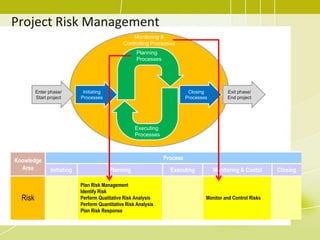
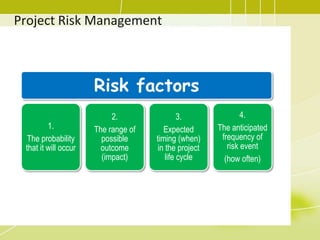
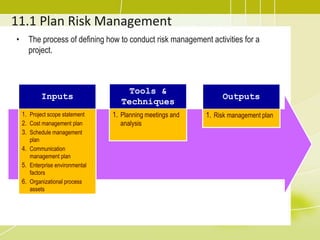
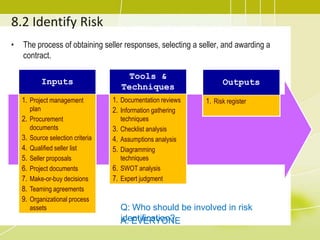
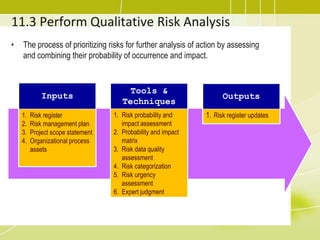
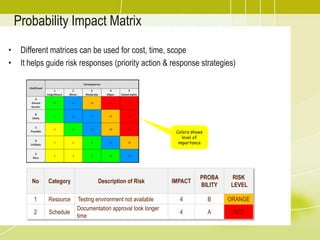
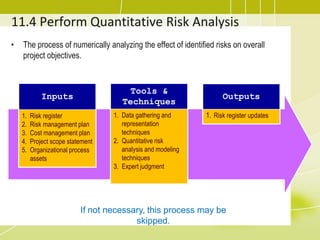
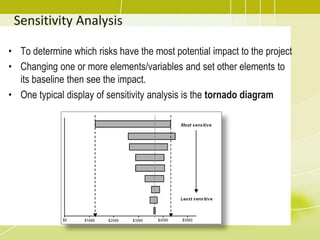
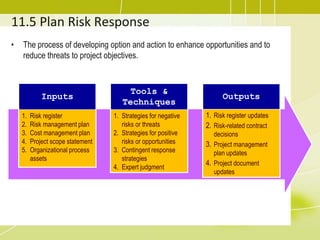
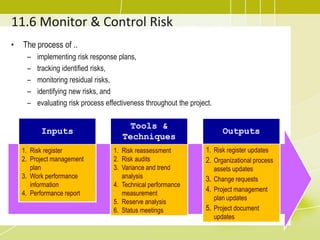
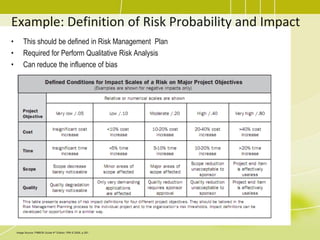
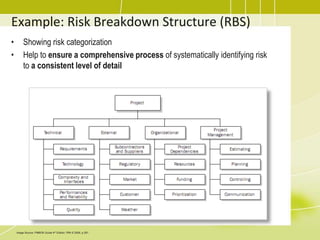
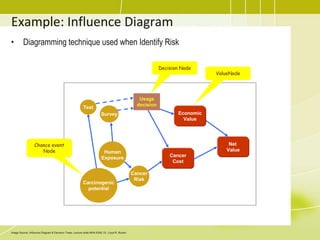
Project risk management involves identifying potential risks, analyzing their likelihood and impact, and developing responses to address threats and opportunities. The key processes include planning risk management, identifying risks, performing qualitative and quantitative risk analyses to prioritize risks, and planning risk responses. Qualitative analysis involves assessing probability and impact, while quantitative analysis uses numerical methods to evaluate risk exposure and determine contingency reserves. Risks are continually monitored and the risk register updated throughout the project life cycle.