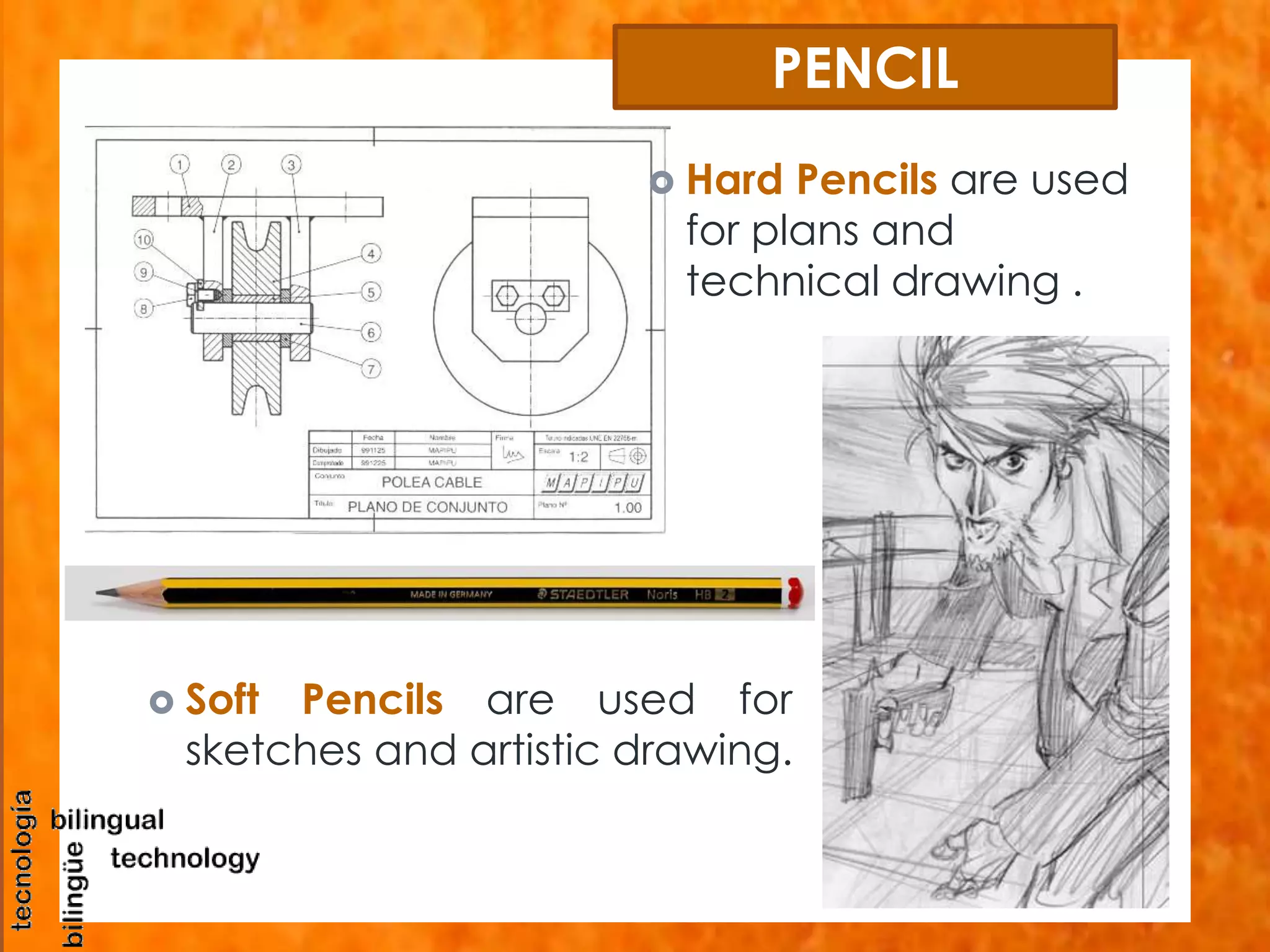
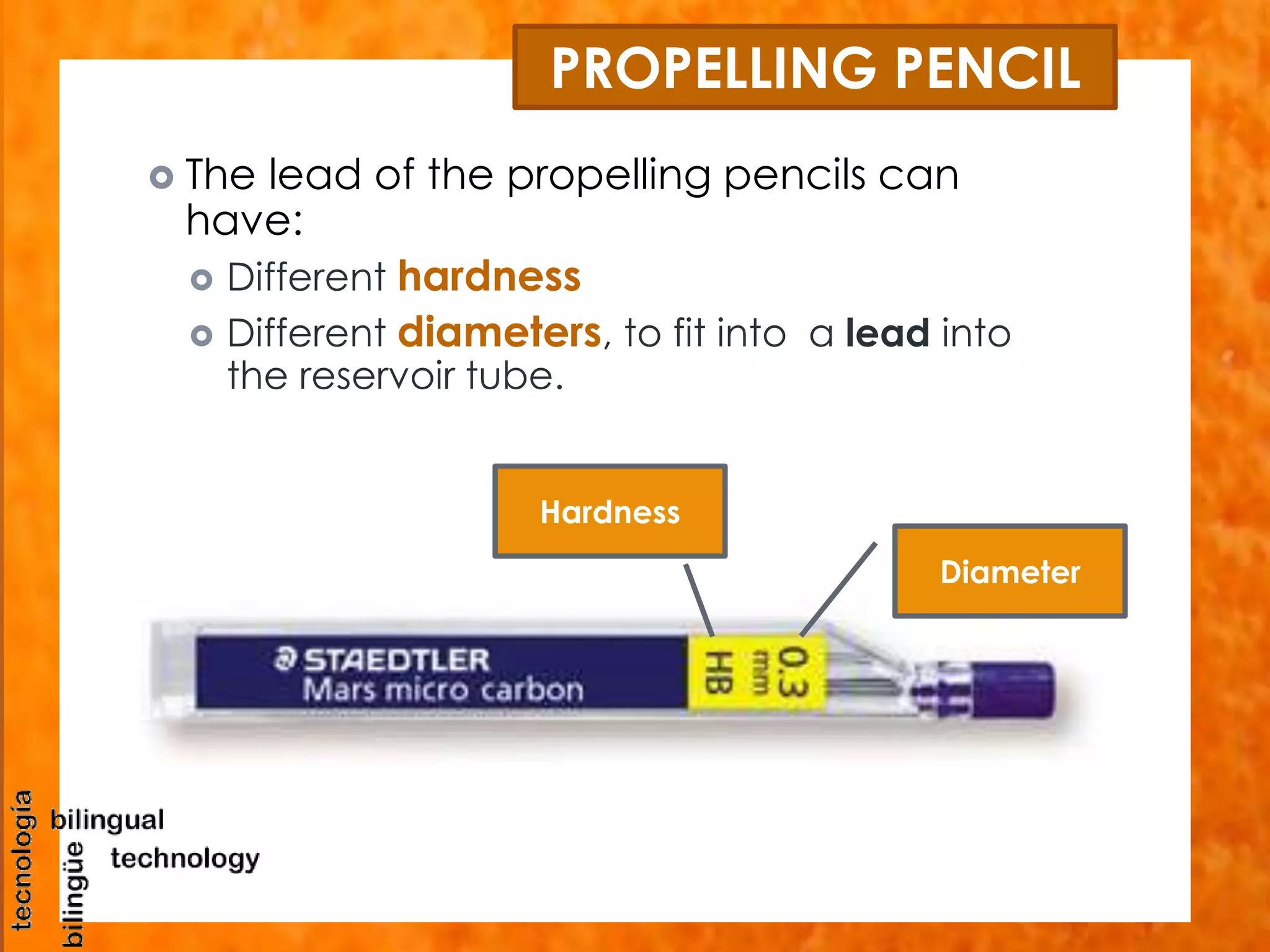
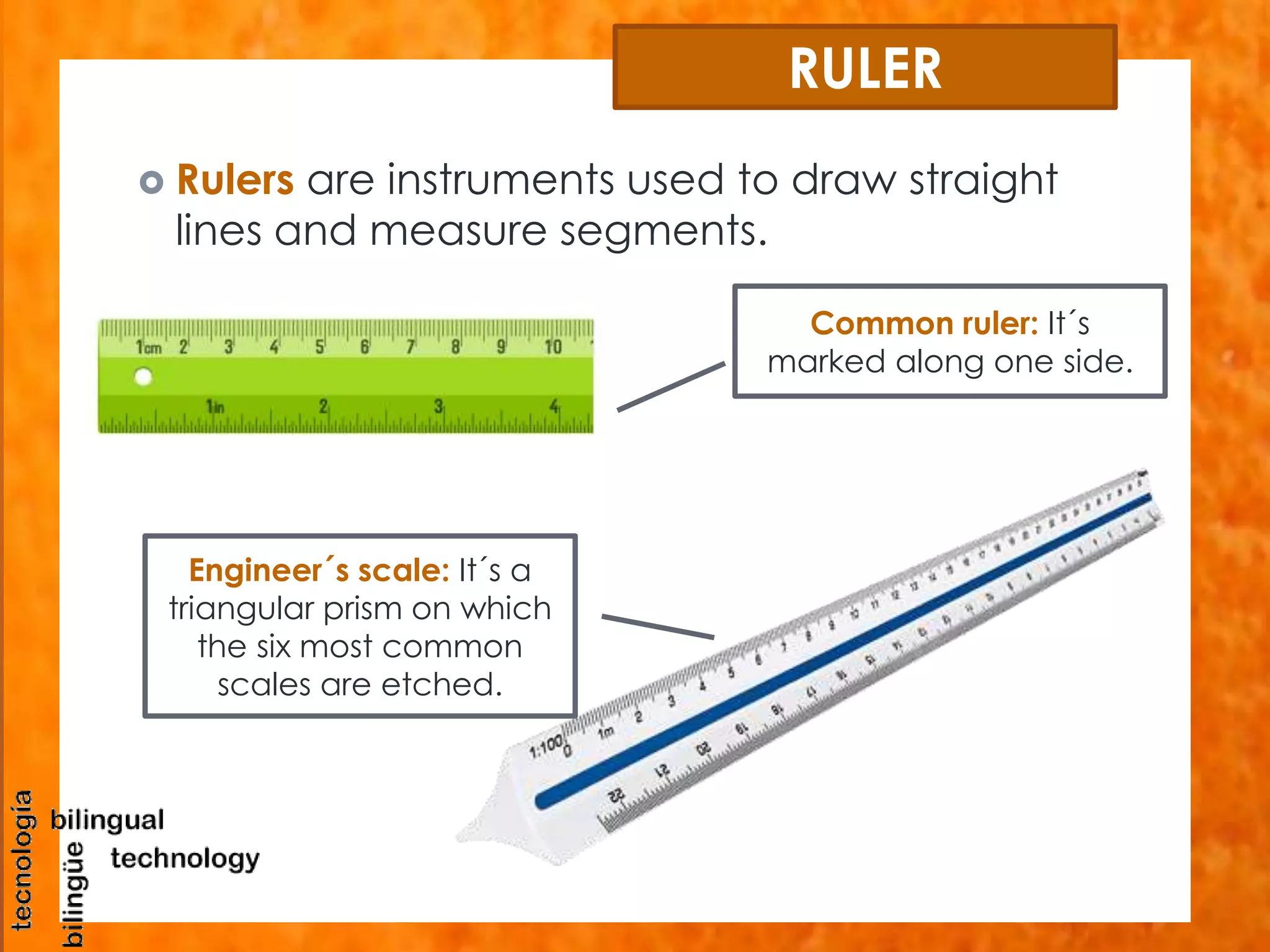
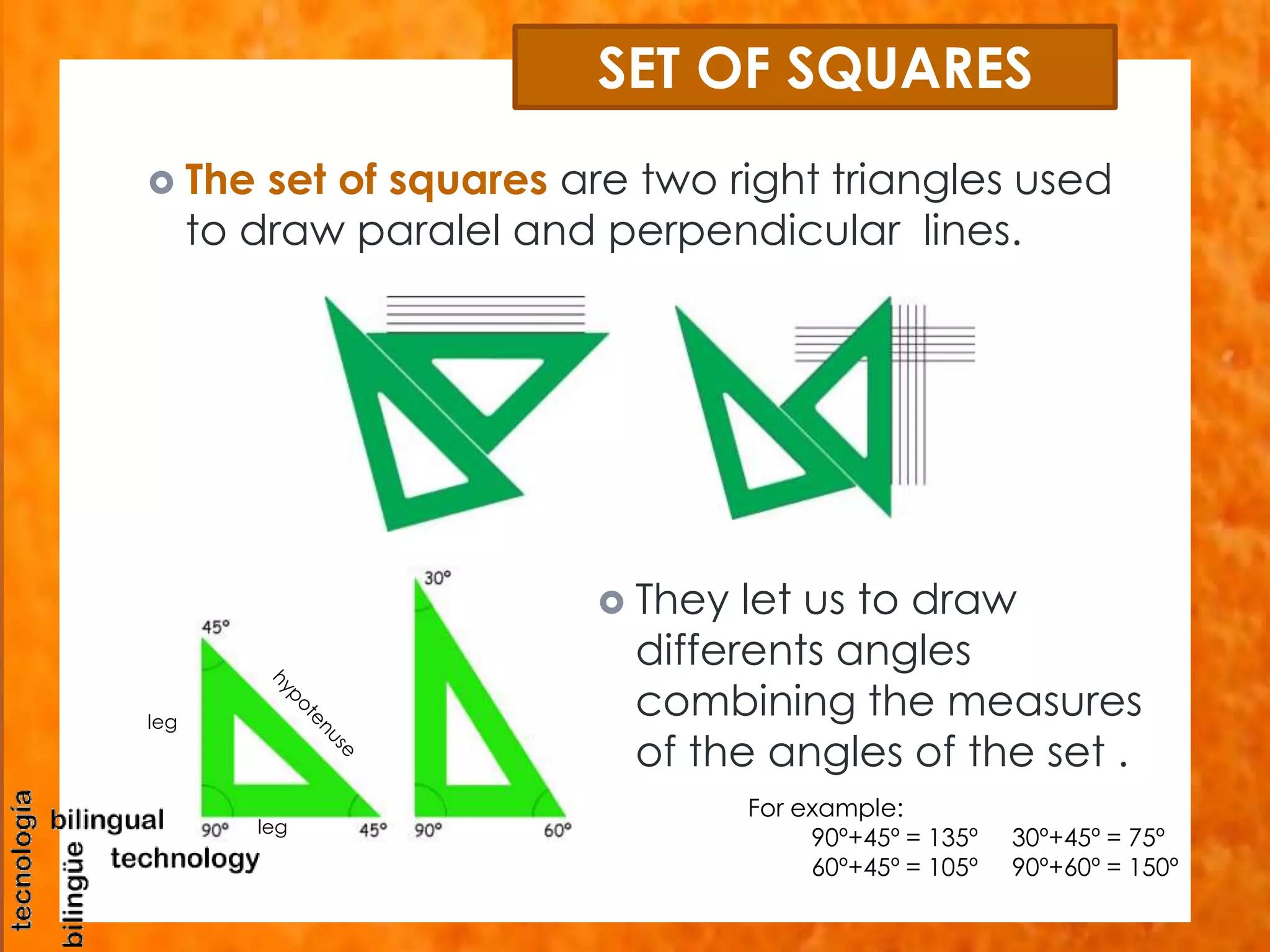
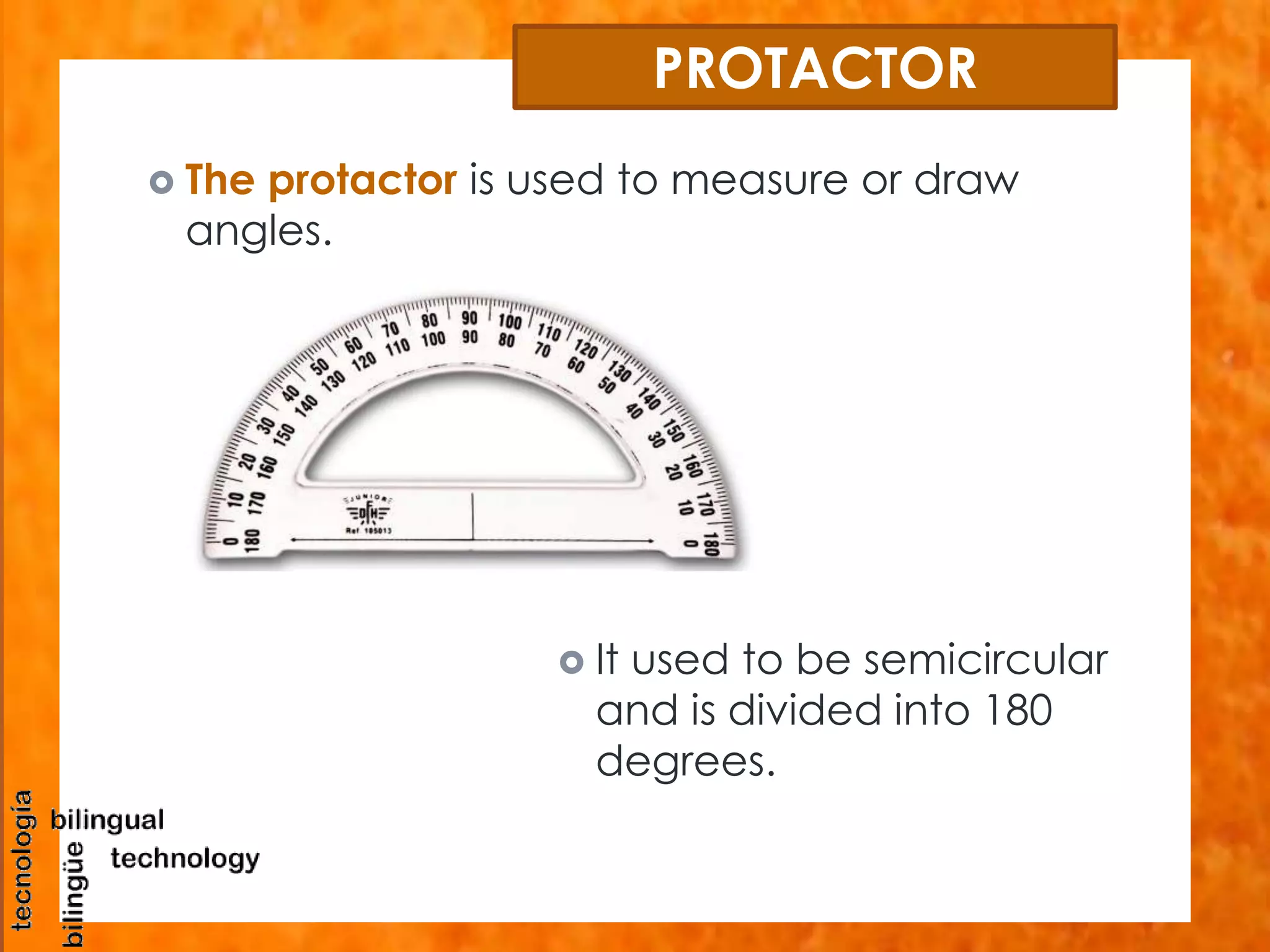
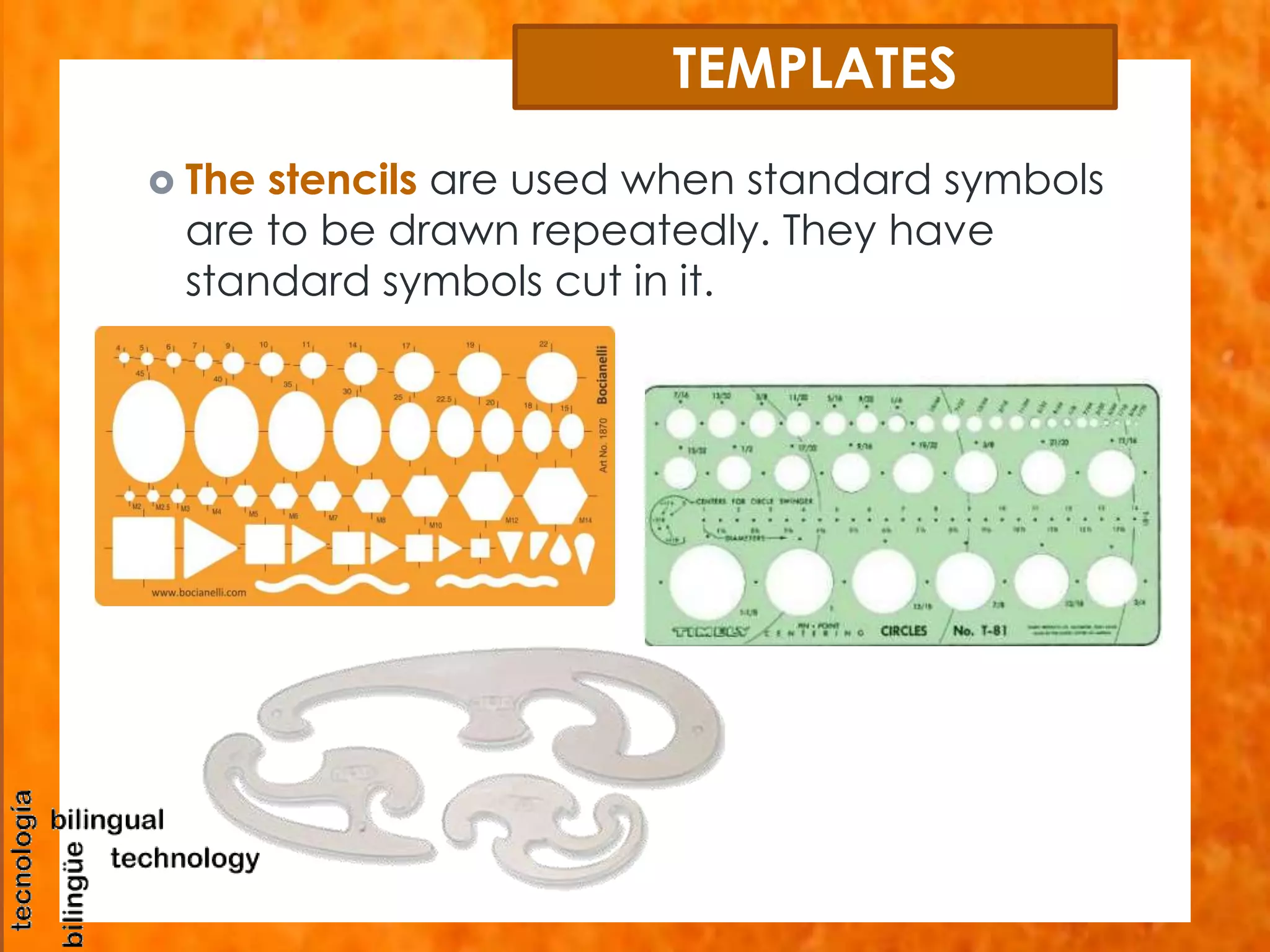
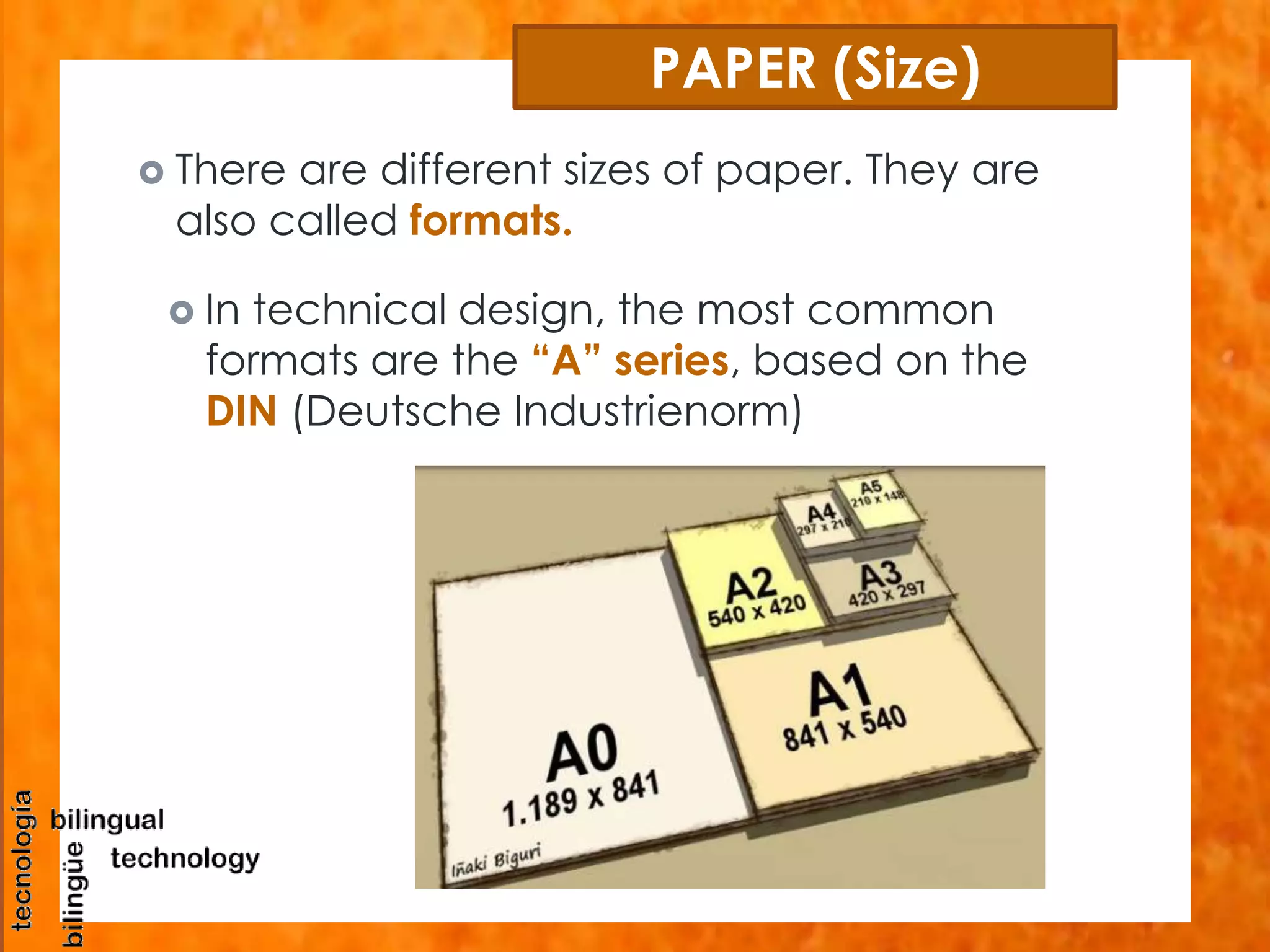
This document discusses the basic tools and materials used for technical drawing. It describes pencils of varying hardness for sketches and plans, propelling pencils for consistent lines, erasers for corrections, pens for tracing lines, rulers and sets of squares for straight and angled lines, protractors for measuring angles, templates for standard symbols, compasses for circles, and paper of different sizes, weights, finishes for the base. Technical drawing uses these tools to precisely communicate engineering and design concepts.