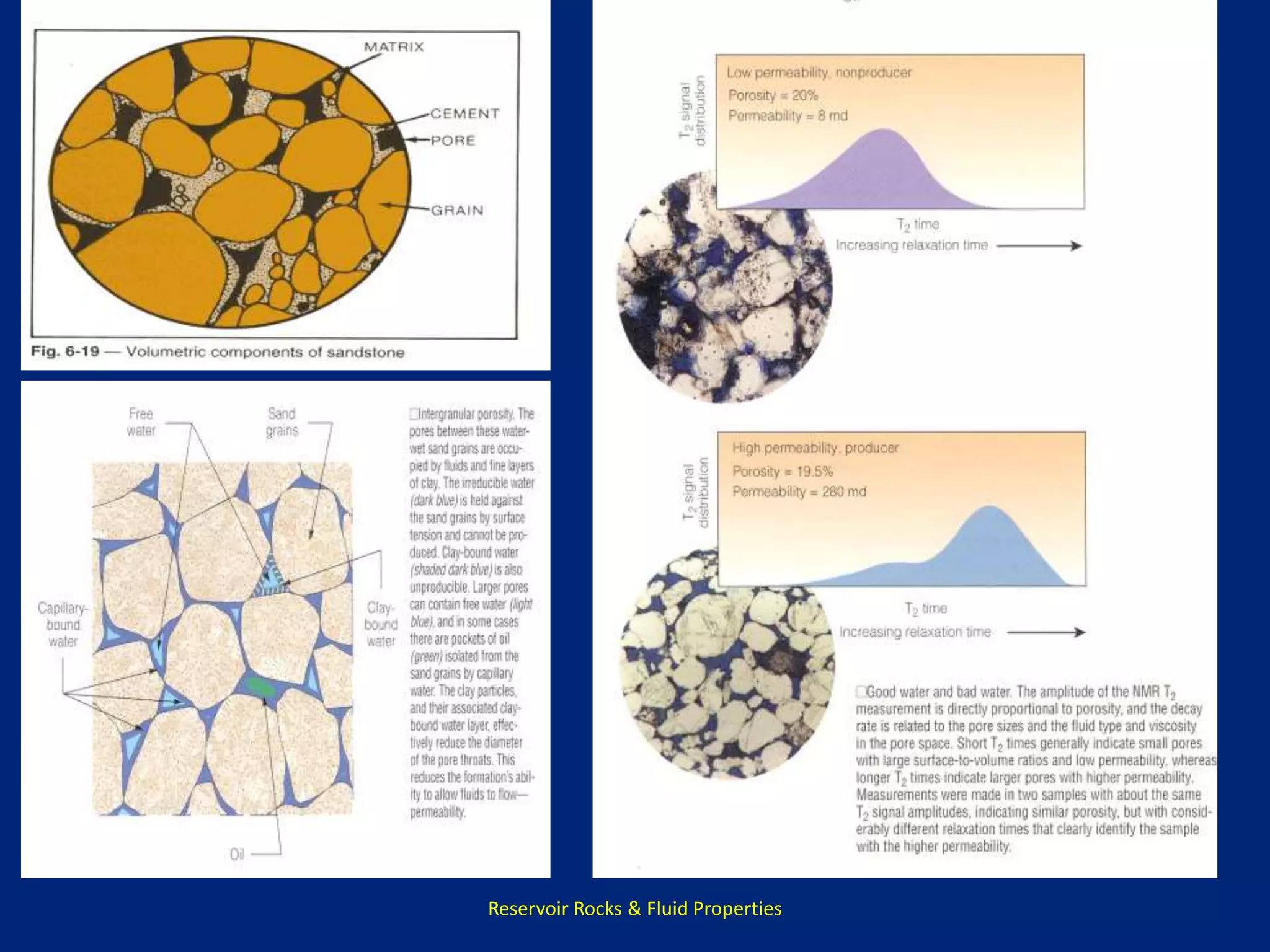
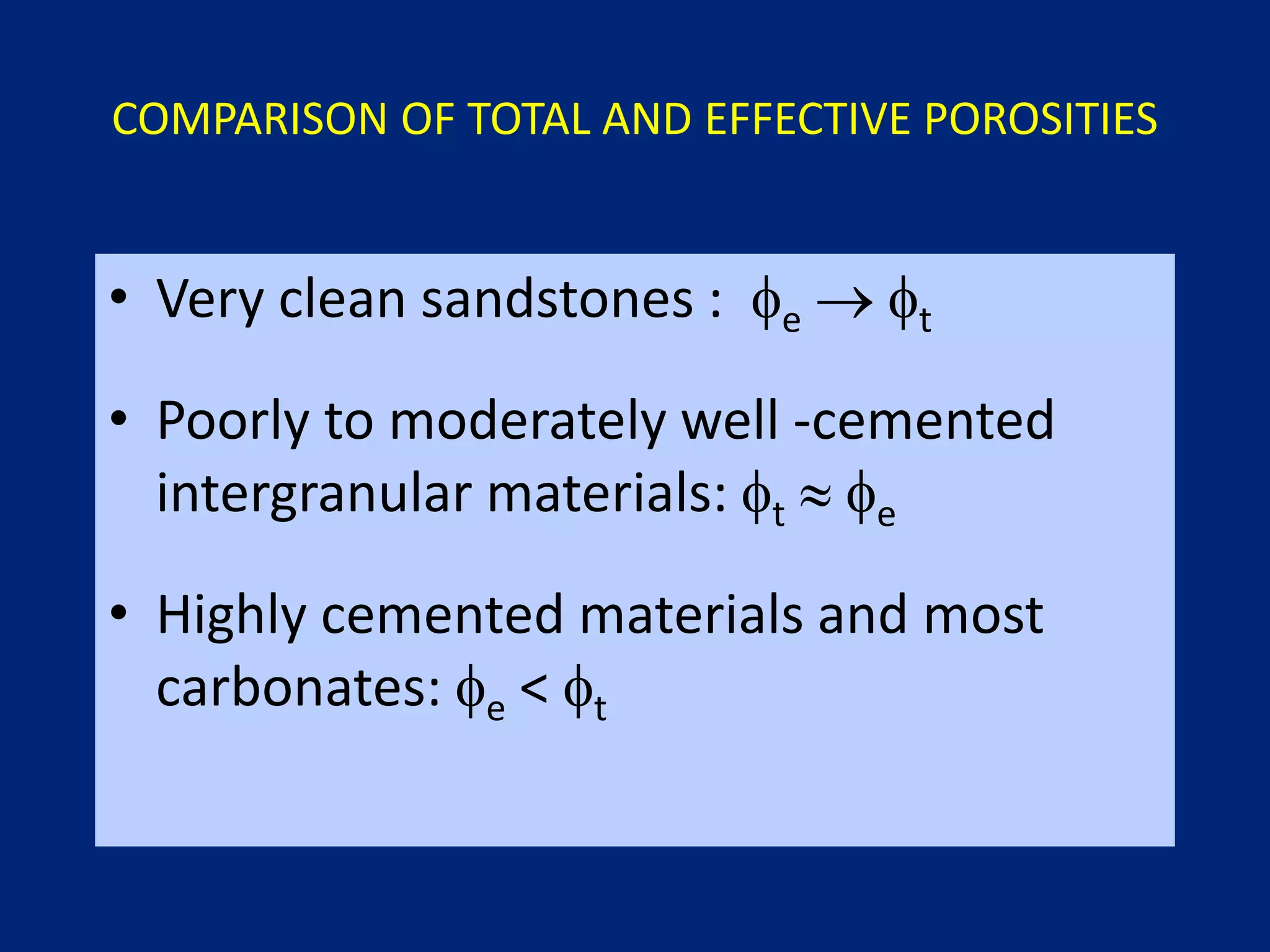
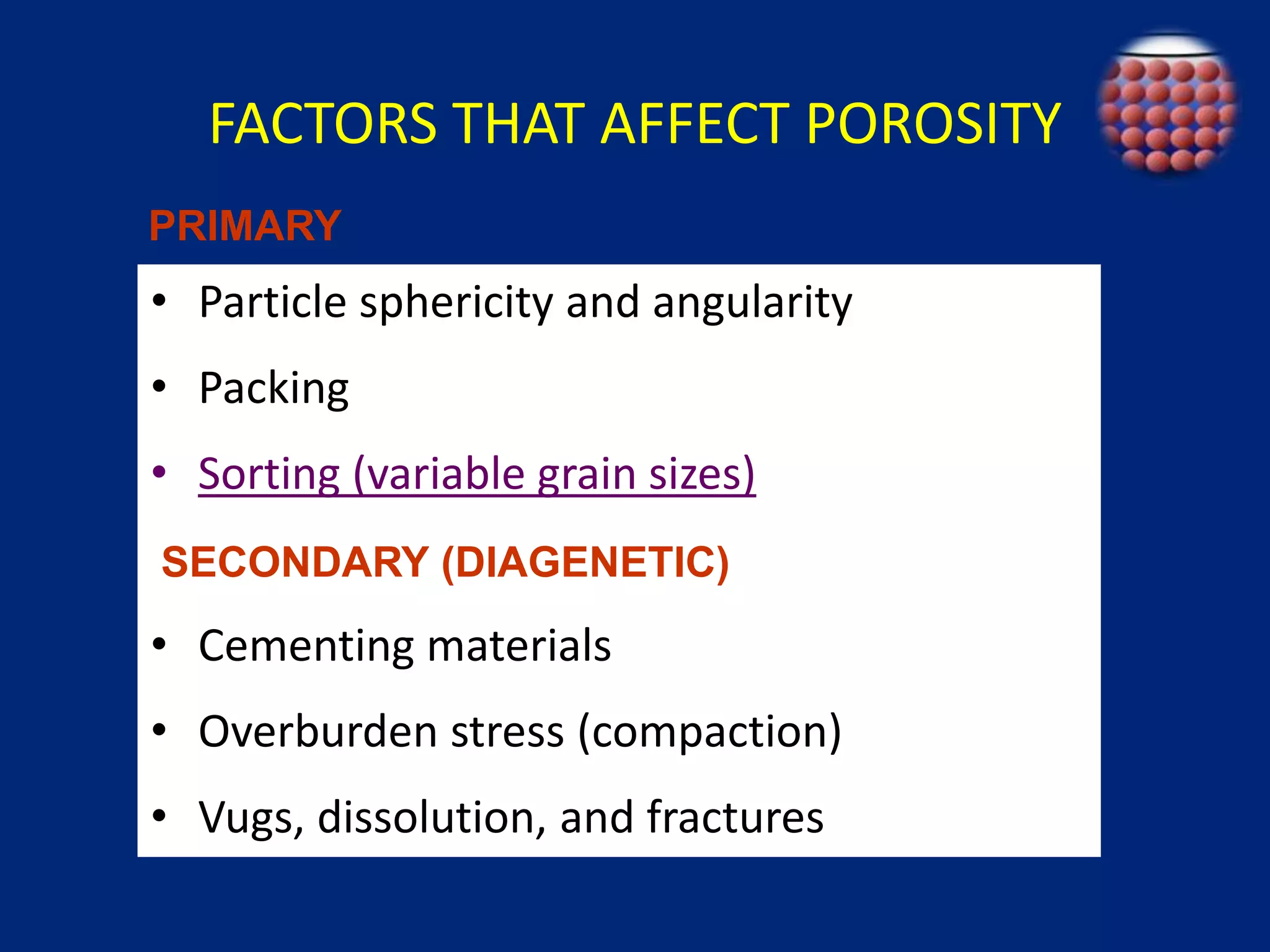
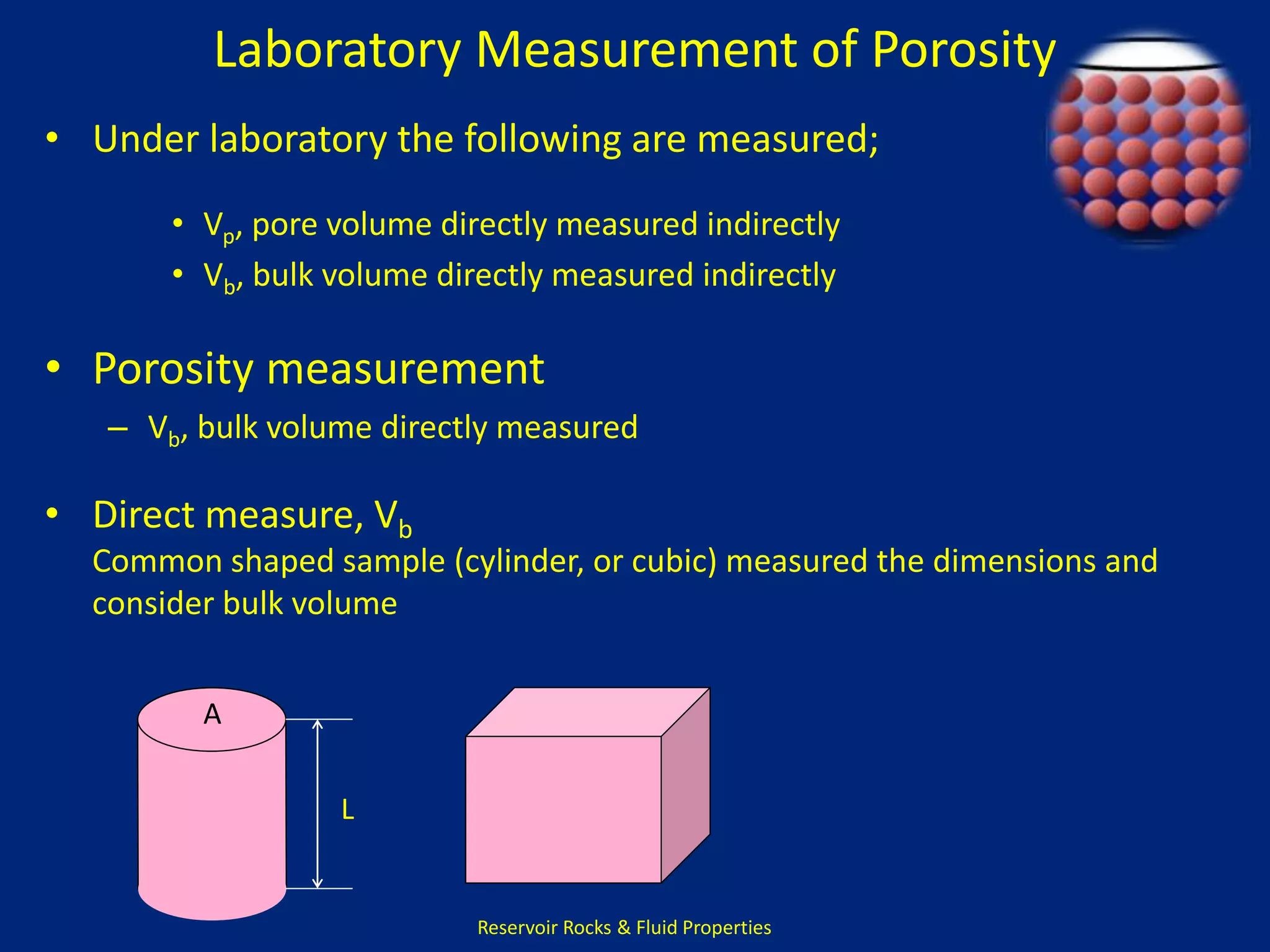
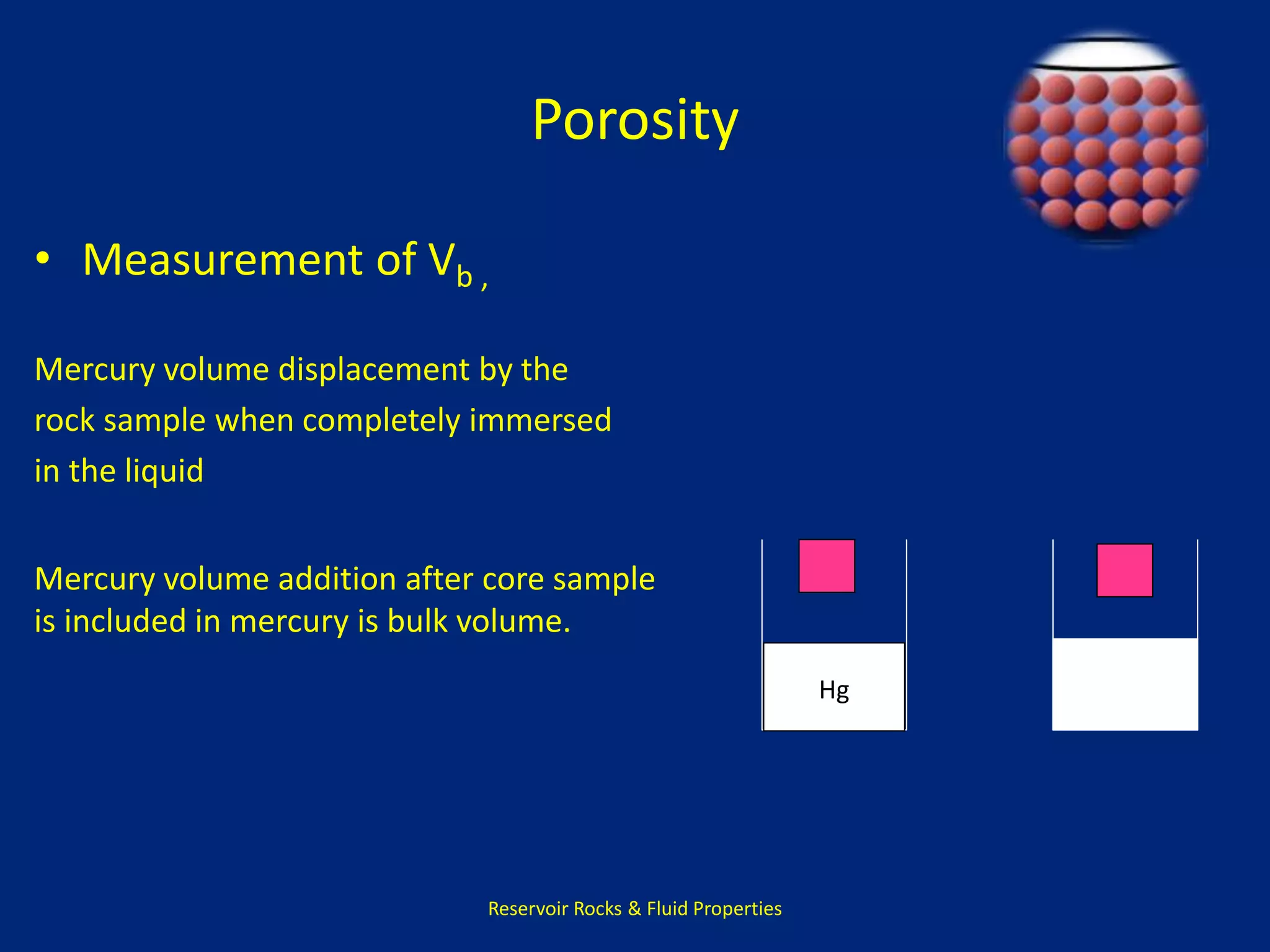
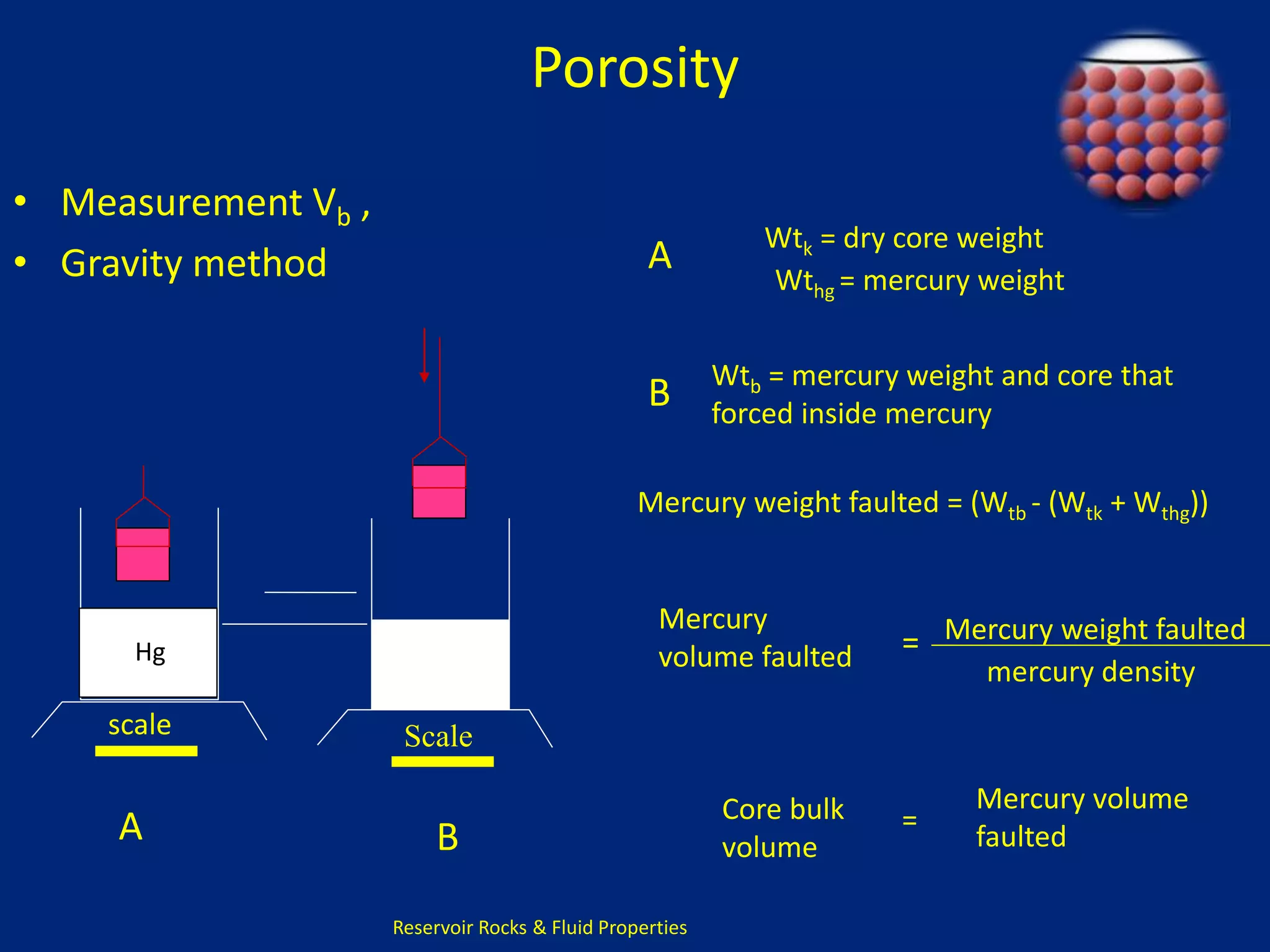
This document discusses porosity of reservoir rocks. It defines porosity as the ratio of pore volume to bulk volume of a rock. Porosity can be classified as original or induced. Factors that affect porosity include particle size, sorting, packing, cementation and stress. Porosity is important for reservoir engineering calculations as it represents the pore space occupied by fluids. It is measured through core analysis, well logging, or well testing. Laboratory methods to determine porosity include measuring bulk volume through fluid displacement or gravimetric techniques and pore volume through fluid saturation.























![ Example 1.2 – Porosity Calculation
• From Example 1.1
• Mass of dry sample in air = 20 gm
• Bulk volume of sample = 9.9 cc
• Grain volume of sample = (mass of dry sample in air)/ (sand-grain
density)
• = 20/2.67 = 7.5 cc
• Total porosity = Øt = [(bulk vol. – grain vol.)/bulk volume] x 100
• = [(9.9 – 7.5)/9.9] x 100 = 24.2 per cent](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/porosity-140910003207-phpapp01/75/Porosity-30-2048.jpg)


