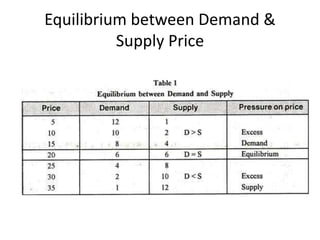
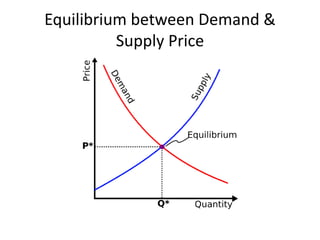
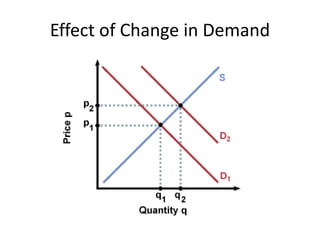
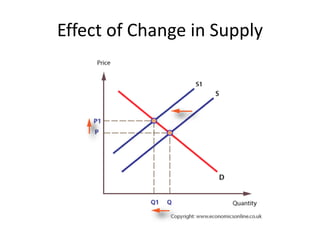
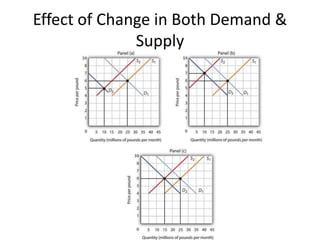
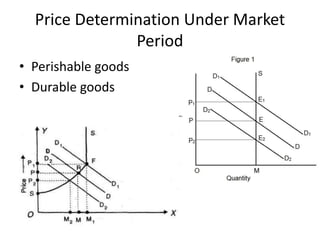
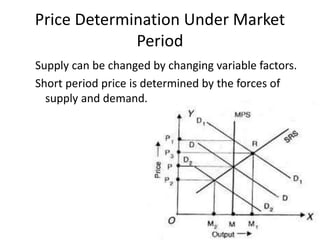
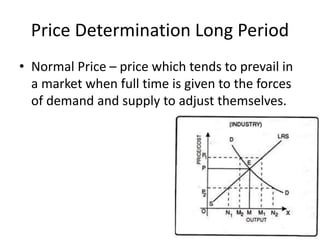
The document discusses price determination in a perfectly competitive market, characterized by many buyers and sellers trading identical products with free entry and exit. It explains equilibrium between demand and supply, how prices change due to shifts in these curves, and the different time elements affecting prices, including market, short, long-run, and secular periods. Additionally, it outlines factors influencing price determination, such as normal price conditions and the laws of returns.