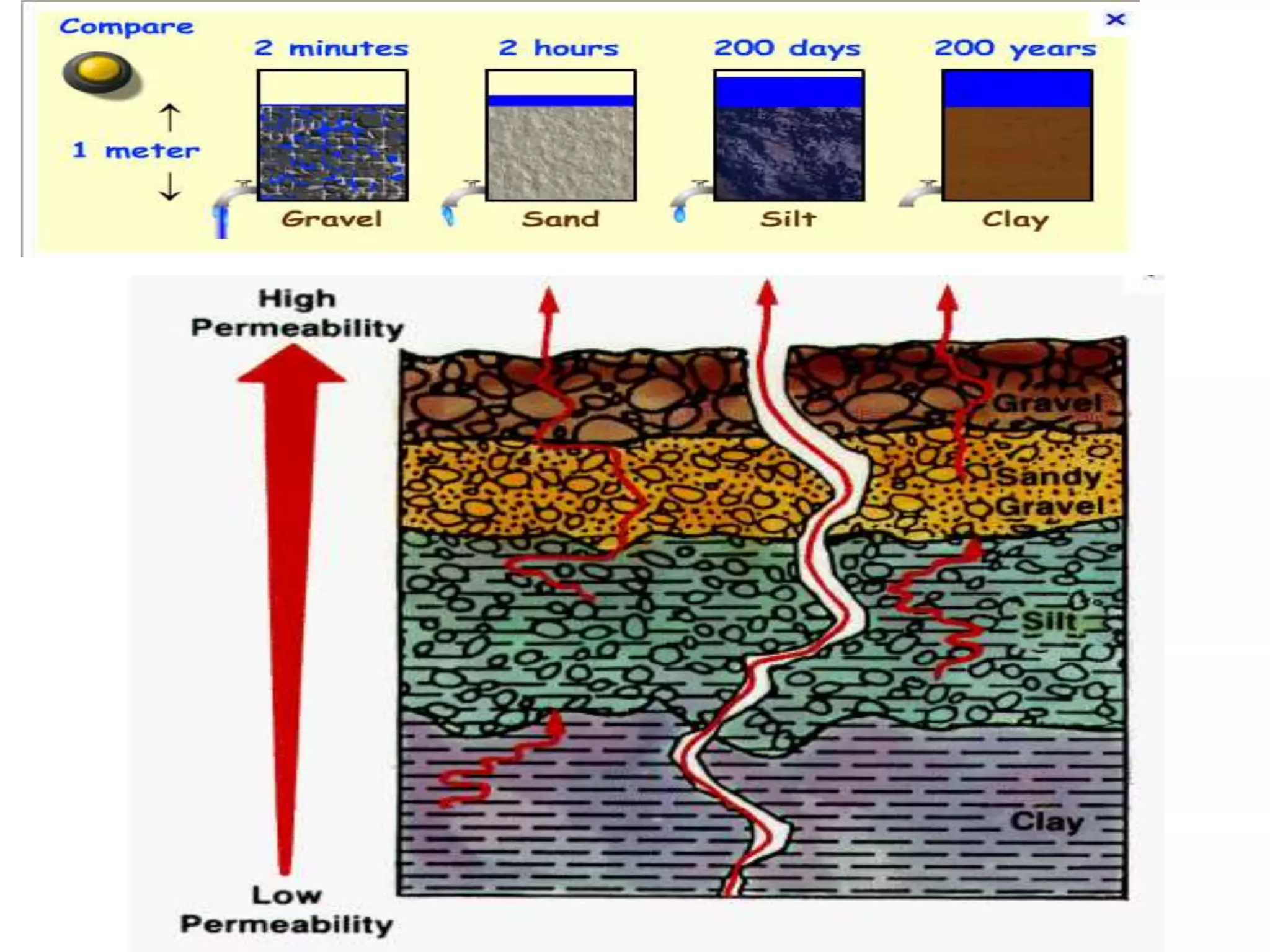
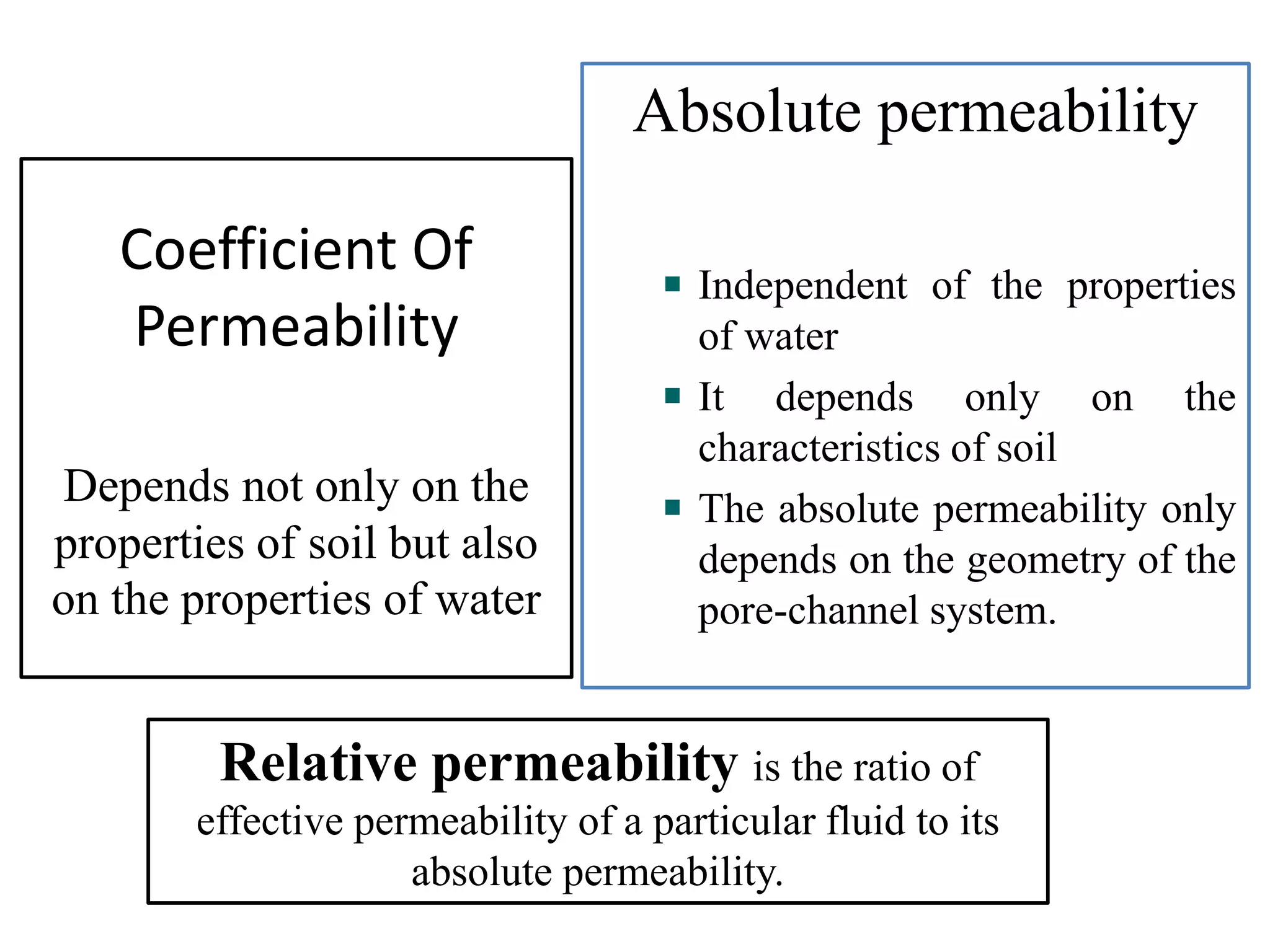
This document discusses soil permeability. It defines permeability as the property of a porous material that allows water to pass through its voids. Permeability depends on factors like particle size, void ratio, and degree of saturation. Darcy's law states that the rate of water flow through a soil is proportional to the hydraulic gradient. Common laboratory tests to measure permeability include constant-head and variable-head tests. Permeability is important for calculating seepage, drainage, settlement, and the stability of earth structures. Soils can be classified based on their permeability rate.