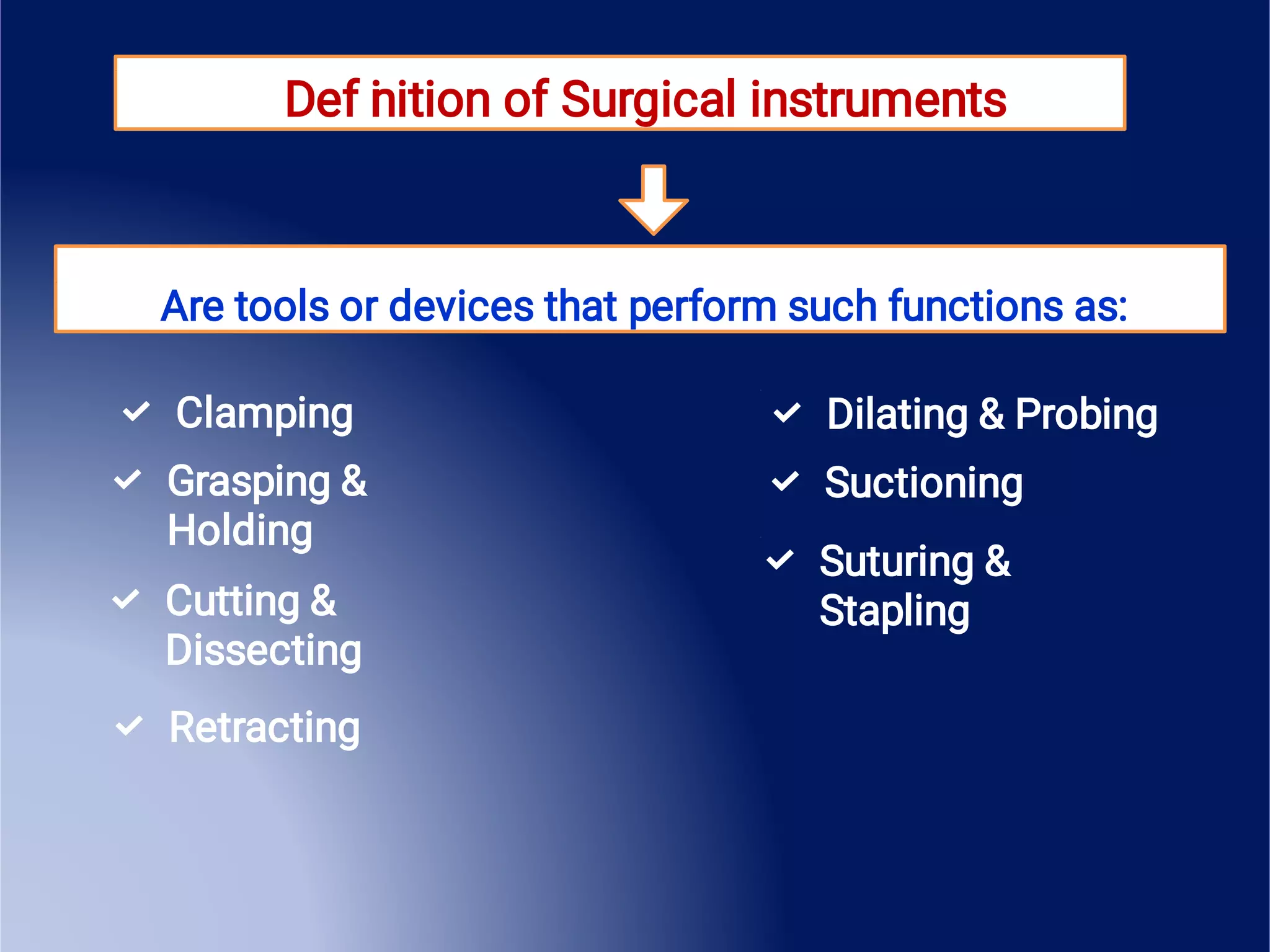
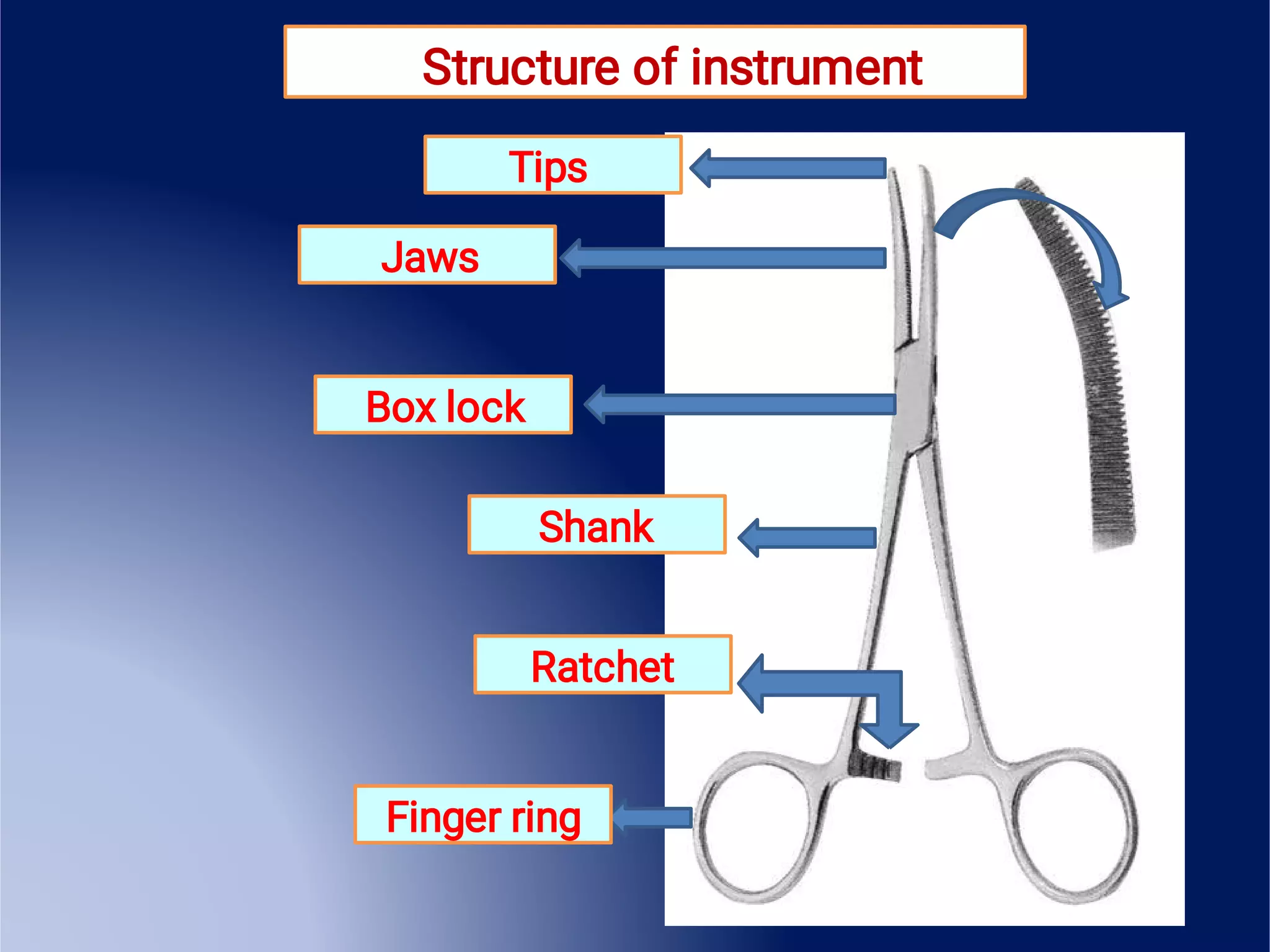
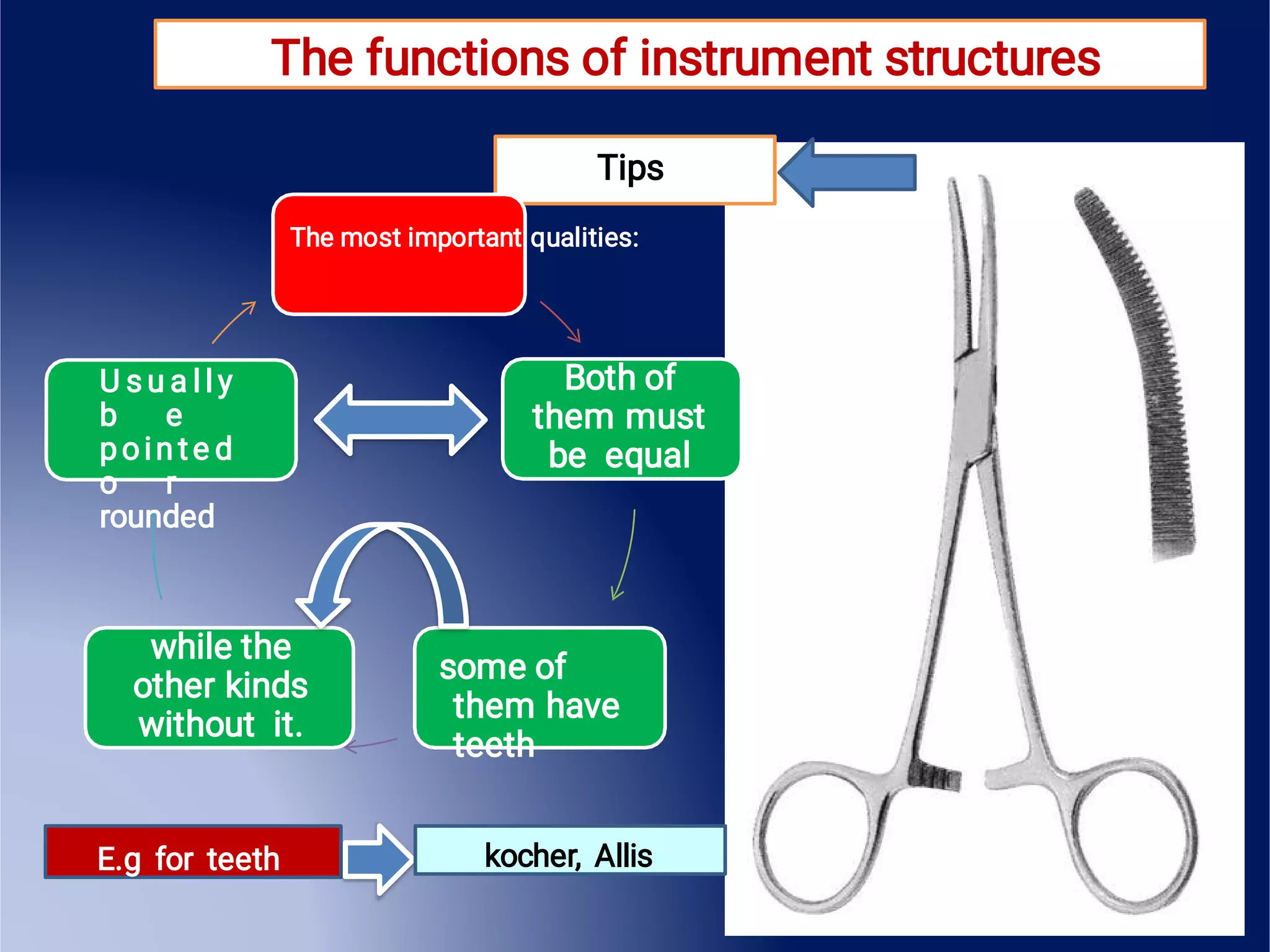
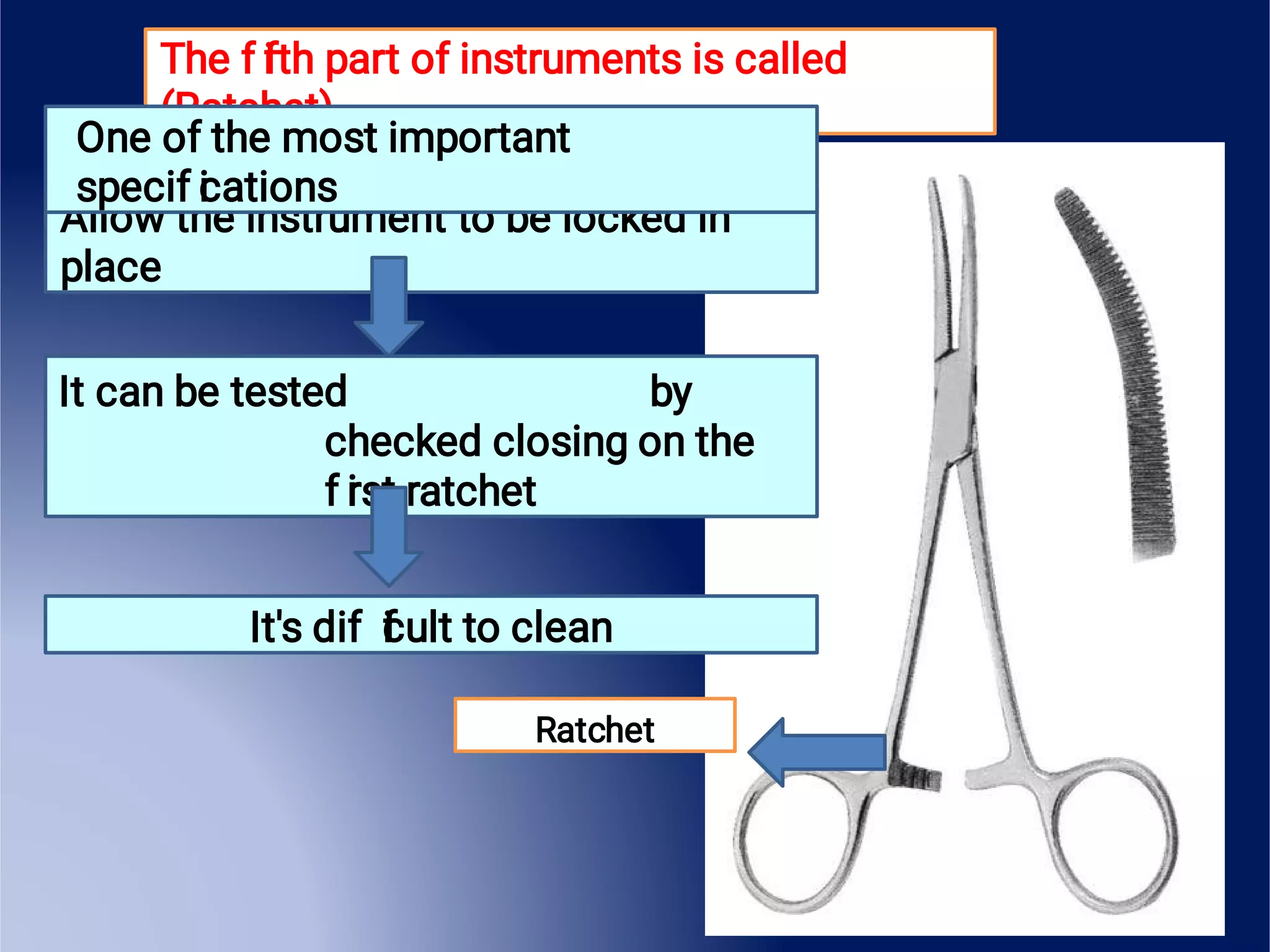
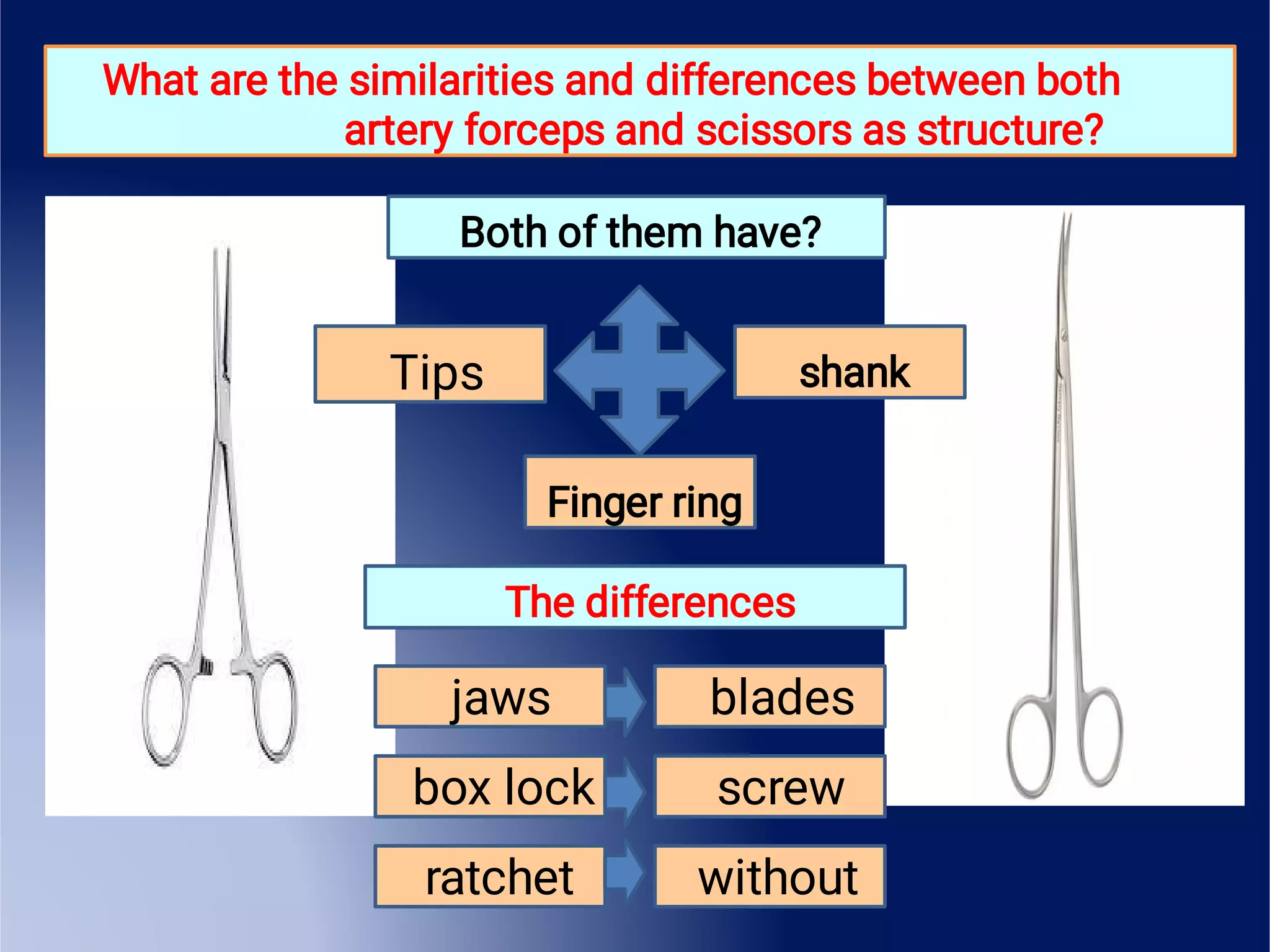
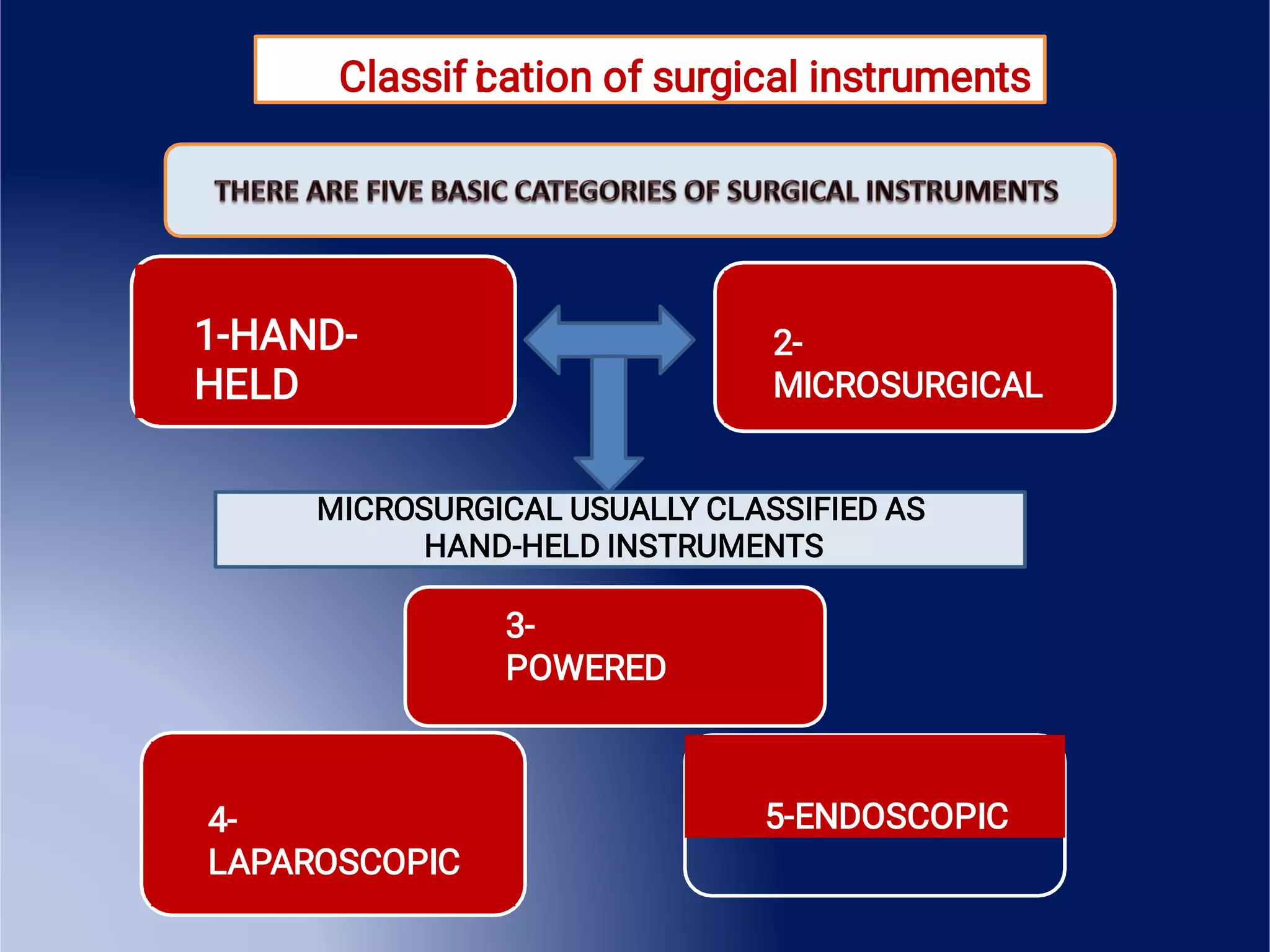
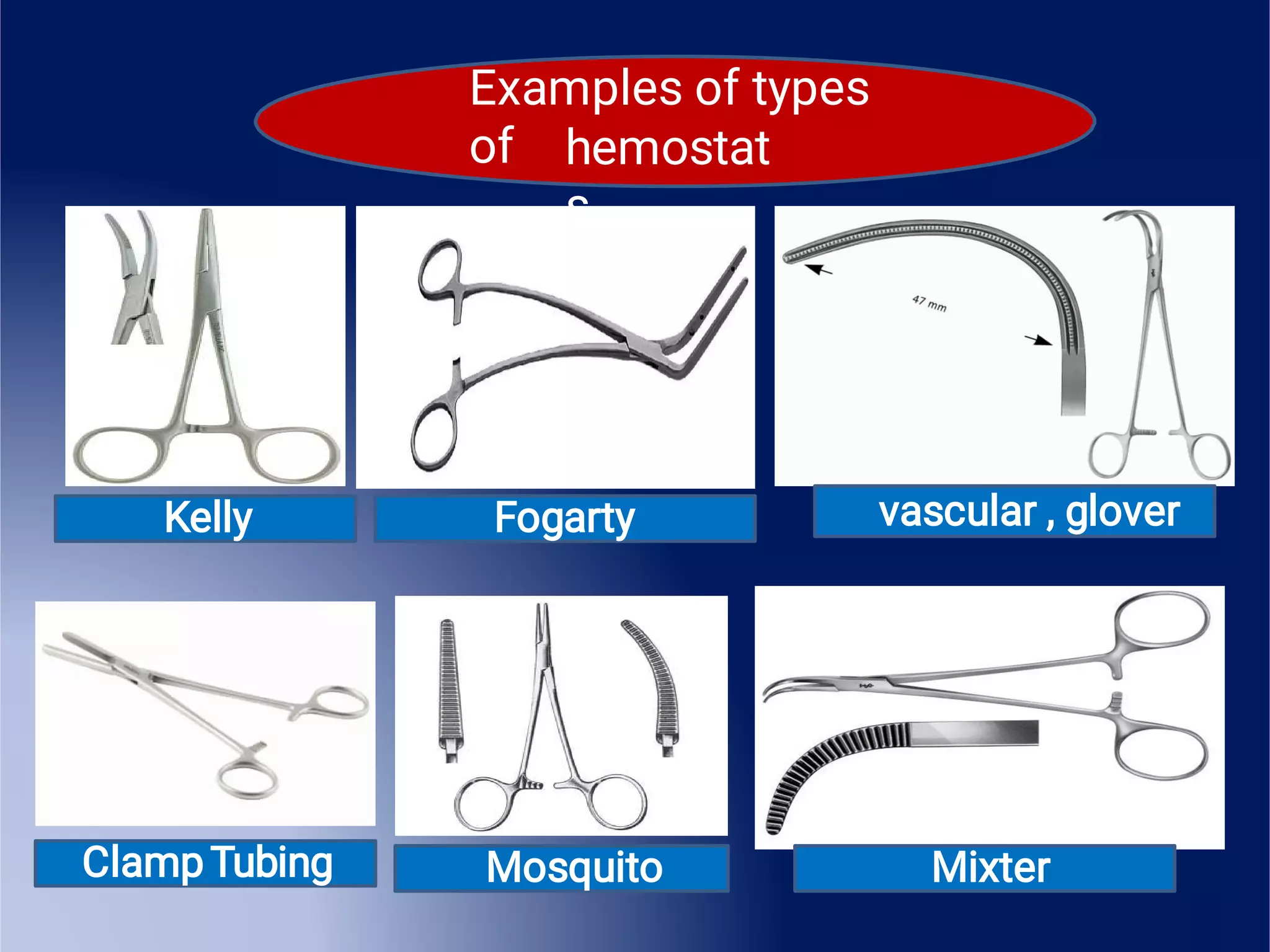
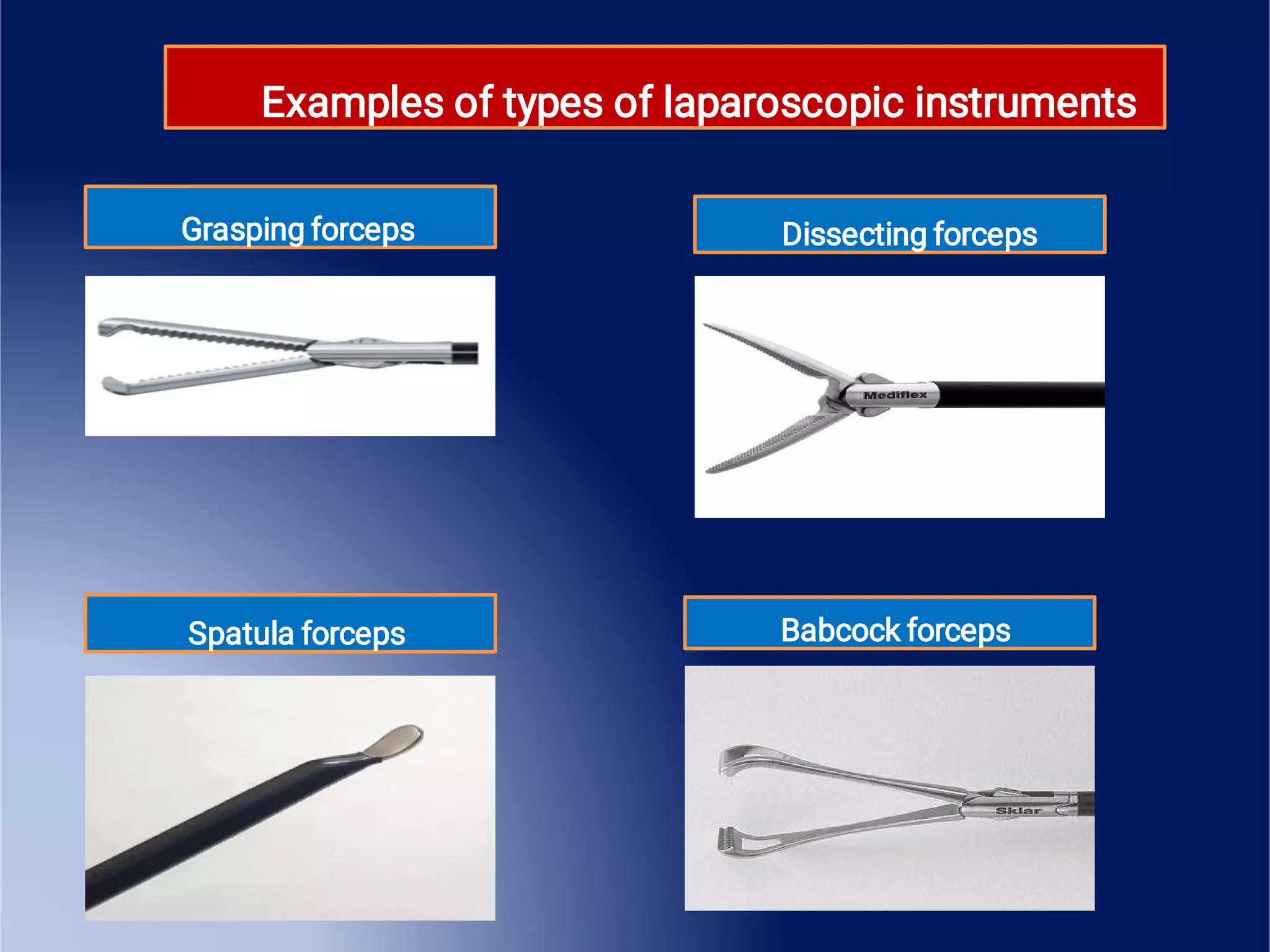
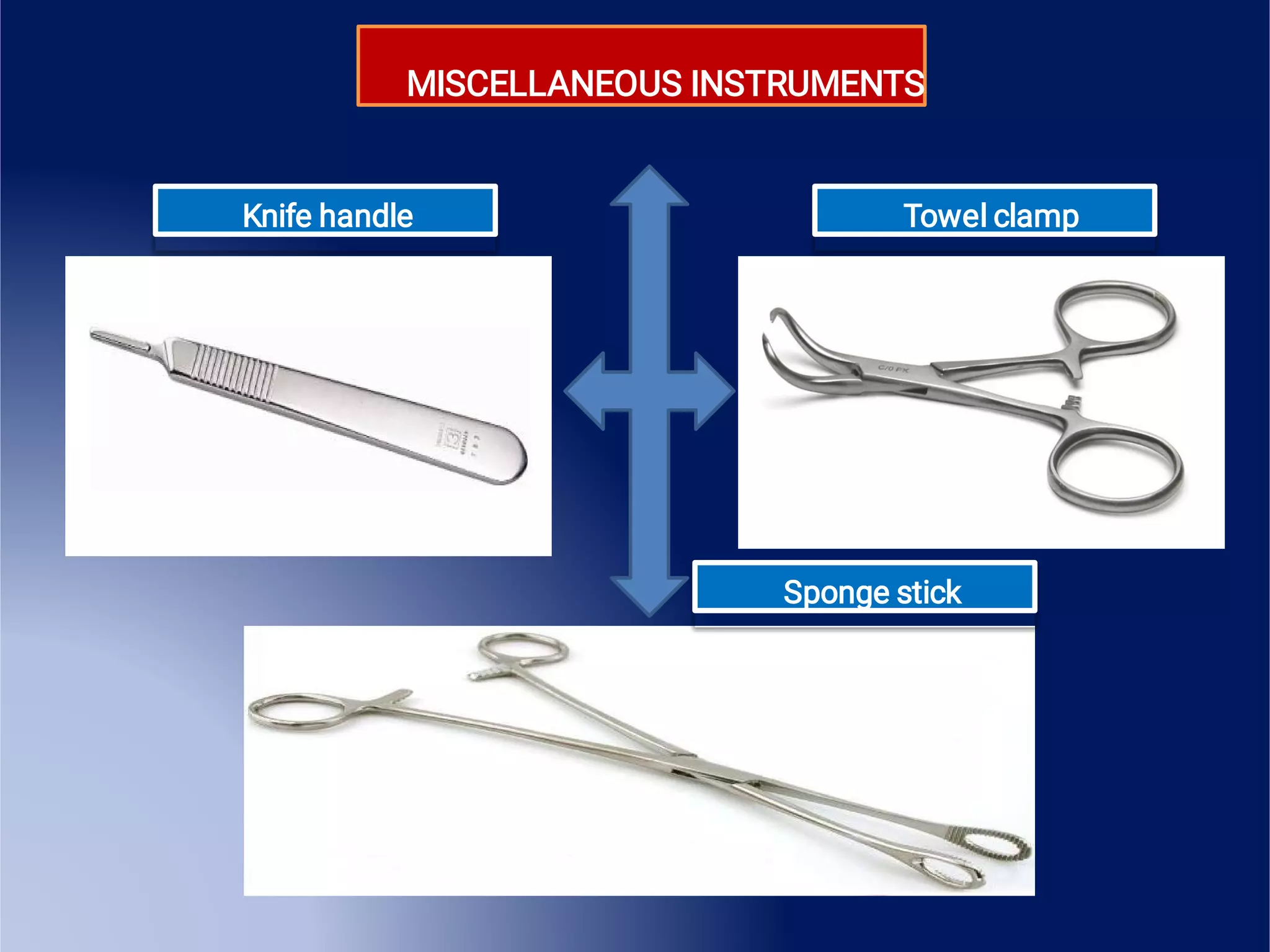
This document provides an overview of surgical instruments, including their history, definition, manufacturing, grading, structure, and classification. It discusses how surgical instruments began as stone knives over 10,000 years ago and have since evolved to modern stainless steel tools. Instruments are classified based on their intended use, such as hand-held, microsurgical, powered, or laparoscopic. Proper inspection and cleaning of instruments is important to ensure sterility and prevent the spread of infection between surgical procedures.