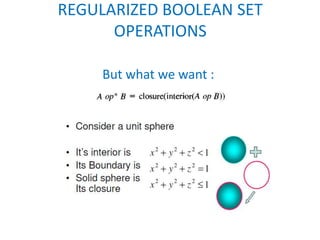
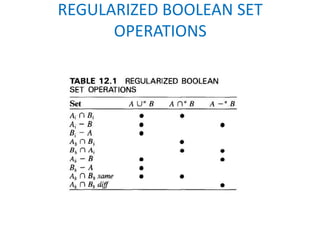
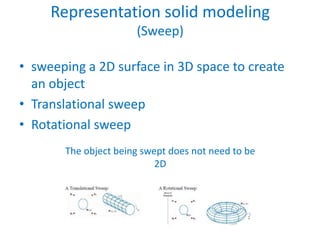
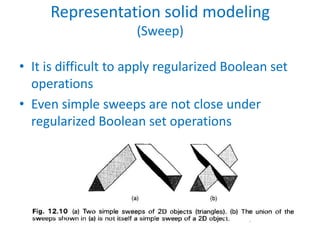
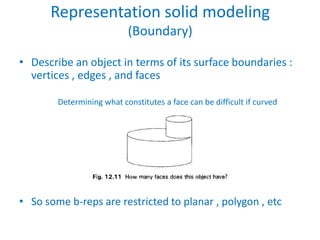
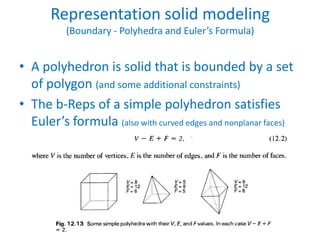
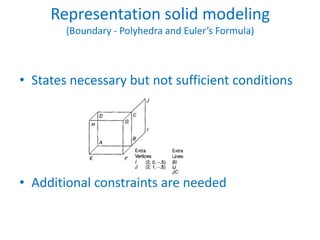
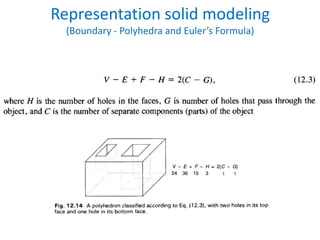
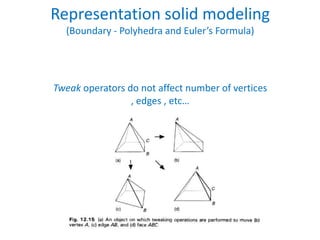
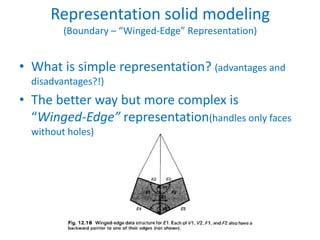
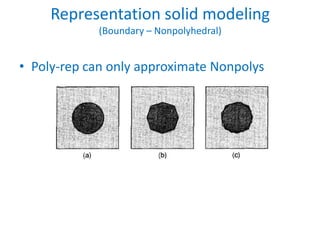
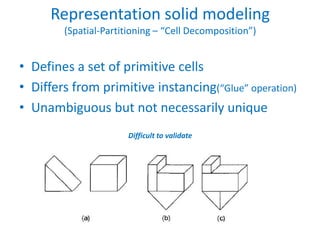
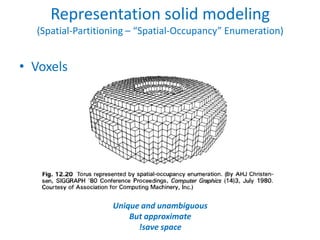
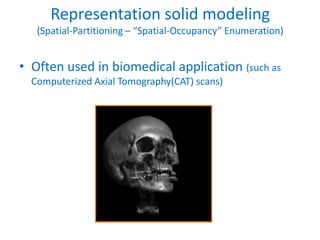
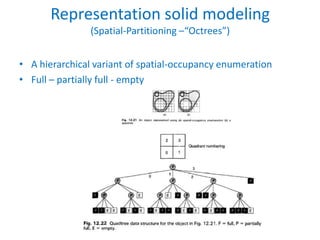
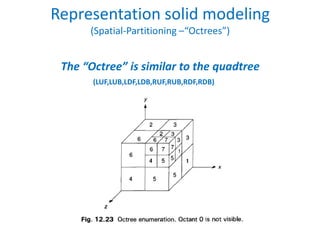
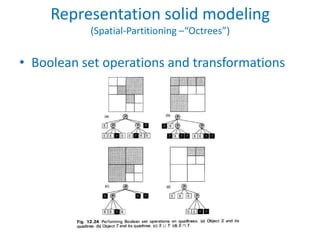
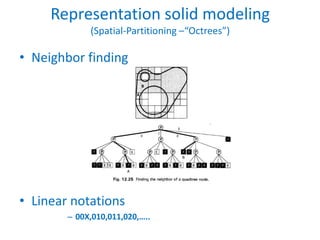
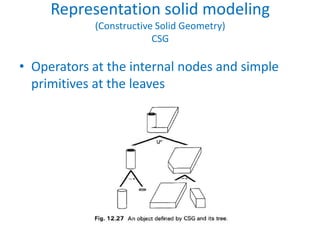
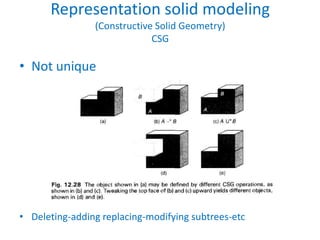
This document discusses different techniques for representing 3D solid objects in computer modeling, including boundary representation (B-rep), constructive solid geometry (CSG), and spatial partitioning. B-rep describes objects by their surface boundaries like vertices and faces. CSG uses Boolean operations on primitives. Spatial partitioning divides space into uniform cells. Each technique has strengths and weaknesses in terms of accuracy, domain of representable objects, uniqueness of representation, and efficiency.