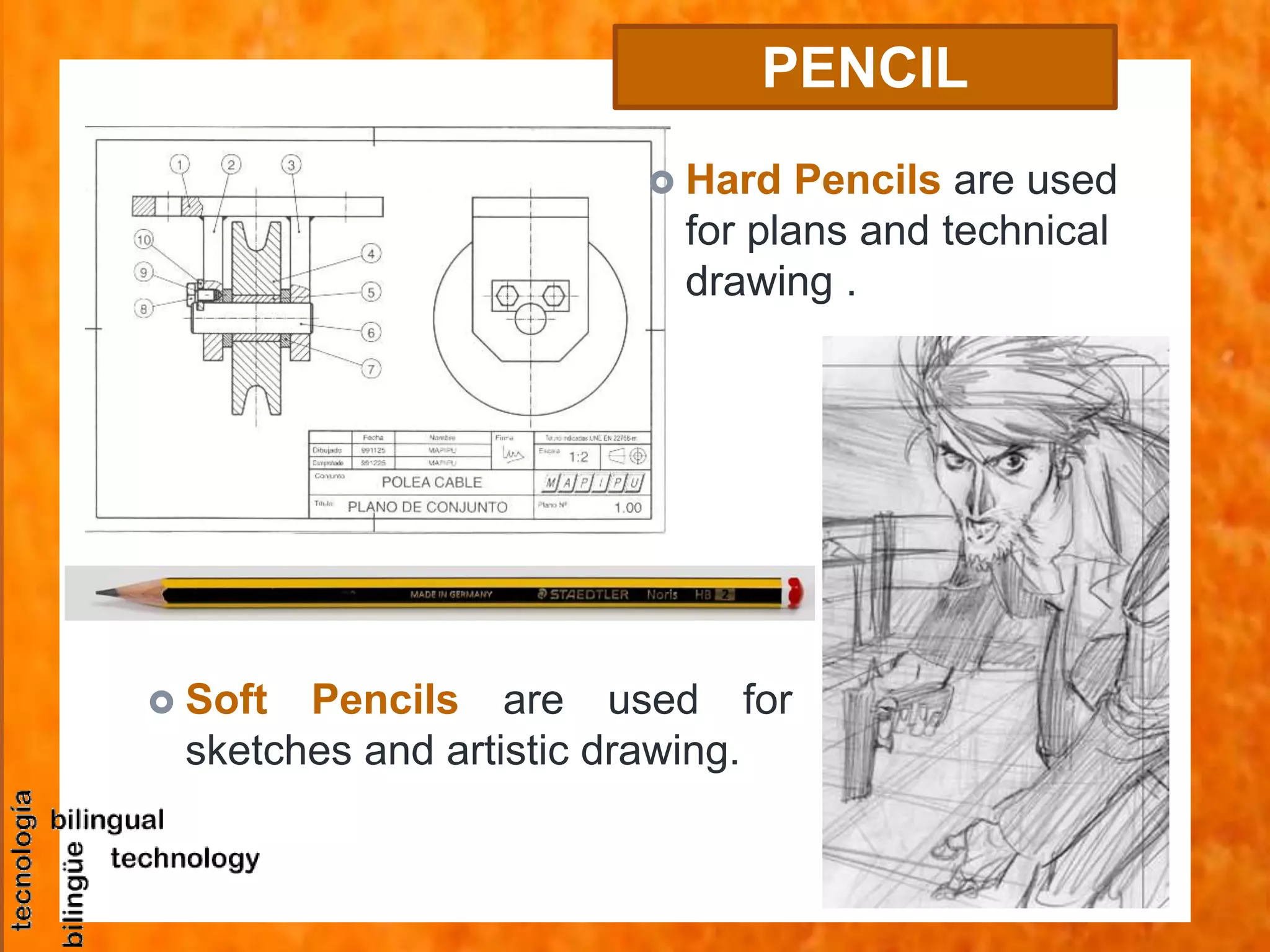
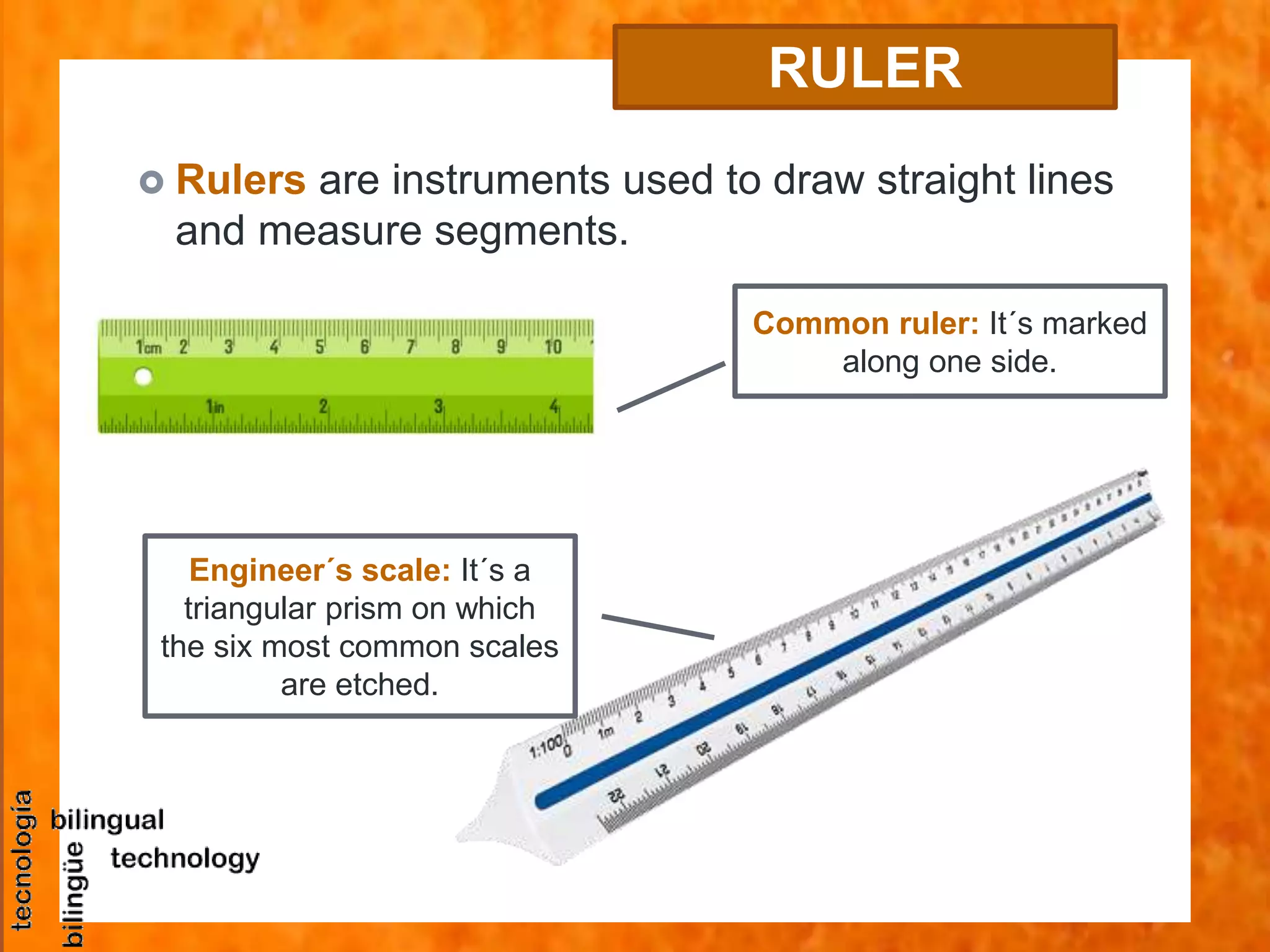
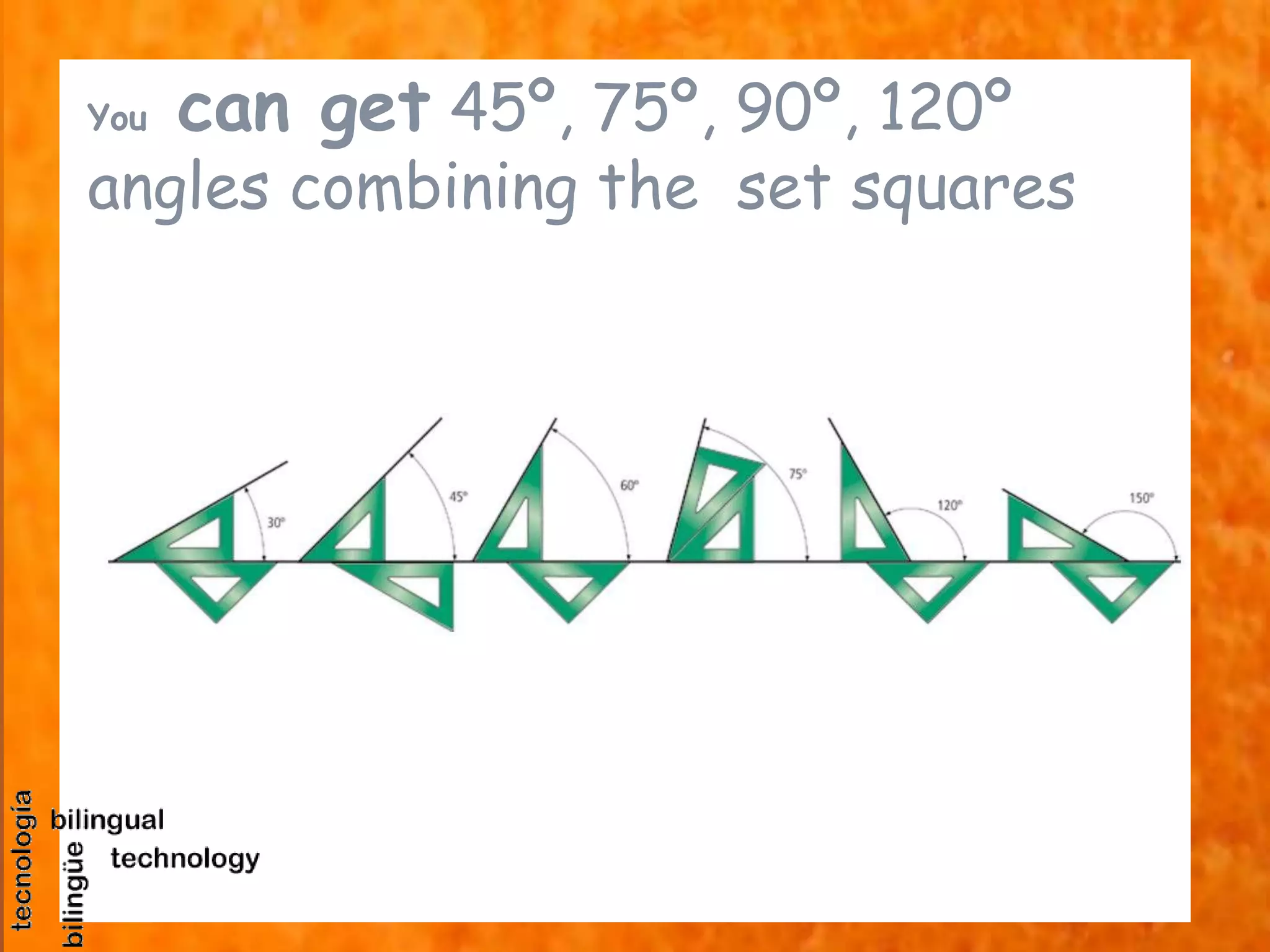
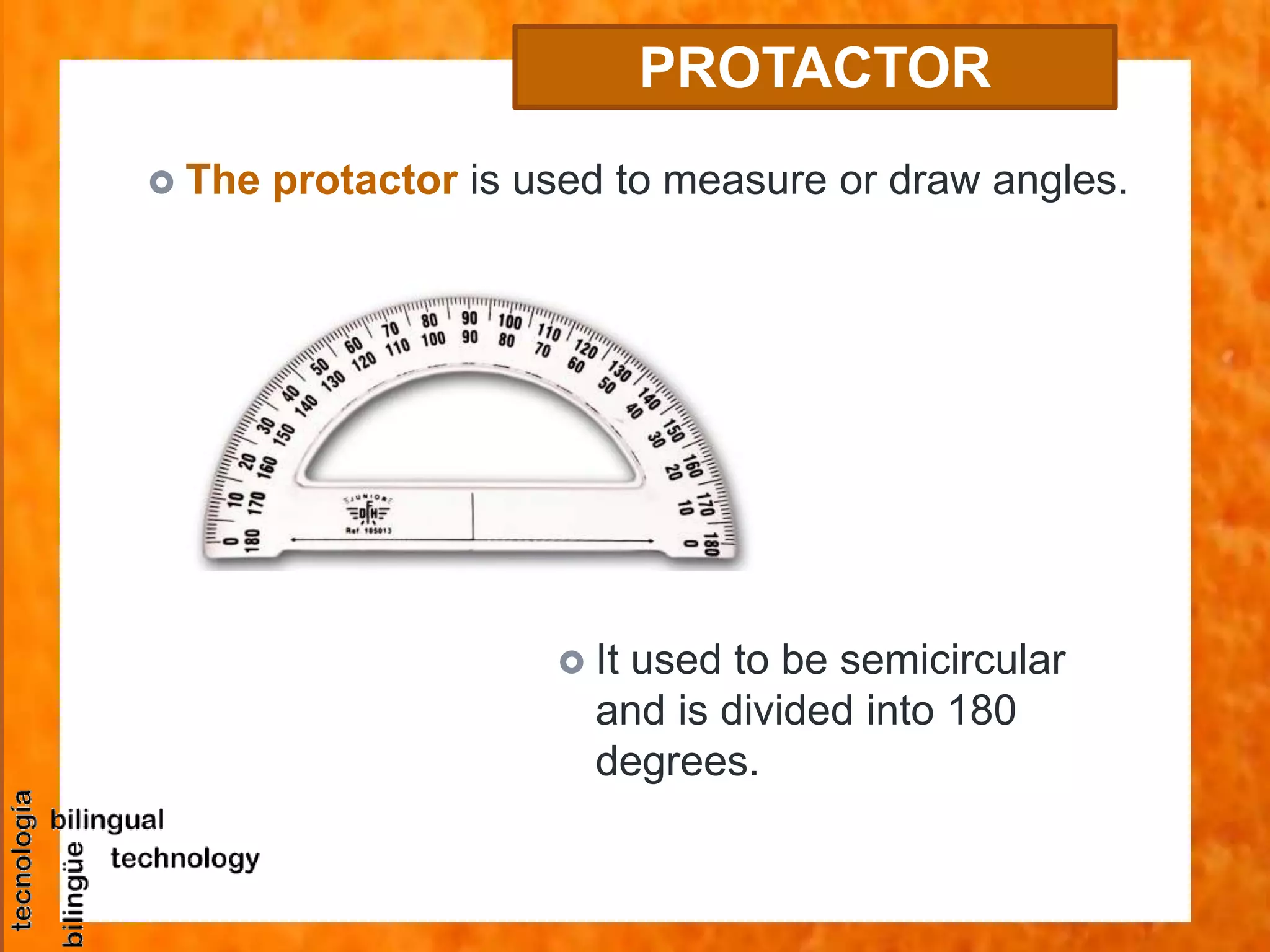
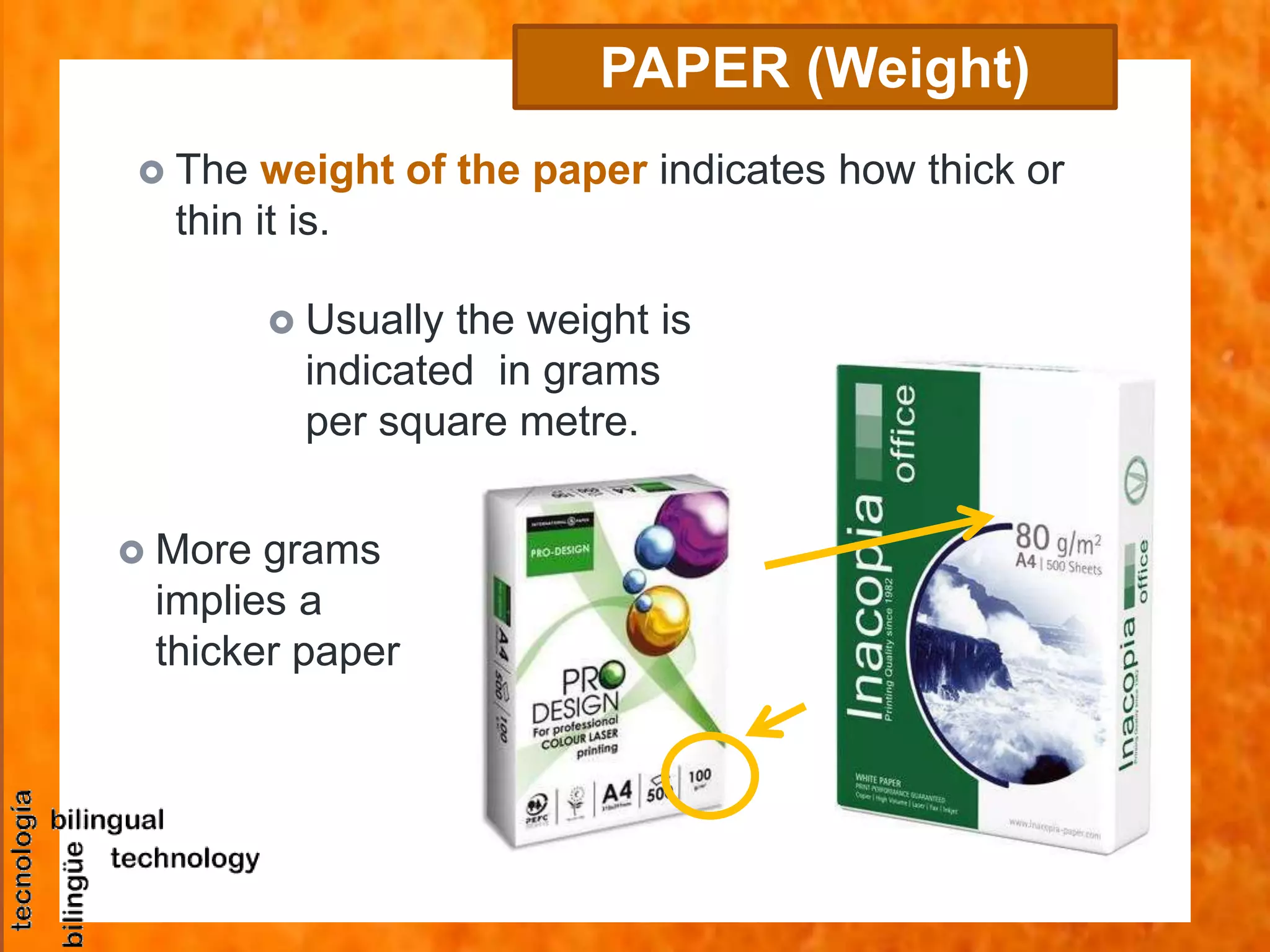
This document discusses the basic tools and materials used for technical drawing. It describes pencils of varying hardness for sketches and plans, propelling pencils, erasers, rulers, set squares, protractors, templates, compasses, and paper of different sizes, weights, and finishes. Technical drawing uses these tools to precisely represent designed and built objects through communication drawings.